0001 MPRG4 EN
Keywords
Raspberry Pi 5 MPRG4 Quad-Gigabit Ethernet Expansion Board Pi OS Ubuntu OpenWrt software router switch
I. Introduction
The MPRG4 (also known as MPG4) is a Quad-Gigabit Ethernet expansion board designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi 5, utilizing the PCIe interface. This expansion board connects the RTL8111H PCIe Ethernet controller via the PCIe interface, and then extends into four Gigabit Ethernet ports through a switch chip. It can be used in the following scenarios:
1. In Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu OS, one network port connected to the upstream router, and the remaining three network ports providing network access to other nearby devices (all four network ports should be in the same subnet), it can save an additional external switch and power supply.
2. In OpenWrt OS, configure the native gigabit port of RPI5 as the WAN port, and the four extended ports as LAN ports, providing network access for up to four devices.

Note1: The four Gigabit ports have independent IP addresses but are located within the same subnet, with addresses assigned by the upstream router from its address pool. If the upstream router is not connected, Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu OS will be unable to obtain a valid IP address (they will receive an IP address in the range of 169.254.xx.xx, indicating that there is only a physical connection but no valid IP address).
Note2: In the Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu OS, if the network cable is not plugged in at startup, the system will obtain an IP address like 169.254.xx.xx after a while. At this time, even if you plug in a network cable from an upstream router, the system will not obtain a valid IP address. You need to press the reset button to acquire a valid IP address again.
The expansion board is driver-free on the official Raspberry Pi OS and OpenWrt. However, on the Ubuntu OS, you need to install the driver.
II. Hardware Resources
1. It connected via a 16-pin 0.5mm PCIe to Raspberry Pi 5.
2. Onboard RTL8111H chip, enabling PCIe to Gigabit Ethernet.
3. Four Gigabit Ethernet.
4. A PWR LED.
5. A switch reset button (Switch RST).
6. One extension power button for Raspberry Pi 5 (Raspberry Pi 5 cotians a power button, with additional reserved pinholes for extension power buttons).
7. Size: 86mm*75mm.
8. The circuit board uses an immersion gold process, is produced in a lead-free manufacturing process, and the material is UL and RoHS certified with a fire resistance rating of 94V-0.
9. Optional metal case.
10. Optional 3D-printed base to protect your desk from scratches.9.






A 4G module can be installed on top of the Raspberry Pi 5 to set up a 4G router. The 4G module is an optional module.


Note: The four-port block cannot be used to connect to an upstream router on a different subnet, you can only select any one port to connect to the upstream router. The remaining three ports are used to connect downstream devices that need network access, such as computers or development boards. These four Ethernet ports are internally connected to a switch.
III. Work with Raspberry Pi OS
Under the Raspberry Pi OS, the necessary drivers are integrated by default, so no additional driver installation is required, and you can use it directly.
The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit
3.1 View Ethernet
After the system starts, execute ifconfig -a, and the red box will indicate the extended RTL8111H Ethernet card (four Gigabit Ethernet ports):

By executing ifconfig -a, you can see that eth0 is the built-in Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5; the eth1 device is the extended RTL8111H network card (which provides four Gigabit Ethernet ports).

3.2 Test Ethernet
Download iperf3(Windows version):
http://www.mcuzone.com/down/Software.asp?ID=10000634
Install iperf3 on Linux:
sudo apt-get install iperf3
After installation, connect one of the four extended Gigabit Ethernet ports to the upstream router, and use iperf3 to test the speed with a PC within the same local network.
In client mode, the speed is about 942 Mbps.
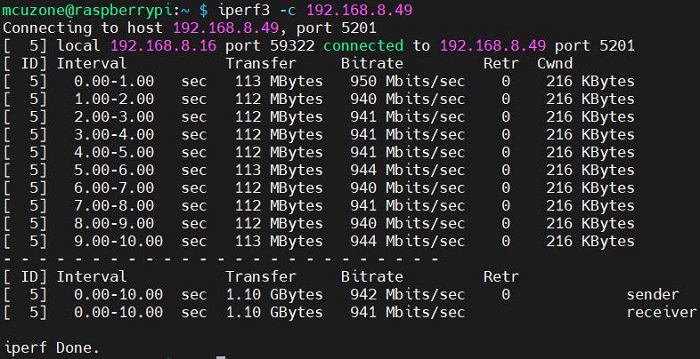
In server mode, the speed is about 948 Mbps.
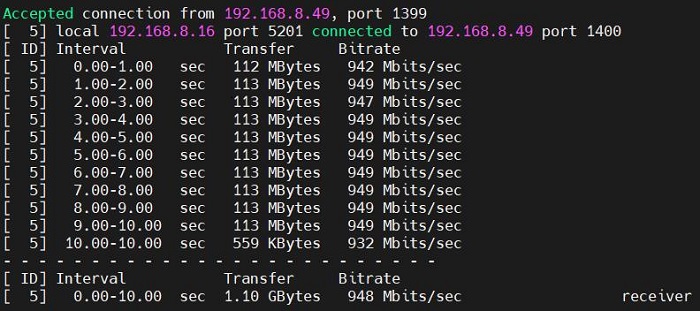
It can basically achieve gigabit speed.
Note1: Network speed tests are affected by the network environment and testing methods. Please refer to the actual speed, as this test is for reference only.
Note2: The four-port switch is a physical layer device, and is not visible in the system.
IV. Work with Ubuntu OS
The process of loading network card drivers in Ubuntu 23.10 is relatively complex and cumbersome, and it is not recommended for use. It is recommended to use Ubuntu 24.04.
The version of the Ubuntu OS is: ubuntu-24.04-preinstalled-desktop-arm64+raspi.img.xz
You can download the Ubuntu OS in:
https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
4.1 Install drivers
On Ubuntu 24.04, you can directly download driver source code and compile it. The steps are as follows:
Connect the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5 to the upstream router.
Update the system:
sudo apt-get update
Preparing the build environment:
sudo apt-get install --reinstall linux-headers-$(uname -r) linux-headers-generic build-essential dkms
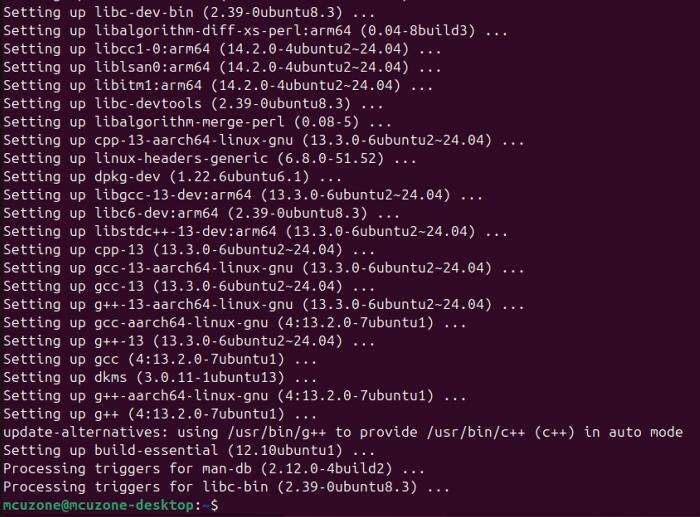
Download and compile driver:
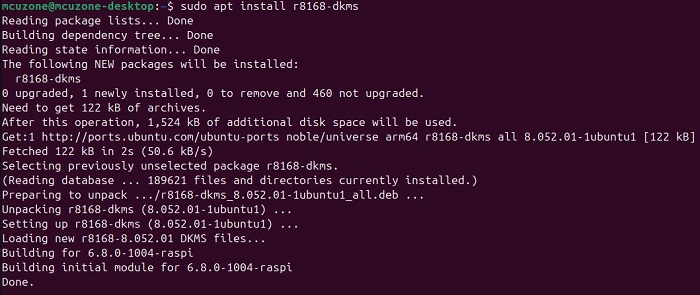
sudo apt install r8168-dkms
sudo modprobe r8168
After the driver installation is complete, install the net-tools package:
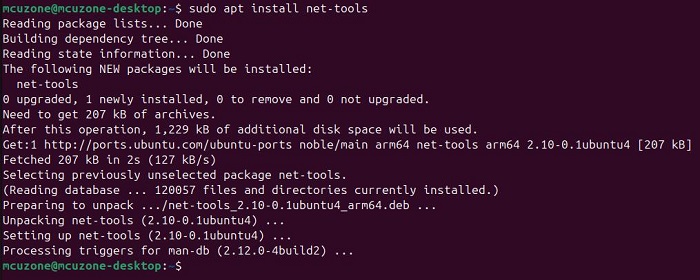
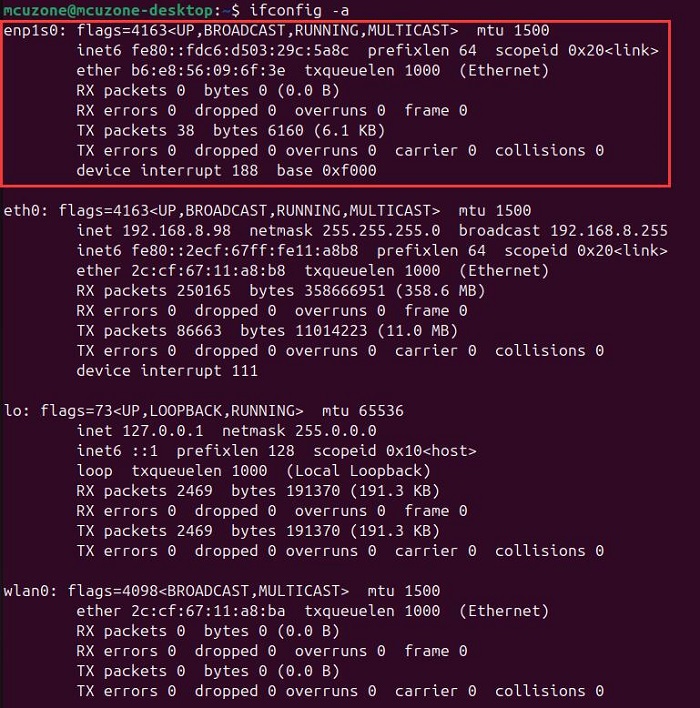
After installation, you can use ifconfig. By executing ifconfig -a, you should see devices starting with enp, which are the four expanded Gigabit Ethernet ports. This indicates that the driver has been installed successfully.
At this moment, the four extended Gigabit Ethernet ports are not connected to the upstream router, so they have not obtained IP addresses.
4.2 Test Ethernet
Install iperf3 on Linux:
sudo apt-get install iperf3
After installation, connect one of the four expanded Gigabit Ethernet ports to the upstream router, restart the system, and run `ifconfig -a`. You should see that the expanded Gigabit Ethernet port has obtained an IP address.
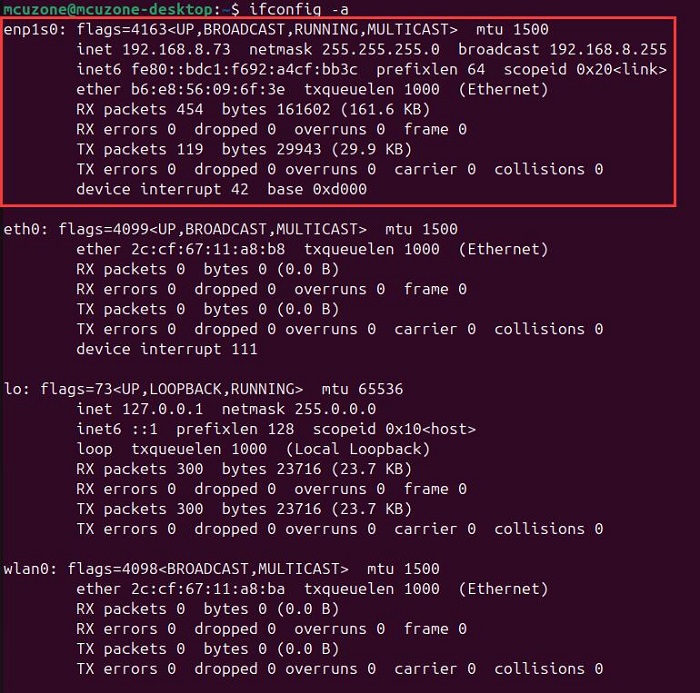
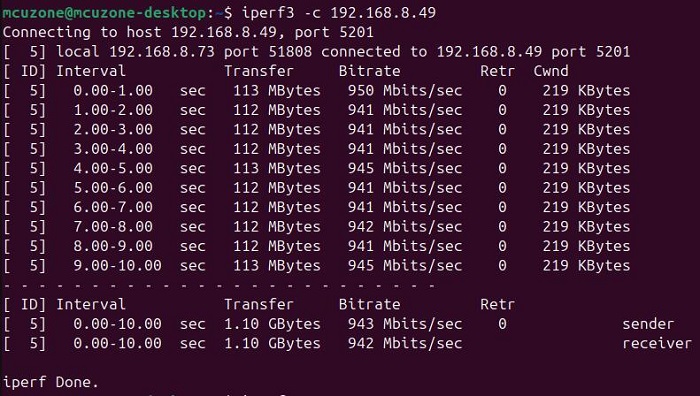
Use iperf3 to test the speed with a PC within the same local network.
In client mode, the speed is about 943 Mbps.
In server mode, the speed is about 948 Mbps.
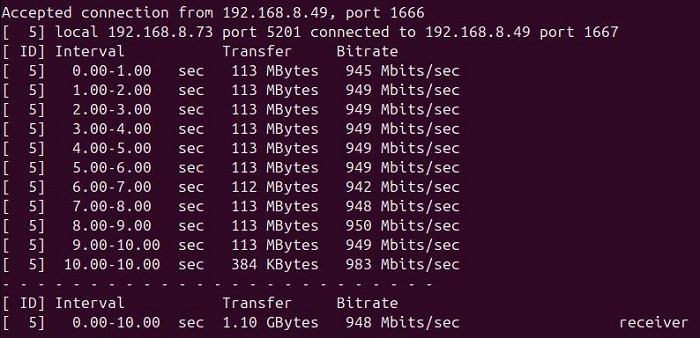
It can basically achieve gigabit speed.
Note1: Network speed tests are affected by the network environment and testing methods. Please refer to the actual speed, as this test is for reference only.
Note2: On an Ubuntu OS, the RTL8111H network card is recognized with a name like enxxxx, while the same switch used as a physical layer chip does not appear in the network card list.
V. Work with OpenWrt
5.1 Overview
The MPRG4 expansion board can be configured in OpenWrt as a switch with one input and four outputs. We can configure the Raspberry Pi5's built-in Ethernet port as the WAN port, and use the four Ethernet ports on the expansion board as LAN ports, which can be used by other devices to obtain IP addresses within the same subnet.
System version: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2712-rpi-5-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.100-20240805.img.gz
5.2 Preparation
We connect the Raspberry Pi 5's built-in port to the PC's Ethernet port, then power on and start the system. Afterward, we navigate to Network and Internet in the Windows settings, and under Ethernet, we open the connected network to view the IP address of the default gateway. This address is the backend configuration page address for the OpenWrt system. As shown in the image, the address tested in this article is 192.168.198.1:
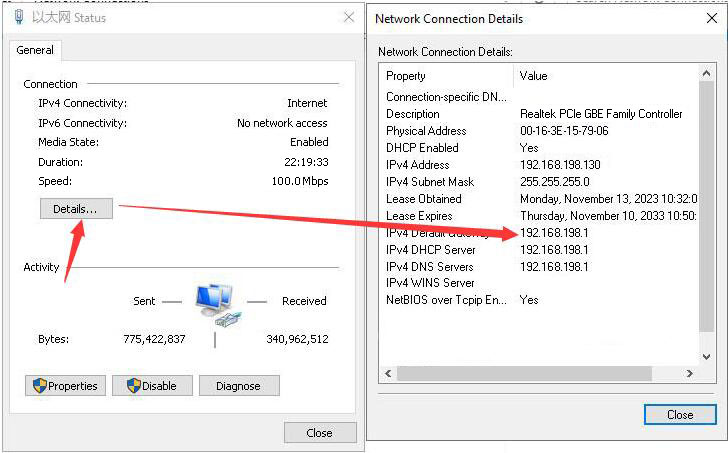
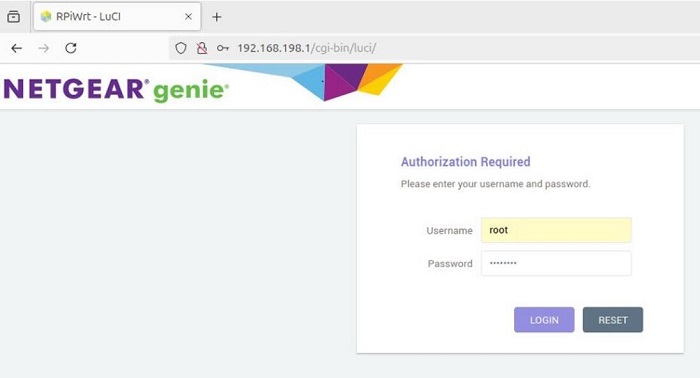
Open a web browser, enter 192.168.198.1, and access the OpenWrt system configuration page.
The default username is root, and the default password is password.
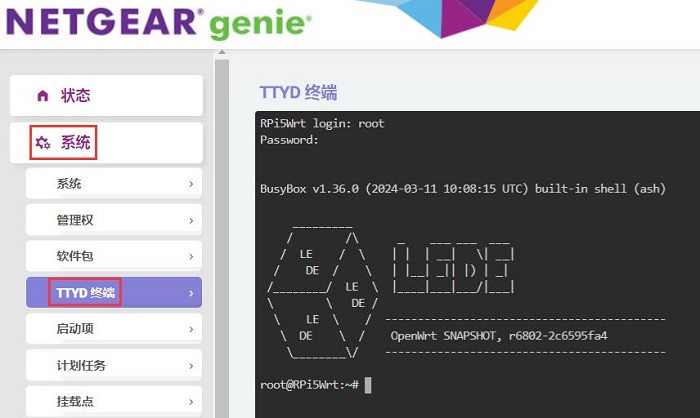
After logging into the OpenWrt, click on "System - TTYD Terminal", We can then access the terminal that comes with OpenWrt, and log in using the username root and the password password.
Run ifconfig -a, and you can see that the extended Gigabit Ethernet port (eth1) has been recognized:

5.3 Configure the WAN port and LAN ports
By default, the native Ethernet port (eth0) of the Raspberry Pi 5 is a LAN port. Now, we need to set the Raspberry Pi 5's native Ethernet port (eth0) as the WAN port and the extended Gigabit Ethernet port (eth1) as the LAN port. The procedure is as follows:
We click on "Network - Interface".
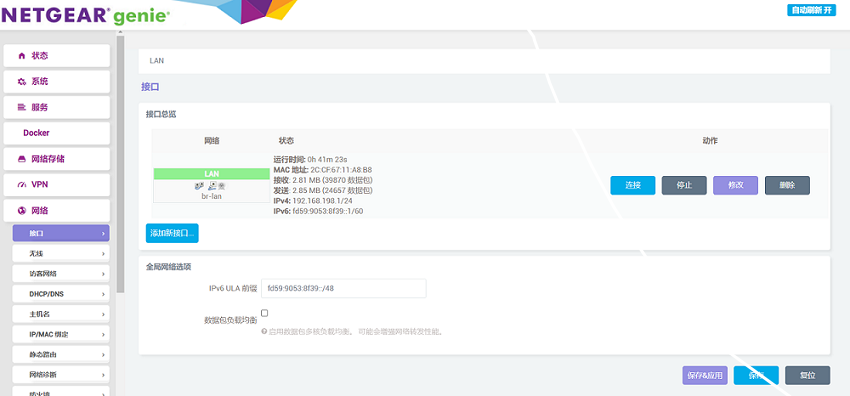
Then we click to Add a new interface, set the name and interface protocol, and set the WAN port to eth0.
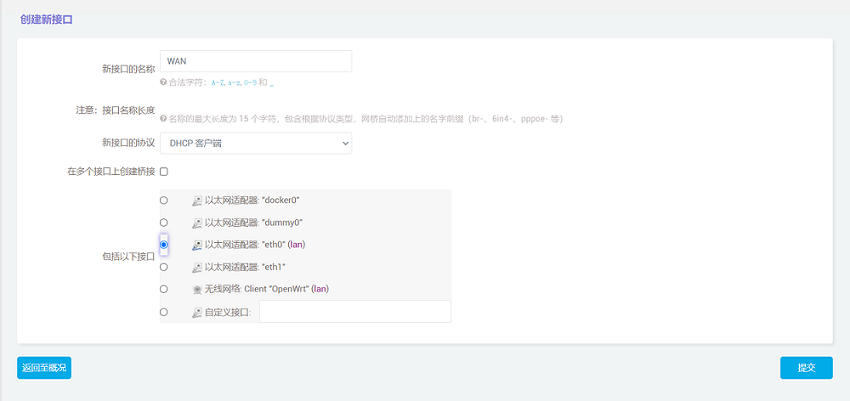
Click "Submit" and then select "WAN" in the Firewall settings.
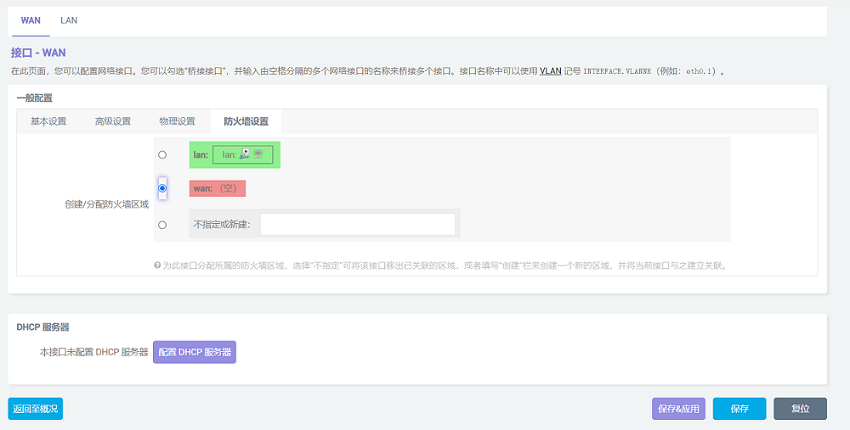
After configuration it complete, click "Save". Be careful, do not click "Save & Apply", or you will not be able to enter the system.
Click "Back" to return to the overview, then click on LAN port modification.

Set the interface to eth1 in the "Physical Settings".
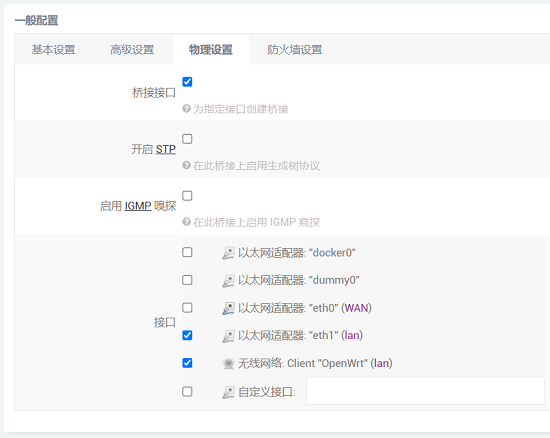
After configuration, we click "Save & Apply". Please note that since the network settings are being changed, it will continuously display "Applying changes". This is not a malfunction, and after waiting for a while, we can proceed to the next step.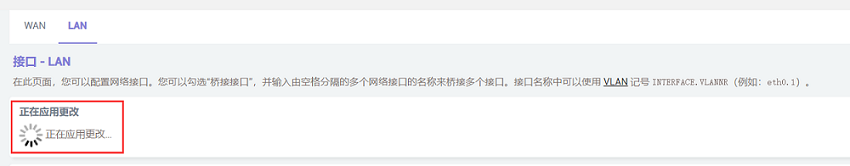
The OpenWrt is currently unavailable due to changes in the network interfaces. You need to connect the new WAN port to the upstream router, then connect the new LAN port to the downstream network devices, reboot the system, and log back into the OpenWrt.
After configuration, connect the new WAN port (the native Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi, eth0) to the upstream router, then connect the new LAN port (the extended Gigabit Ethernet port, eth1) to downstream network devices (such as PCs, etc.). Restart the system, and then log into the OpenWrt.
5.4 Ethernet test
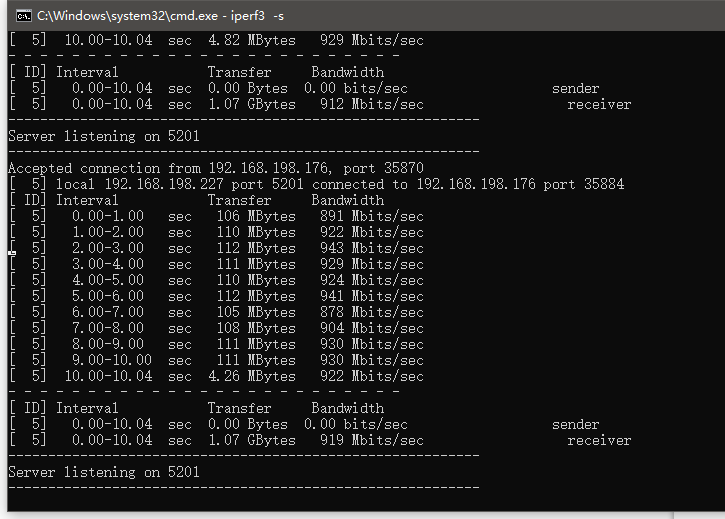
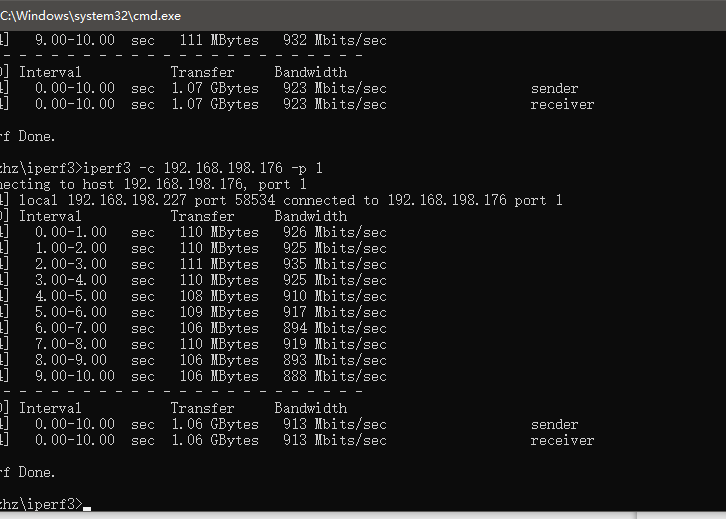
We will connect two of the four LAN ports to two PCs to simply test the network bandwidth.
Using iperf3 to test between two computers shows that the test results are normal.
VI. Radxa Rock 5C (RK3588S2) with MPRG4
6.1 Overview
The Radxa Rock 5C is designed based on the RK3588S2, dimensions are compatible with the Raspberry Pi 5. It have one gigabit ethernet port and four USB ports, along with a PCIe interface compatible with the Raspberry Pi 5. This interface allows us to expand with various PCIe extension boards designed for the Raspberry Pi 5. In this demonstration, we are using a MRG4 board.
System version: rock-5c_bookworm_kde_b1.output.img.xz
You can download it in github:
https://github.com/radxa-build/rock-5c/releases/tag/rsdk-b1

6.2 Preparation
1. Upon system startup, the username and login password for the default account are both radxa:
2. Entering the system, find Konsole in the menu to access the terminal.
3. Execute lspci to ensure that the device information for RTL8111 is visible (the red box):
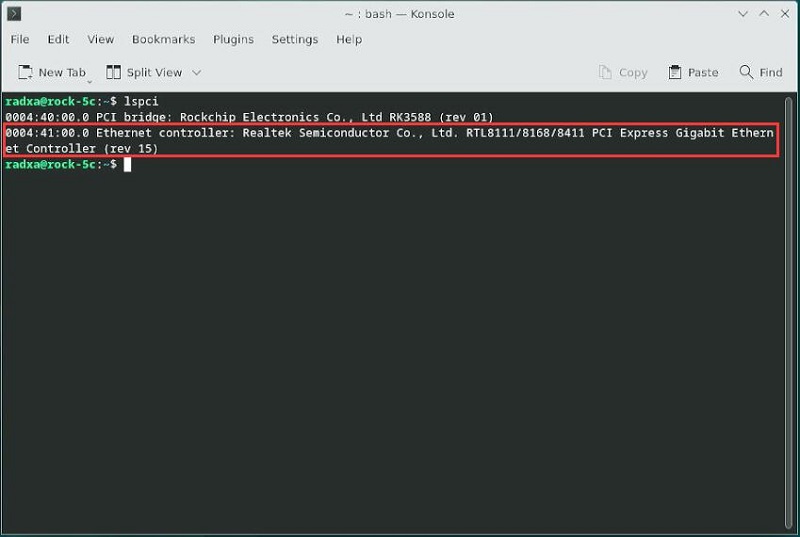
(If you cannot see it, check the reliability of the FPC connection. Note that the FPC cable has an orientation, with one side indicating that it should be connected to the RPi5 on the Rock 5C ).
4. Connect the native Gigabit Ethernet port of the Radxa Rock 5C to the upstream router, then execute:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get install net-tools
You can use the ifconfig after installing net-tools. Of course, you can also use other tools to operate the network.
6.3 Install drivers and test Ethernet
Using DKMS to install the drivers.
sudo apt-get install r8168-dkms
sudo modprobe r8168
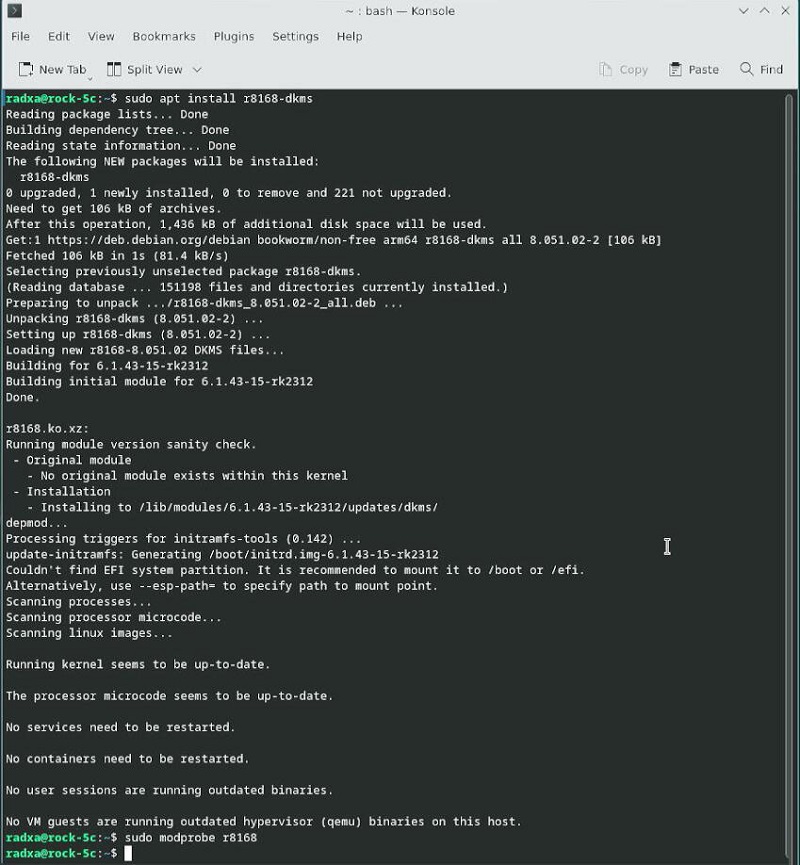
After installing the drivers, execute sudo ifconfig -a to check for network cards starting with enp, which indicates the RTL8111 network card. Note that the switch is a physical layer device and cannot be seen with ifconfig.
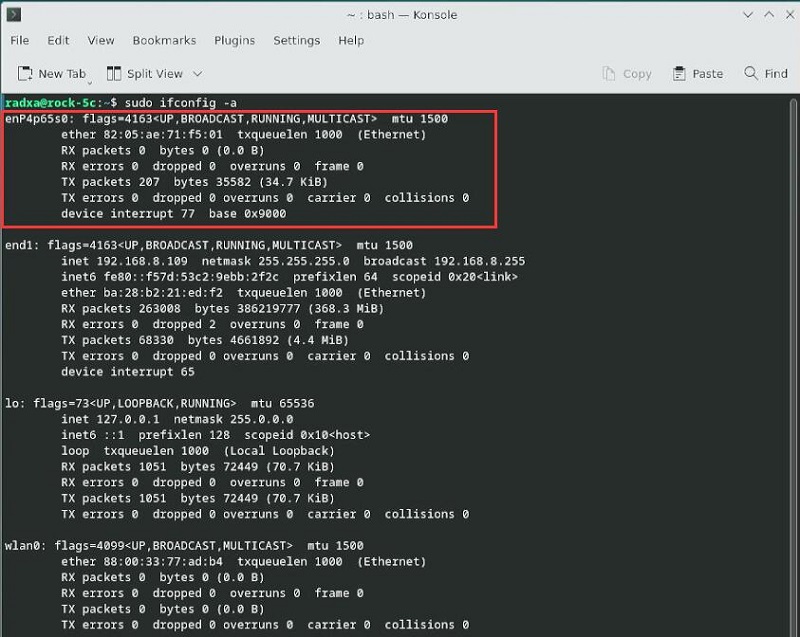
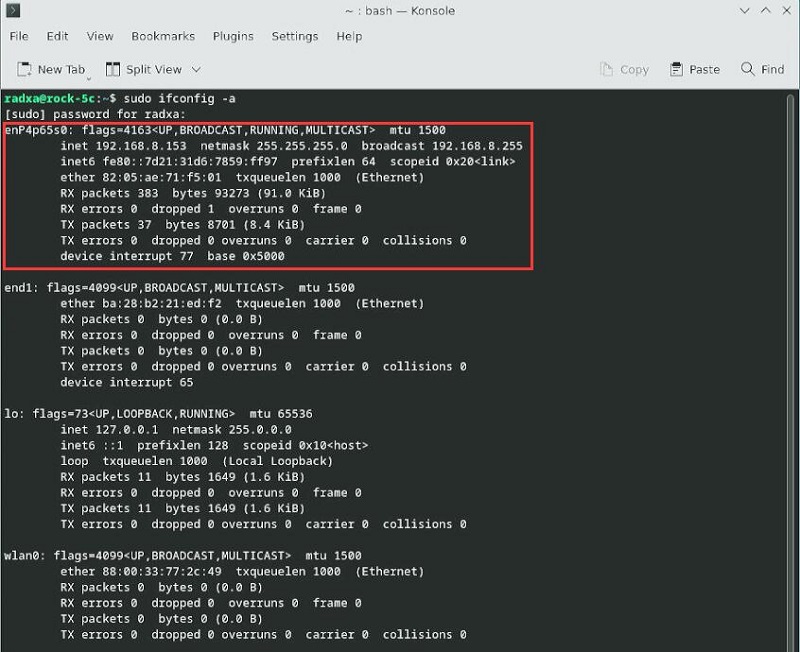
Connect one of the four extended Gigabit Ethernet ports to the upstream router, restart the system, and then execute sudo ifconfig -a. You should see that the extended Gigabit Ethernet port has correctly obtained an IP address.
Confirm network connectivity by using ping packets:
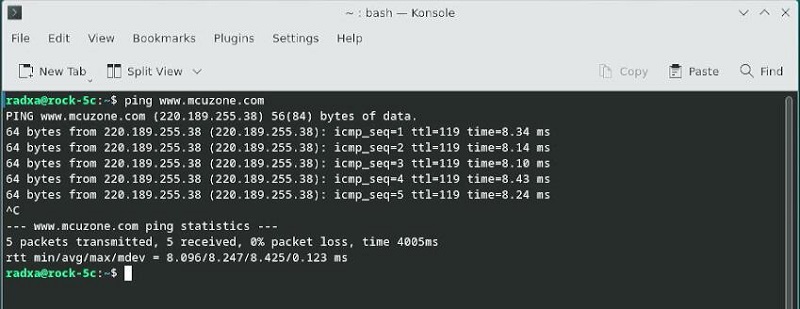
Now, the network card drivers has been successfully installed and is functioning normally.
Install iperf3 on Linux:
sudo apt-get install iperf3
After installation, connect one of the four expanded Gigabit Ethernet ports to the upstream router, restart the system, use iperf3 to test the speed with a PC within the same local network.
In client mode, the speed is about 942 Mbps.
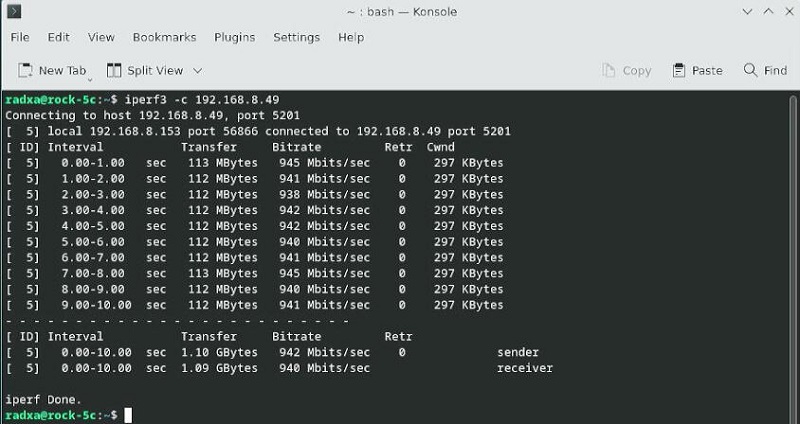
In server mode, the speed is about 947 Mbps.
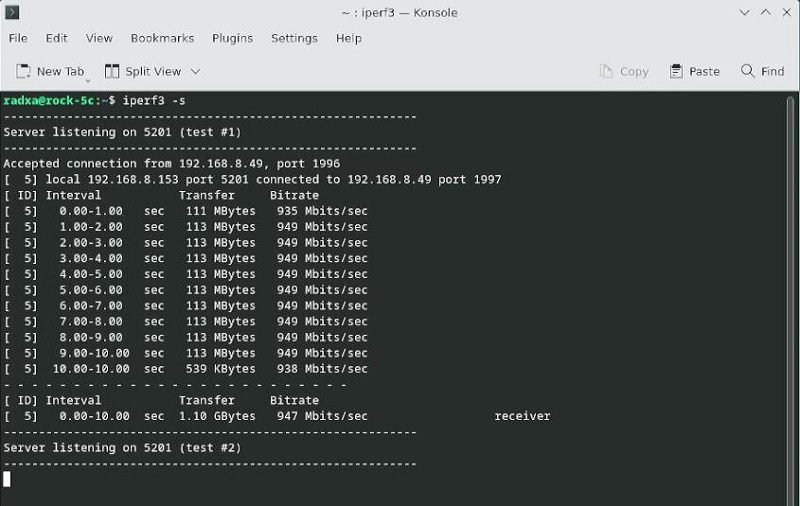
It can basically achieve gigabit speed.
Note: Network speed tests are affected by the network environment and testing methods. Please refer to the actual speed, as this test is for reference only.
6.4 Test 4G module
我司配套的4G模块均具有免驱免拨号、系统自动识别、即插即用等功能。Rock 5C可配CAT4 4G和高通4G,在系统中自动识别成以enx开头的设备。
6.4.1 联网4G
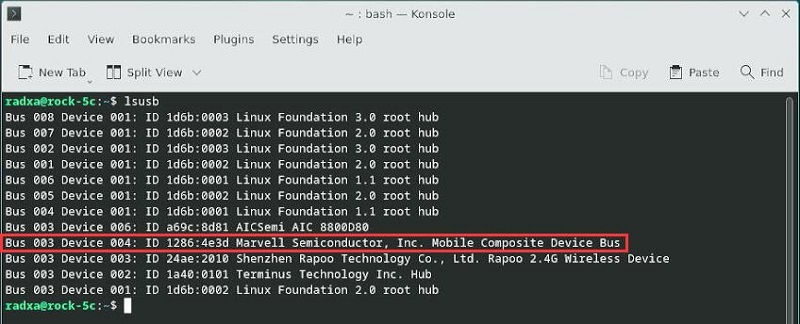
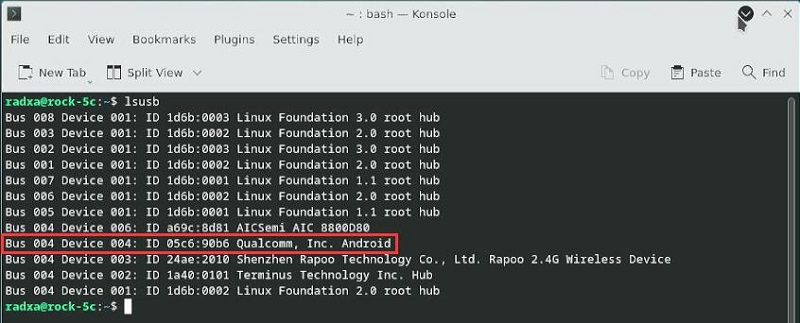
将4G模块通过USB接口与Rock 5C连接,启动系统,在终端中执行lsusb,显示如下,红框处即为4G模块:
CAT4 4G:
高通4G:
下面以CAT4 4G为例,将Rock 5C的原生网口和四个扩展千兆网口中的一个接入上级路由器,重启系统,执行sudo ifconfig -a,显示如下:

可见已经正确获取了IP(红框处)。
执行ip route,可见enx开头的设备排在第一位,因此优先通过4G网络上网:
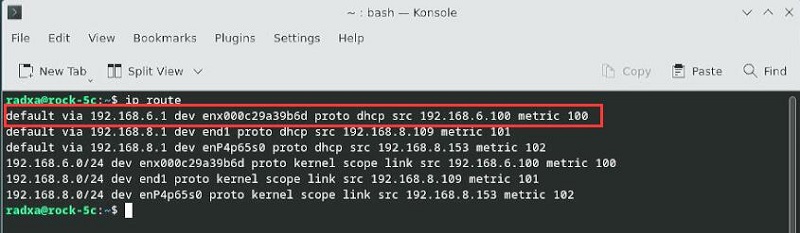
此时我们ping IP和域名,均成功,说明4G模块工作正常:
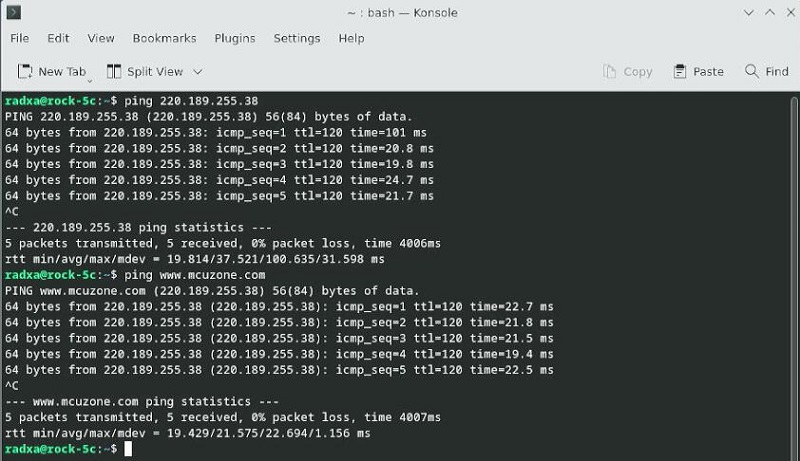
打开https://www.speedtest.cn/进行网速测试,结果如下:

注意:网络测速受网络环境和测试方法影响,速度请以实际为准,本测试仅供参考。
6.4.2 网络优先级的修改
以CAT4 4G为例,上一节我们查看了路由表,默认情况下,优先通过4G网络上网。
如果要优先使用有线网络上网的话,可以运行命令:
sudo ip route del default && sudo route add -net default netmask 0.0.0.0 gw 192.168.8.1
这两条命令(以“&&”分隔)的解释:
sudo ip route del default:删除路由表中的默认路由;
sudo route add -net default netmask 0.0.0.0 gw 192.168.8.1:添加有线网络的网关为新的默认路由(网关地址以实际为准)。
执行完毕后,再执行route,查看路由表,目前的默认路由为有线网络的网关(end1排第一位,即Rock 5C的原生网口):
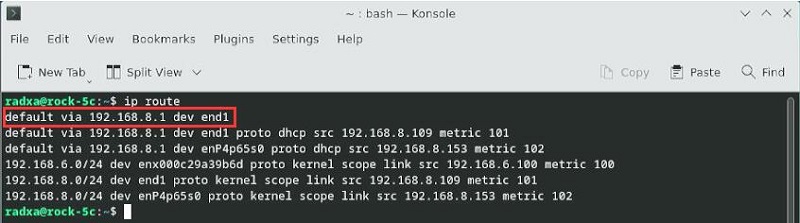
这样网络就默认走有线网络了,如果需要改回默认走4G网络,请运行:
sudo ip route del default && sudo route add -net default netmask 0.0.0.0 gw 192.168.6.1
或者重启系统即可。
其中192.168.6.1为4G模组的默认网关,请以实际为准。
注意,重启后路由表还是会恢复原状,所以如果重启后要网络继续默认走有线网络,需要再执行一次sudo ip route del default && sudo route add -net default netmask 0.0.0.0 gw 192.168.8.1。
6.4.3 AT命令操作
以CAT4 4G为例,使用lsusb查看USB设备,红框处即为4G模组:

记下4G模块的ID值:1286 4e3d
使用下列命令打开ttyUSB串口,其中echo后面的值就是上面记录的ID值:
sudo modprobe option
sudo sh -c 'echo 1286 4e3d > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/option1/new_id'
执行上述两条命令之后执行:
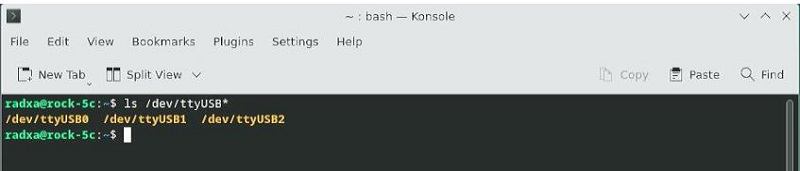
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
此时应该能看到dev设备下有ttyUSB0-3四个设备:
然后用串口工具打开特定串口(AT命令串口):
安装minicom工具:
sudo apt-get install minicom
通过minicom打开AT命令串口:
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB1
(注意:使用哪个串口,应以在进入此串口后,可输入运行AT命令,显示不乱码,不乱跳结果为准)
如果需要查看回显,请键入命令:ate1,然后回车,继续键入其它命令,回车可以看到结果。
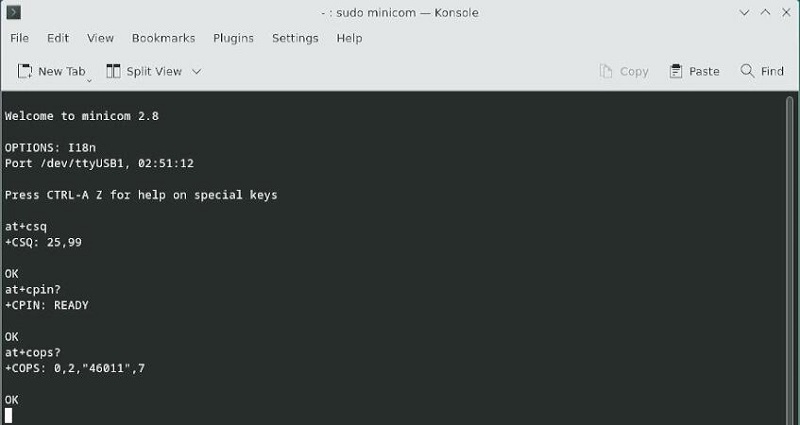
常用AT命令: 1. 检查SIM卡是否识别到:
at+cpin?
返回ready表示卡已识别,返回error要检查硬件
2. 检查天线信号质量:
at+csq
返回值在26-31表示信号OK,信号满格31;返回值在20-25表示信号勉勉强强;返回值在20以下表示信号比较糟糕或者天线没接
3. 检查注网情况:
at+cops?
正常应该返回运营商代码和7,7代表4G。
注意,以上命令只有at+csq不要加问号,另外两条命令需要加问号。
4. 查看4G模块的IMEI码:
at+cgsn
5. 重启4G模块(有时候如果重插SIM卡,热插拔不一定管用,可以用这个reset命令来复位模块):
at+reset
6. 关闭射频:
at+cfun=0
开启射频:
at+cfun=1
上述两条命令成对使用,可以在不重启4G模组的情况下让模组重新注网。
6.4.4 修改4G模组的IP地址
如果出厂默认的4G IP地址和用户使用的IP地址有冲突,或有修改IP地址的需求,可按照下列步骤进行修改:
CAT4 4G模块:
执行AT命令:
AT+ROUTEIP=<newip>
注意,只支持192.168.x.1这样格式的地址,如果设置了AT+ROUTEIP=192.168.3.1,最终获得的IP为192.168.3.100,修改完后需断电重启系统。
查询当前IP:AT+ROUTEIP?,返回两个值,前一个为旧IP,后一个为新IP。
测试命令:AT+ROUTEIP=?
高通 4G模块:
将4G模块的IP改为直接获取公网IP即可,请执行AT命令:
设置IP为公网:AT+GTIPPASS=1
设置IP为内网:AT+GTIPPASS=0
查询当前IP为公网还是内网:AT+GTIPPASS?
修改IP完毕后需要断电重启才能生效。
Contact Us
Email: mcuzone@vip.qq.com
Tel: +86(0)13957118045
If there are any omissions, errors, or infringements on this page, please contact us through the above methods. Thank you!
Copyright 2004-2025 Wildchip




 QQ:8204136
QQ:8204136