0001 MPRG4 EN
Keywords
Raspberry Pi 5 MPRG4 Quad-Gigabit Ethernet Expansion Board Pi OS Ubuntu OpenWrt software router switch
I. Introduction
The MPRG4 (also known as MPG4) is a Quad-Gigabit Ethernet expansion board designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi 5, utilizing the PCIe interface. This expansion board connects the RTL8111H PCIe Ethernet controller via the PCIe interface, and then extends into four Gigabit Ethernet ports through a switch chip. It can be used in the following scenarios:
1. In Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu OS, one network port connected to the upstream router, and the remaining three network ports providing network access to other nearby devices (all four network ports should be in the same subnet), it can save an additional external switch and power supply.
2. In OpenWrt OS, configure the native gigabit port of RPI5 as the WAN port, and the four extended ports as LAN ports, providing network access for up to four devices.

Note1: The four Gigabit ports have independent IP addresses but are located within the same subnet, with addresses assigned by the upstream router from its address pool. If the upstream router is not connected, Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu OS will be unable to obtain a valid IP address (they will receive an IP address in the range of 169.254.xx.xx, indicating that there is only a physical connection but no valid IP address).
Note2: In the Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu OS, if the network cable is not plugged in at startup, the system will obtain an IP address like 169.254.xx.xx after a while. At this time, even if you plug in a network cable from an upstream router, the system will not obtain a valid IP address. You need to press the reset button to acquire a valid IP address again.
The expansion board is driver-free on the official Raspberry Pi OS and OpenWrt. However, on the Ubuntu OS, you need to install the driver.
II. Hardware Resources
1. It connected via a 16-pin 0.5mm PCIe to Raspberry Pi 5.
2. Onboard RTL8111H chip, enabling PCIe to Gigabit Ethernet.
3. Four Gigabit Ethernet.
4. A PWR LED.
5. A switch reset button (Switch RST).
6. One extension power button for Raspberry Pi 5 (Raspberry Pi 5 cotians a power button, with additional reserved pinholes for extension power buttons).
7. Size: 86mm*75mm.
8. The circuit board uses an immersion gold process, is produced in a lead-free manufacturing process, and the material is UL and RoHS certified with a fire resistance rating of 94V-0.
9. Optional metal case.
10. Optional 3D-printed base to protect your desk from scratches.9.






A 4G module can be installed on top of the Raspberry Pi 5 to set up a 4G router. The 4G module is an optional module.


Note: The four-port block cannot be used to connect to an upstream router on a different subnet, you can only select any one port to connect to the upstream router. The remaining three ports are used to connect downstream devices that need network access, such as computers or development boards. These four Ethernet ports are internally connected to a switch.
III. Work with Raspberry Pi OS
Under the Raspberry Pi OS, the necessary drivers are integrated by default, so no additional driver installation is required, and you can use it directly.
The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit
3.1 View Ethernet
After the system starts, execute ifconfig -a, and the red box will indicate the extended RTL8111H Ethernet card (four Gigabit Ethernet ports):

By executing ifconfig -a, you can see that eth0 is the built-in Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5; the eth1 device is the extended RTL8111H network card (which provides four Gigabit Ethernet ports).

3.2 Test Ethernet
Download iperf3(Windows version):
http://www.mcuzone.com/down/Software.asp?ID=10000634
Install iperf3 on Linux:
sudo apt-get install iperf3
After installation, connect one of the four extended Gigabit Ethernet ports to the upstream router, and use iperf3 to test the speed with a PC within the same local network.
In client mode, the speed is about 942 Mbps.
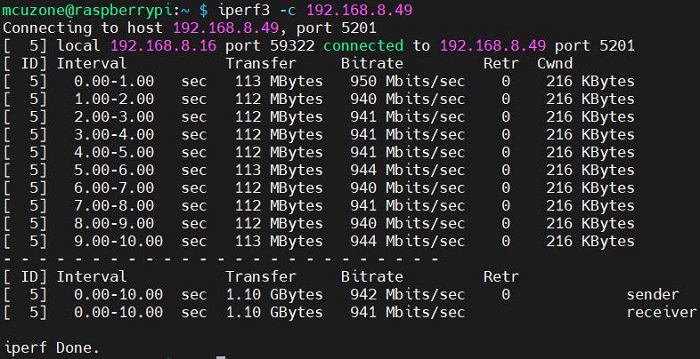
In server mode, the speed is about 948 Mbps.
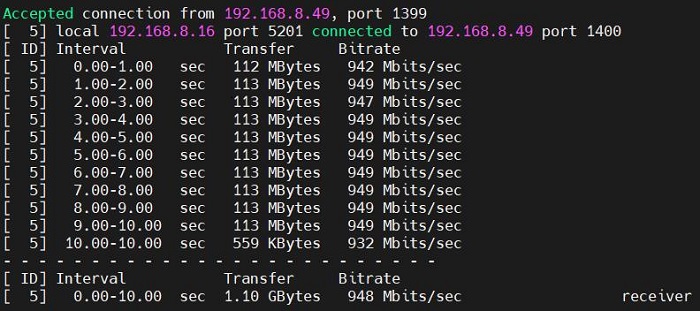
It can basically achieve gigabit speed.
Note1: Network speed tests are affected by the network environment and testing methods. Please refer to the actual speed, as this test is for reference only.
Note2: The four-port switch is a physical layer device, and is not visible in the system.
IV. Work with Ubuntu OS
The process of loading network card drivers in Ubuntu 23.10 is relatively complex and cumbersome, and it is not recommended for use.
The version of the Ubuntu OS is: ubuntu-24.04-preinstalled-desktop-arm64+raspi.img.xz
You can download the Ubuntu OS in:
https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
4.1 Install drivers
On Ubuntu 24.04, you can directly download driver source code and compile it. The steps are as follows:
Preparing the build environment:
sudo apt-get install --reinstall linux-headers-$(uname -r) linux-headers-generic build-essential dkms


Download and compile driver:
sudo apt install r8168-dkms
sudo modprobe r8168


Run the following command to view the wired network interface which is named enxxx:
ifconfig -a

4.2 Test Ethernet
Using iperf3 for speed testing, it can be run on gigabit speed.
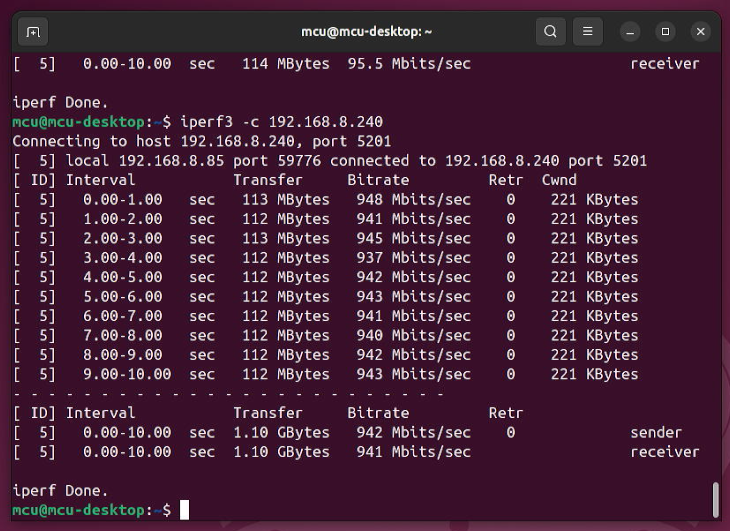
Note: On an Ubuntu OS, the RTL8111H network card is recognized with a name like enxxxx, while the same switch used as a physical layer chip does not appear in the network card list.
V. Work with OpenWrt
5.1 Overview
The MPRG4 expansion board can be configured in OpenWrt as a switch with one input and four outputs. We can configure the Raspberry Pi5's built-in Ethernet port as the WAN port, and use the four Ethernet ports on the expansion board as LAN ports, which can be used by other devices to obtain IP addresses within the same subnet.
System version: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2712-rpi-5-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.92-20240530a.img.gz
5.2 Preparation
We connect the Raspberry Pi 5's built-in port to the PC's Ethernet port, then power on and start the system. Afterward, we navigate to Network and Internet in the Windows settings, and under Ethernet, we open the connected network to view the IP address of the default gateway. This address is the backend configuration page address for the OpenWrt system. As shown in the image, the address tested in this article is 192.168.198.1:
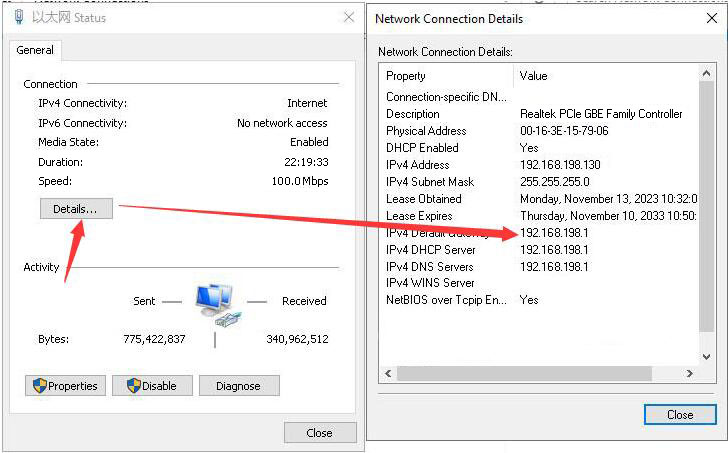
Open a web browser, enter 192.168.198.1, and access the OpenWrt system configuration page.
The default username is root, and the default password is password.
After logging into the OpenWrt, click on "System - TTYD Terminal", We can then access the terminal that comes with OpenWrt, and log in using the username root and the password password.

Then we can use this terminal to run Linux commands.
5.3 Configure the Ethernet ports
After the device is properly recognized, we open the "network - interface".
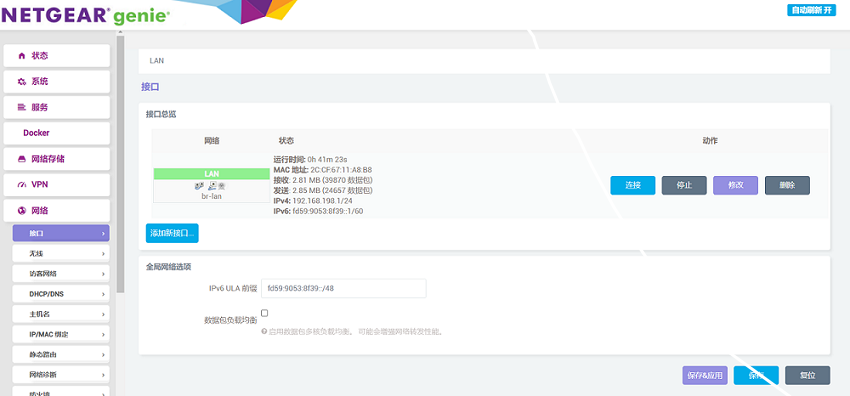
Then we click to add a new interface, set the name and interface protocol, and set the WAN port to eth0.
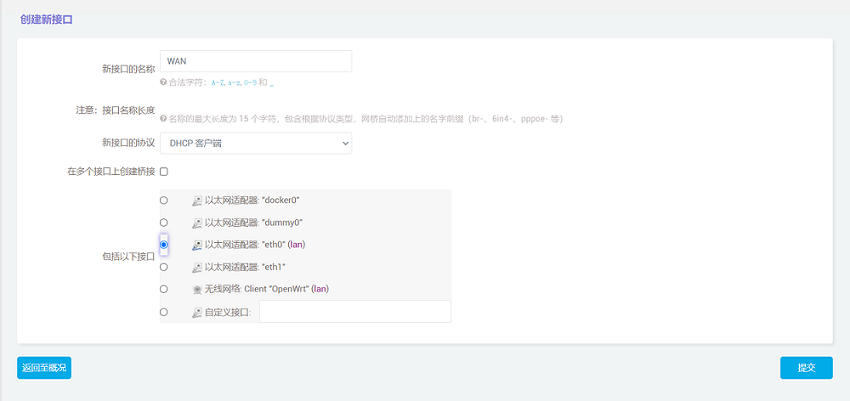
Click "Submit" and then select "WAN" in the firewall settings.
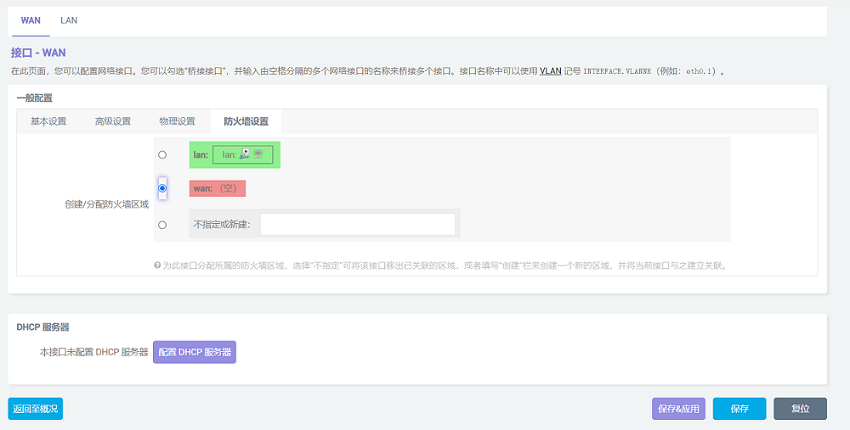
After configuration it complete, click "Save". Be careful, do not click "Save & Apply", or you will not be able to enter the system.
Click "Back" to return to the overview, then click on LAN port modification.

Set the interface to eth1 in the "Physical Settings".
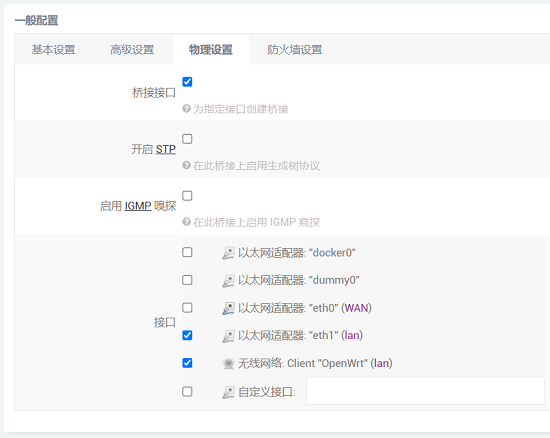
After configuration, we click "Save & Apply". Please note that since the network settings are being changed, it will continuously display "Applying changes". This is not a malfunction, and after waiting for a while, we can proceed to the next step.
The OpenWrt is currently unavailable due to changes in the network interfaces. You need to connect the new WAN port to the upstream router, then connect the new LAN port to the downstream network devices, reboot the system, and log back into the OpenWrt.
5.4 Ethernet test
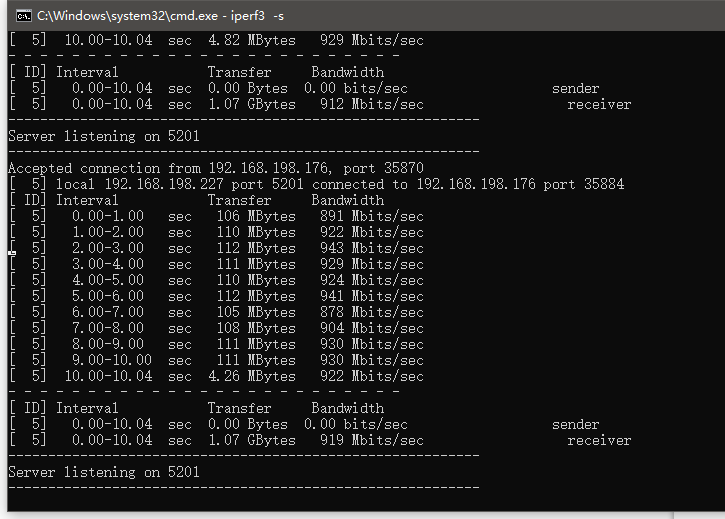
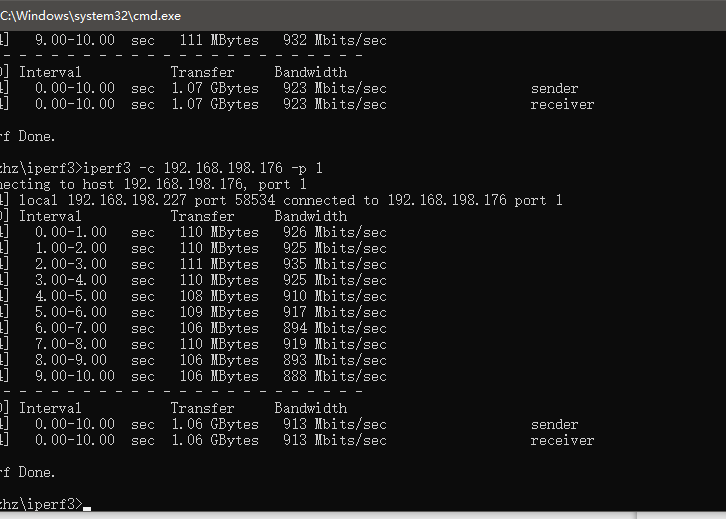
We will connect two of the four LAN ports to two PCs to simply test the network bandwidth.
Using iperf3 to test between two computers shows that the test results are normal.
VI. Radxa Rock 5C (RK3588S2) with MPRG4
6.1 Overview
The Radxa Rock 5C is designed based on the RK3588S2, it have one gigabit ethernet port and four USB ports, along with a PCIe interface compatible with the Raspberry Pi 5. This interface allows us to expand with various PCIe extension boards designed for the Raspberry Pi 5. In this demonstration, we are using a MRG4 board.
6.2 Software and Hardware
System version: debian bullseye kde b3, you can download it on github:
https://github.com/radxa-build/rock-5c/releases/
Expansion Board: MPRG4 Expansion Board with four ethernet ports.

6.3 Log in to the system
1. The default account login password for system is radxa.
2. Entering the system, find Konsole in the menu to access the terminal.
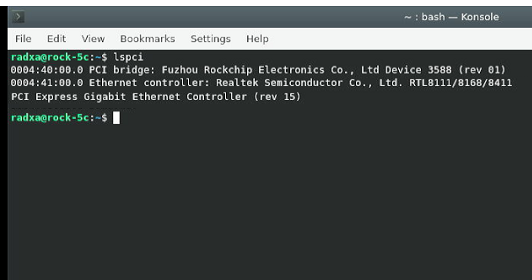
3. Execute lspci to ensure that the device information for RTL8111 is visible ( If you can see RTL8111, it indicates that the expansion board hardware is functioning normally. If you cannot see it, check the reliability of the FPC connection. Note that the FPC cable has an orientation, with one side indicating that it should be connected to the RPi5 on the Rock 5C ).
4. Connect the native Gigabit Ethernet port of the Radxa Rock 5C to the upstream router, then execute:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade


sudo apt-get install net-tools
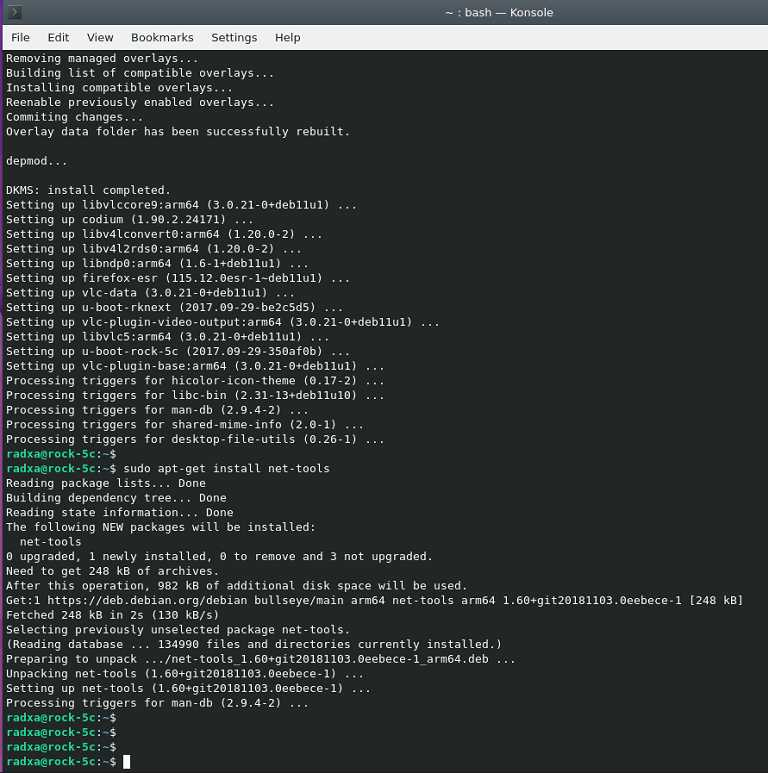
You can use the ifconfig after installing net-tools. Of course, you can also use other tools to operate the network.
6.4 Install drivers
1. Using DKMS to install the drivers.
sudo apt-get install r8168-dkms
sudo modprobe r8168
The operations in the above two steps are the same as those in section 4.1.
2. After installing the drivers, execute sudo ifconfig -a to check for network cards starting with 'enp', which indicates the RTL8111 network card. Note that the switch is a physical layer device and cannot be seen with ifconfig.

3. Confirm network connectivity by using ping packets:
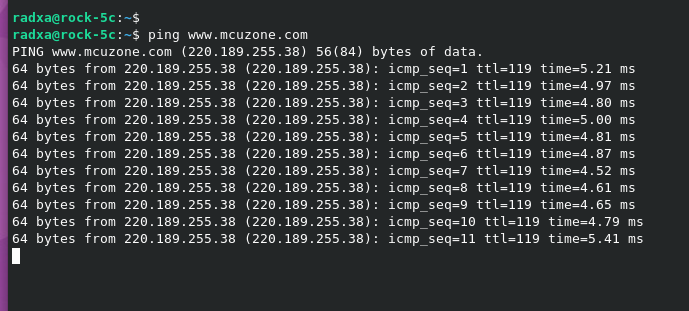
Now, the network card drivers has been successfully installed and is functioning normally.
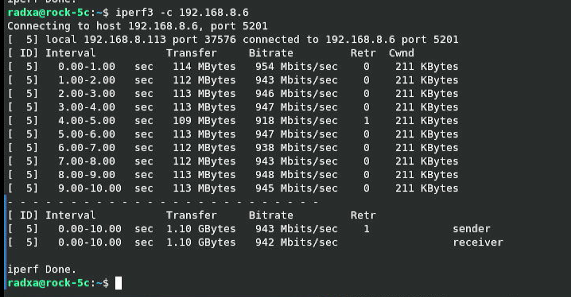
4. Using iperf3 for speed testing, it can be run on gigabit speed.
Contact Us
Email: mcuzone@vip.qq.com
Tel: +86(0)13957118045
If there are any omissions, errors, or infringements on this page, please contact us through the above methods. Thank you!
Copyright 2004-2025 Wildchip




 QQ:8204136
QQ:8204136