0015 MP2.5G(Single 2.5G ETH OPT PoE):修订间差异
| (未显示同一用户的5个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
[[0015 MP2.5G(单2. | [[0015 MP2.5G(单2.5G以太网 可选PoE供电)|切换语言为中文]] | ||
== '''Keywords''' == | == '''Keywords''' == | ||
| 第76行: | 第76行: | ||
'''''Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.''''' | '''''Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.''''' | ||
=== 4.3 | === 4.3 Fix the MAC address of the 2.5G Ethernet port === | ||
{{RTL8125_MAC_SINGLE_EN}} | |||
== '''V. Work with Ubuntu System''' == | |||
=== 5.1 Install the RTL8125 driver in Ubuntu system === | |||
The 2.5G Ethernet port on the MP2.5G expansion board is not plug-and-play in Ubuntu system and requires the installation of the RTL8125 driver. | |||
Since the wireless network card module of the Raspberry Pi 5 is plug-and-play in the Ubuntu system, we need to use the wireless network card to connect to a wireless network: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_11.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_11.jpg | ||
You can also use an Ethernet cable to connect to the native Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi 5. | |||
The ifconfig tool is not installed by default in Ubuntu system, so it needs to be installed manually: | |||
<code>sudo apt install net-tools</code> | <code>sudo apt install net-tools</code> | ||
| 第154行: | 第96行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0008_MPS2_5G/0008_MPS2_5G_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0008_MPS2_5G/0008_MPS2_5G_13.jpg | ||
Excute <code>ifconfig</code> -a, and you can see that the 2.5G network card is not displayed at this time. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_12.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_12.jpg | ||
Next, we will begin installing the RTL8125 driver: | |||
First, you need to update the system: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get update</code> | <code>sudo apt-get update</code> | ||
| 第166行: | 第108行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_13.jpg | ||
Next, prepare the compilation environment: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get install --reinstall linux-headers-$(uname -r) linux-headers-generic build-essential dkms</code> | <code>sudo apt-get install --reinstall linux-headers-$(uname -r) linux-headers-generic build-essential dkms</code> | ||
| 第172行: | 第114行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_14.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_14.jpg | ||
Then install the driver: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get install r8125-dkms</code> | <code>sudo apt-get install r8125-dkms</code> | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_15.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_15.jpg | ||
After installation is complete, excute: | |||
<code>sudo modprobe r8125</code> | <code>sudo modprobe r8125</code> | ||
| 第186行: | 第126行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_16.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_16.jpg | ||
Enter <code>ifconfig -a</code> to see the network interface called enxxx, which indicates that the 2.5G network card driver has been successfully installed: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_05.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_05.jpg | ||
=== 5.2 | === 5.2 Internet test === | ||
Open https://test.ustc.edu.cn/ on the PC to test speed. The speed test results for the 2.5G Ethernet port connected to the Internet (200M broadband) are as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_06.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_06.jpg | ||
''''' | '''''Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.''''' | ||
If the built-in Firefox browser in Ubuntu system runs very slowly or frequently becomes unresponsive, it is recommended to install the lightweight browser Falkon: | |||
<code>sudo apt install falkon</code> | <code>sudo apt install falkon</code> | ||
=== 5.3 2. | === 5.3 2.5G intranet test === | ||
Install the network speed testing tool iperf3: | |||
<code>sudo apt install iperf3</code> | <code>sudo apt install iperf3</code> | ||
| 第208行: | 第148行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_20.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0009_MP2_5GD/0009_MP2_5GD_20.jpg | ||
Use iperf3 to perform speed tests between the Raspberry Pi OS and the PC through a 2.5G router. | |||
''''' | '''''The speed test results are as follows:''''' | ||
When Ubuntu system acts as a client, the speed is about 2.35 Gbps: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_07.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_07.jpg | ||
When Ubuntu system acts as a server, the speed is about 1.85Gbps: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_08.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_08.jpg | ||
''''' | '''''Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.''''' | ||
== | == '''VI. Work with OpenWrt System''' == | ||
=== 6. | === 6.1 Overview === | ||
Under the OpenWrt system, the MP2.5G expansion board defaults to the native Gigabit Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi 5 as the LAN port. We can set the 2.5G Ethernet port on the expansion board as another LAN port and use the native Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi 5 as the WAN port. This way, we can leverage the 2.5G port for high-speed file transfer within the local network. | |||
=== 6.2 Preparation === | |||
After flashing the OpenWrt system and powering it up, we connect an Ethernet cable from the Raspberry Pi 5's built-in Ethernet port to the PC's Ethernet port, Once the connection between the PC's network card and the Raspberry Pi 5's Ethernet port is successful, we find Network and Internet settings in Windows, then open the connected network under Ethernet to view the default gateway IP address. This address is the backend configuration page address for the OpenWrt system. As shown in the figure, the address for this test is 192.168.198.1: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/2001_CM4_Ultra/2001_CM4_Ultra_53.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/2001_CM4_Ultra/2001_CM4_Ultra_53.jpg | ||
Then open a web browser and enter 192.168.198.1 to access the OpenWrt system. The default username is <code>root</code>, and the default password is <code>password</code>: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/2001_CM4_Ultra/2001_CM4_Ultra_54.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/2001_CM4_Ultra/2001_CM4_Ultra_54.jpg | ||
=== 6.3 MP2. | === 6.3 Configuration and Application of the 2.5G Ethernet Port on the MP2.5G === | ||
Go to "System - TTYD Terminal," enter the <code>ifconfig -a</code> command, and you can see two network interfaces, eth0 and eth1. eth0 is the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5, and eth1 is the 2.5G Ethernet port of the expansion board: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_09.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_09.jpg | ||
The broadband we typically use does not exceed gigabit speeds. To achieve better intranet performance, it is recommended to configure the native Gigabit port of the Raspberry Pi 5 from its default LAN setting to WAN, and then configure the 2.5G Ethernet port (eth1) of the expansion board as LAN: | |||
Open "Network - Interfaces", and click "EDIT": | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_10.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_10.jpg | ||
In the "Physical Settings", select eth1 and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_11.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_11.jpg | ||
Remove the network cable from the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5 and insert it into the 2.5G Ethernet port (eth1). After the PC's network card successfully connects to the 2.5G port, refresh the management page, click on "Network - Interfaces", and then click "EDIT": | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_12.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_12.jpg | ||
In the "Physical Settings", remove the checkmark from in front of eth0, and then click the "SAVE" button. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_13.jpg | ||
Go back to "Network - Interfaces", and click "Add new interface": | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_14.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_14.jpg | ||
Set "Name of the new interface" as WAN, choose "DHCP client" for "Protocol of the new interface," select "eth0" for "Cover the following interface," and then click the "SUBMIT" button: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_15.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_15.jpg | ||
In the "Firewall Settings", select the WAN and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_16.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_16.jpg | ||
Plug the network cable connected to the Internet into the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5, then go back to "Network - Interfaces". After a moment, you will see that the newly created WAN interface has obtained an IP address. This way, the PC can access the internal network through the 2.5G Ethernet port (eth1). At this point, the network structure is such that the Gigabit Ethernet port (connected to the Internet on the Raspberry Pi) is the incoming connection, and the 2.5G Ethernet port (connected to the internal network on the expansion board) is the outgoing connection. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_17.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_17.jpg | ||
We insert a USB3.0-supported USB drive or mobile hard disk into the USB3.0 port of the Raspberry Pi 5, and refer to the following link to configure this USB drive or mobile hard disk as a shared directory: | |||
[[2001 CM4 Ultra(CM4核心板的扩展板)#5.5 SSD硬盘测试|设置SSD硬盘为共享目录]] | [[2001 CM4 Ultra(CM4核心板的扩展板)#5.5 SSD硬盘测试|设置SSD硬盘为共享目录]] | ||
After setting it up, enter \\192.168.198.1 in the File Explorer (the address is that of the expansion board and may differ based on actual conditions), and you will be able to see the mapped shared directory: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_18.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_18.jpg | ||
Read test for SSD: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_19.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_19.jpg | ||
Write test for SSD: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_20.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0015_MP2_5G/0015_MP2_5G_20.jpg | ||
''''' | '''''Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.''''' | ||
=== 6.4 | === 6.4 Other Applications === | ||
The wireless module of the Raspberry Pi 5 can function as a wireless AP or as a wireless WAN port. For the implementation of these applications, please refer to the following link: | |||
[[0008 MPS2. | [[0008 MPS2.5G(SSD and 2.5G ETH)#6.4 Use the Raspberry Pi's built-in WiFi as a wireless AP (in master mode)|1. Use the Raspberry Pi's built-in WiFi as a wireless AP (in master mode)]] | ||
[[0008 MPS2. | [[0008 MPS2.5G(SSD and 2.5G ETH)#6.5 Use the Raspberry Pi's built-in WiFi as a Client|2. Use the Raspberry Pi's built-in WiFi as a Client]] | ||
{{ | == '''VII. PoE Ethernet Introduction''' == | ||
{{Contact_Us_icon}} | |||
2024年10月17日 (四) 11:38的最新版本
Keywords
Raspberry Pi 5, PCIe, RL8125, 2.5Gbps, Ethernet, iperf3 Ethernet Speed Test
I. Introduction
The Raspberry Pi 5 is equipped with a 16-pin PCIe interface, through which we can attach various PCIe devices. This time, we utilize the PCIe interface to achieve the expansion of a single 2.5Gbps Ethernet port using the RTL8125 chip. The expansion board is automatically recognized as eth1 in the Raspberry Pi OS without requiring any drivers upon power-up. If using Ubuntu system, the RTL8125 driver needs to be installed first before it can be used.
II. Hardware Spec
1. Use a 0.5mm 16-pin PCIe cable to connect to the PCIe interface on the Raspberry Pi 5.
2. Expand one 2.5Gbps Ethernet port.
3. The RTL8125 2.5G Ethernet adapter is driver-free in the official Raspberry Pi OS and OpenWrt systems, but requires driver installation in Ubuntu systems.
4. Gold immersion PCB process, lead-free production, certified by UL, compliant with ROHS standards, and has a fire rating of 94V-0.
5. The board has four M2.5 mounting holes, with a recessed design on the top of the board to facilitate the use of the 40-Pin GPIO.

III. Software Spec
3.1 Overview
This document uses the Raspberry Pi OS, Ubuntu system and OpenWrt system for testing.
1)The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit
2)The version of the Ubuntu system is: ubuntu-24.04-preinstalled-desktop-arm64+raspi.img.xz
You can download the Ubuntu system in:
https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
3)The version of the OpenWrt system is: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2712-rpi-5-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.100-20240805.img.gz
3.2 System flashed onto the SD (TF) card
Click here to read the instructions for System flashing
IV. Work with Raspberry Pi OS
4.1 Internet test
The 2.5G Ethernet port on the MP2.5G expansion board is plug-and-play without requiring drivers under Raspberry Pi OS. Once the system is up, excute the command ifconfig -a in the Raspberry Pi terminal, and the 2.5G Ethernet port will be recognized as eth1:
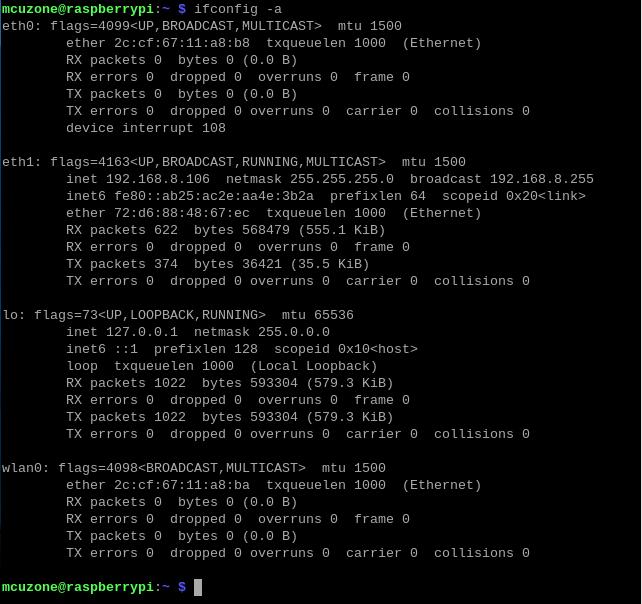
Open https://test.ustc.edu.cn/ on the PC to test speed. The speed test results for the 2.5G Ethernet port connected to the Internet (200M broadband) are as follows:
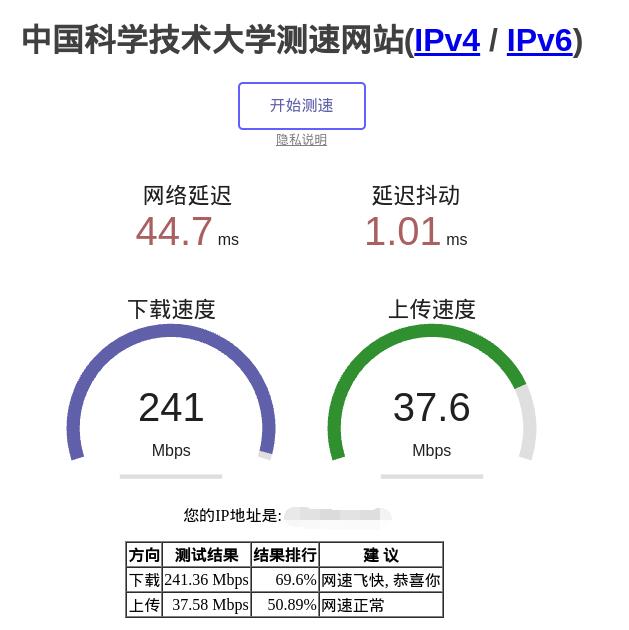
Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.
4.2 2.5G intranet test
Install the network speed testing tool iperf3:
sudo apt install iperf3
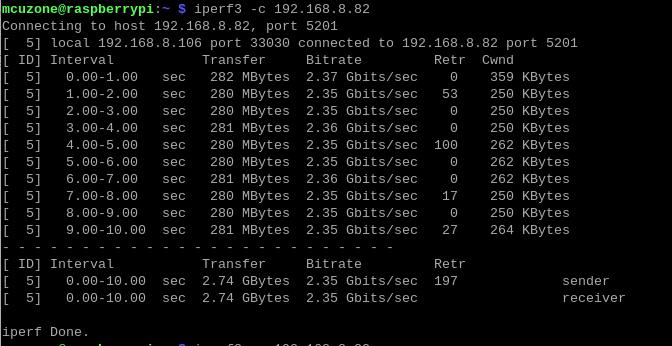
Use iperf3 to perform speed tests between the Raspberry Pi OS and the PC through a 2.5G router.
The speed test results for eth1 are as follows:
When Raspberry Pi OS acts as a client, the speed is about 2.35 Gbps:
When Raspberry Pi OS acts as a server, the speed is about 1.82 Gbps:
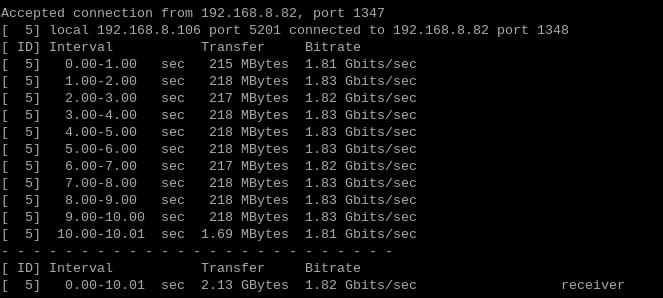
Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.
4.3 Fix the MAC address of the 2.5G Ethernet port
The 2.5G Ethernet port uses the RTL8125 network card, and during use, the MAC address is not fixed. Each time the device is powered on again, the MAC address changes randomly. The following explains how to set a fixed MAC address for the RTL8125 network card.
This explanation also applies to the Ubuntu system.
First, check the identification information of the RTL8125 network card in terminal:
ipconfig -a
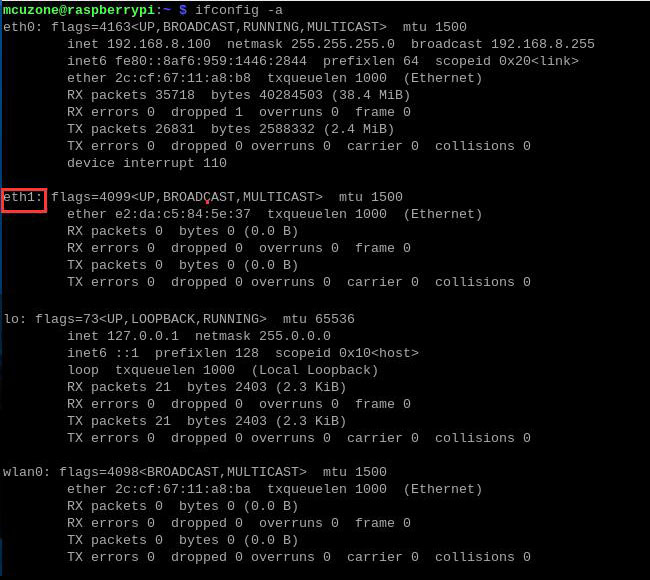
Here, the RTL8125 network card is identified as eth1, but in practice, the name recognized by the system might be different.
Then input:
sudo mousepad /etc/systemd/system/macspoof@eth1.service
Or:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/macspoof@eth1.service
eth1 is the name recognized by the system for the network card shown above.
Executing the above command will create a new document, then enter the following text:
[Unit]
Description=MAC Address Change %I
Wants=network-pre.target
Before=network-pre.target
BindsTo=sys-subsystem-net-devices-%i.device
After=sys-subsystem-net-devices-%i.device
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/bin/ip link set dev %i address xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
ExecStart=/usr/bin/ip link set dev %i up
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Here, "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx" represents the MAC address you wish to assign. You can determine it according to the MAC address format (make sure it does not duplicate the MAC address of other network devices). After setting it, save and exit.
Then execute the following command to enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable macspoof@eth1.service
This completes the fixation of the MAC address for eth1.
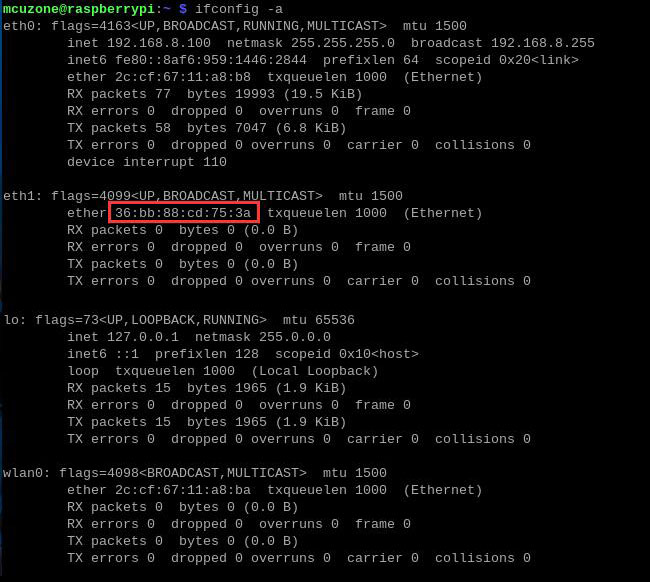
After completing all operations, restart the system. Once the system has finished rebooting, execute ipconfig -a to see that the MAC address has been successfully changed.
V. Work with Ubuntu System
5.1 Install the RTL8125 driver in Ubuntu system
The 2.5G Ethernet port on the MP2.5G expansion board is not plug-and-play in Ubuntu system and requires the installation of the RTL8125 driver.
Since the wireless network card module of the Raspberry Pi 5 is plug-and-play in the Ubuntu system, we need to use the wireless network card to connect to a wireless network:
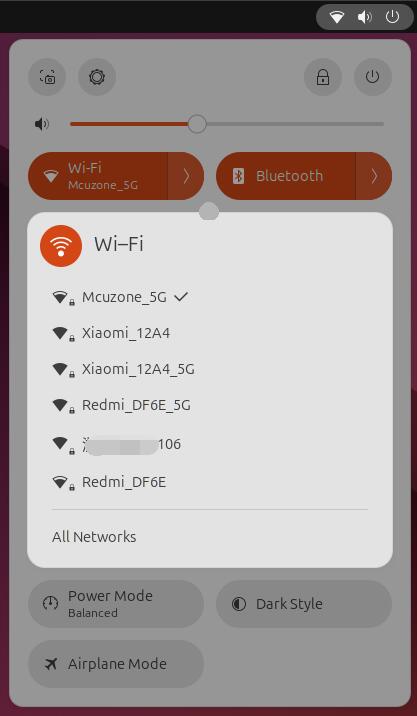
You can also use an Ethernet cable to connect to the native Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi 5.
The ifconfig tool is not installed by default in Ubuntu system, so it needs to be installed manually:
sudo apt install net-tools
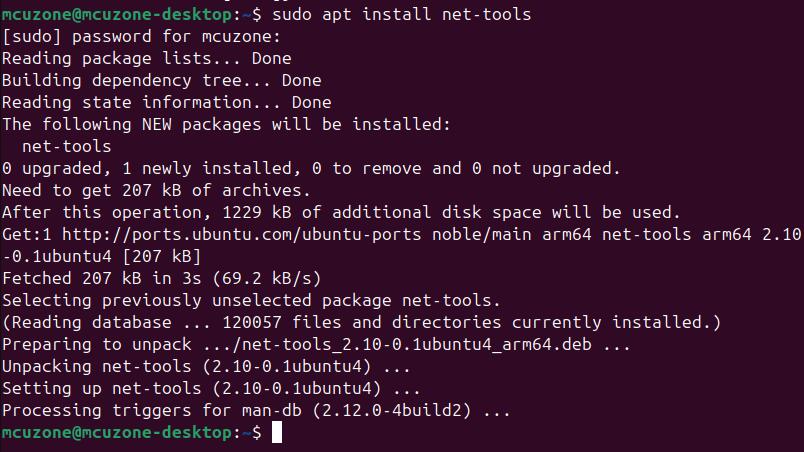
Excute ifconfig -a, and you can see that the 2.5G network card is not displayed at this time.
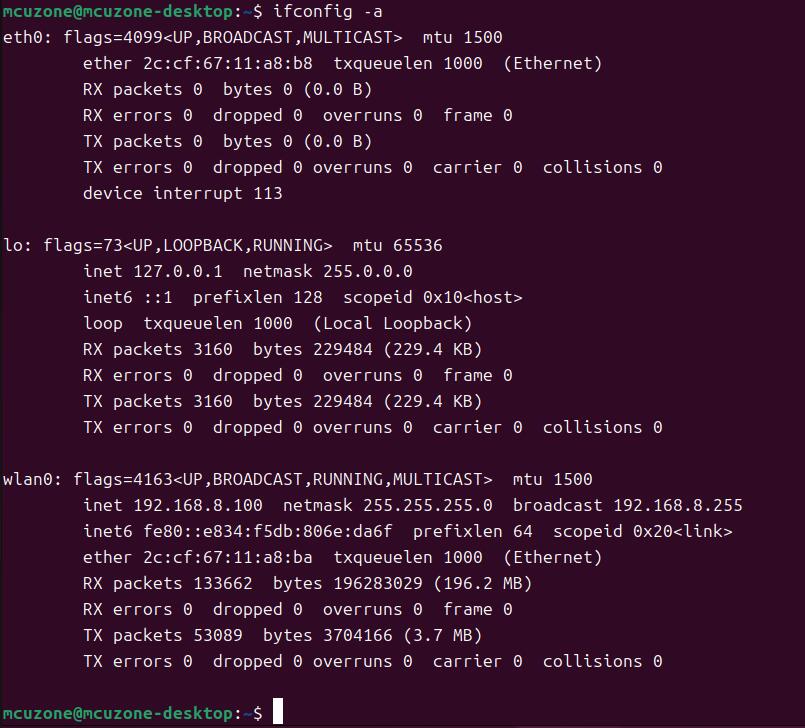
Next, we will begin installing the RTL8125 driver:
First, you need to update the system:
sudo apt-get update
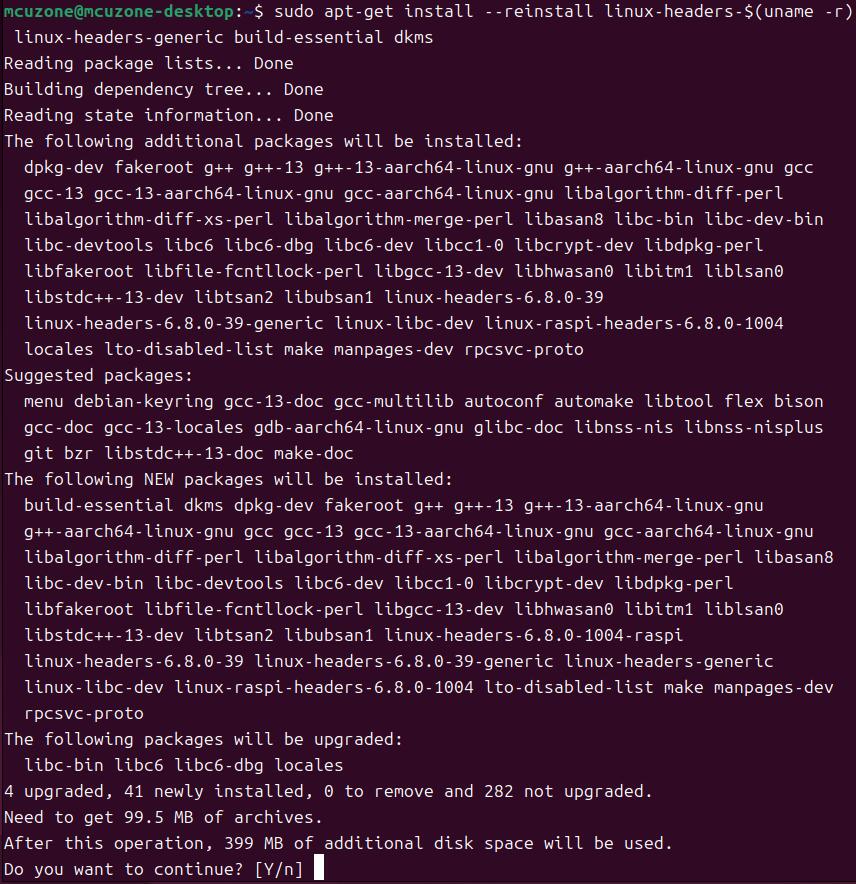
Next, prepare the compilation environment:
sudo apt-get install --reinstall linux-headers-$(uname -r) linux-headers-generic build-essential dkms
Then install the driver:
sudo apt-get install r8125-dkms
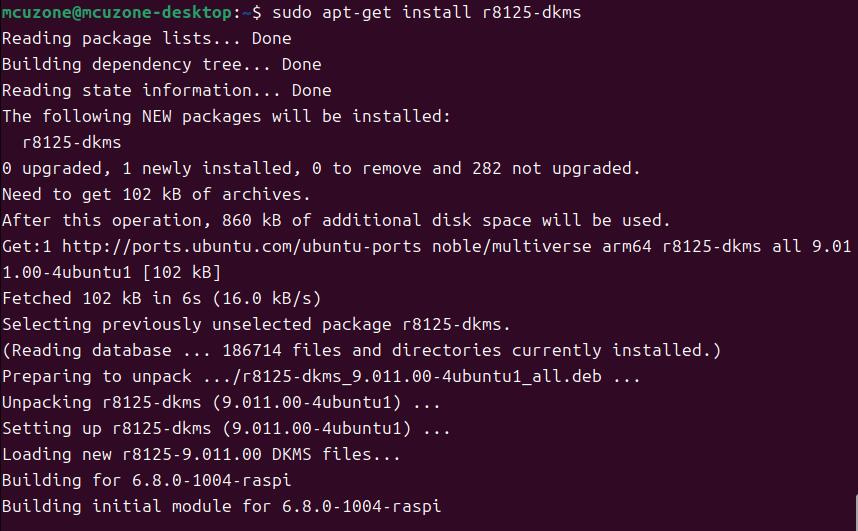
After installation is complete, excute:
sudo modprobe r8125

Enter ifconfig -a to see the network interface called enxxx, which indicates that the 2.5G network card driver has been successfully installed:
5.2 Internet test
Open https://test.ustc.edu.cn/ on the PC to test speed. The speed test results for the 2.5G Ethernet port connected to the Internet (200M broadband) are as follows:
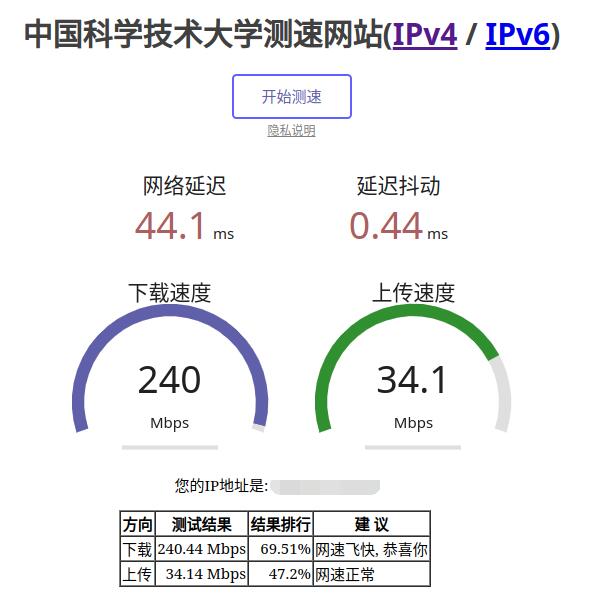
Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.
If the built-in Firefox browser in Ubuntu system runs very slowly or frequently becomes unresponsive, it is recommended to install the lightweight browser Falkon:
sudo apt install falkon
5.3 2.5G intranet test
Install the network speed testing tool iperf3:
sudo apt install iperf3
Use iperf3 to perform speed tests between the Raspberry Pi OS and the PC through a 2.5G router.
The speed test results are as follows:
When Ubuntu system acts as a client, the speed is about 2.35 Gbps:
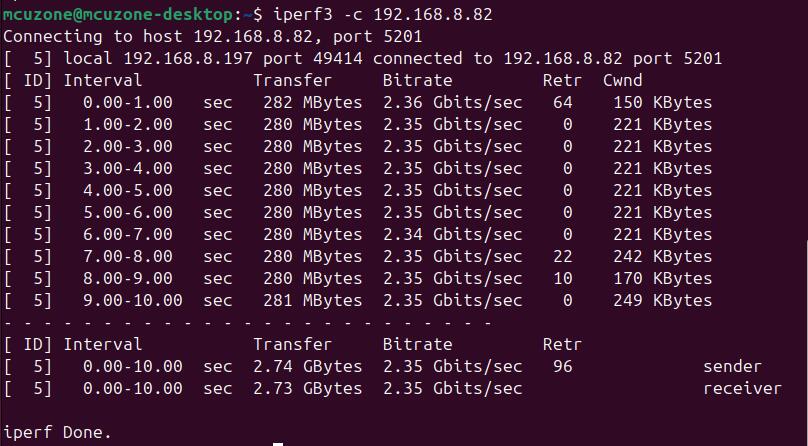
When Ubuntu system acts as a server, the speed is about 1.85Gbps:
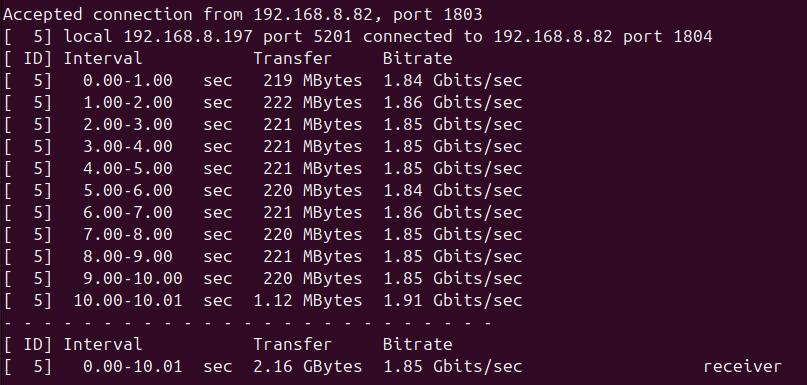
Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.
VI. Work with OpenWrt System
6.1 Overview
Under the OpenWrt system, the MP2.5G expansion board defaults to the native Gigabit Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi 5 as the LAN port. We can set the 2.5G Ethernet port on the expansion board as another LAN port and use the native Ethernet port on the Raspberry Pi 5 as the WAN port. This way, we can leverage the 2.5G port for high-speed file transfer within the local network.
6.2 Preparation
After flashing the OpenWrt system and powering it up, we connect an Ethernet cable from the Raspberry Pi 5's built-in Ethernet port to the PC's Ethernet port, Once the connection between the PC's network card and the Raspberry Pi 5's Ethernet port is successful, we find Network and Internet settings in Windows, then open the connected network under Ethernet to view the default gateway IP address. This address is the backend configuration page address for the OpenWrt system. As shown in the figure, the address for this test is 192.168.198.1:
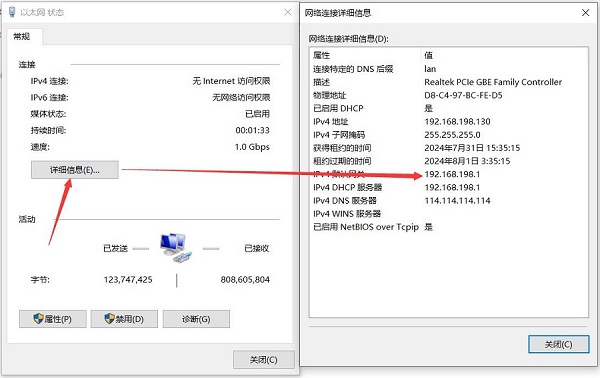
Then open a web browser and enter 192.168.198.1 to access the OpenWrt system. The default username is root, and the default password is password:
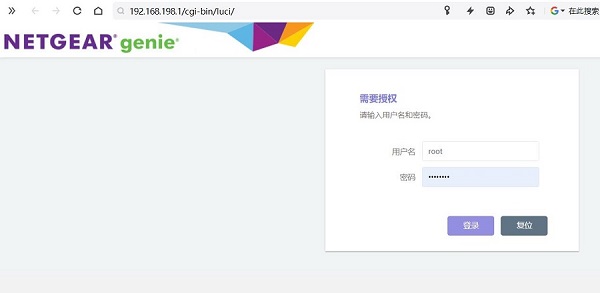
6.3 Configuration and Application of the 2.5G Ethernet Port on the MP2.5G
Go to "System - TTYD Terminal," enter the ifconfig -a command, and you can see two network interfaces, eth0 and eth1. eth0 is the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5, and eth1 is the 2.5G Ethernet port of the expansion board:
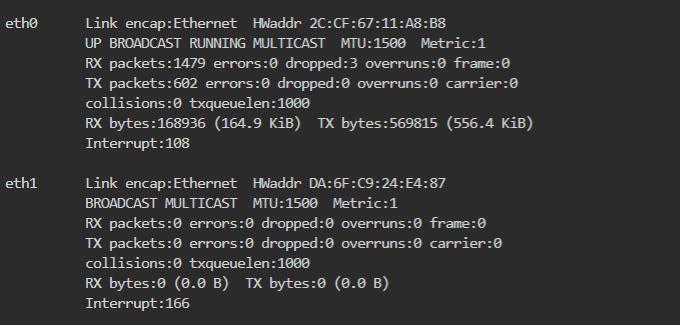
The broadband we typically use does not exceed gigabit speeds. To achieve better intranet performance, it is recommended to configure the native Gigabit port of the Raspberry Pi 5 from its default LAN setting to WAN, and then configure the 2.5G Ethernet port (eth1) of the expansion board as LAN:
Open "Network - Interfaces", and click "EDIT":
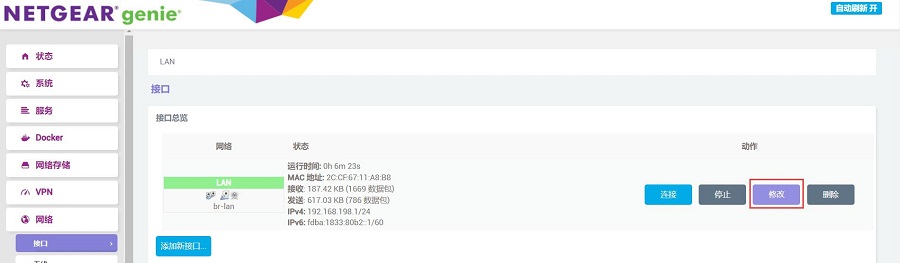
In the "Physical Settings", select eth1 and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button.
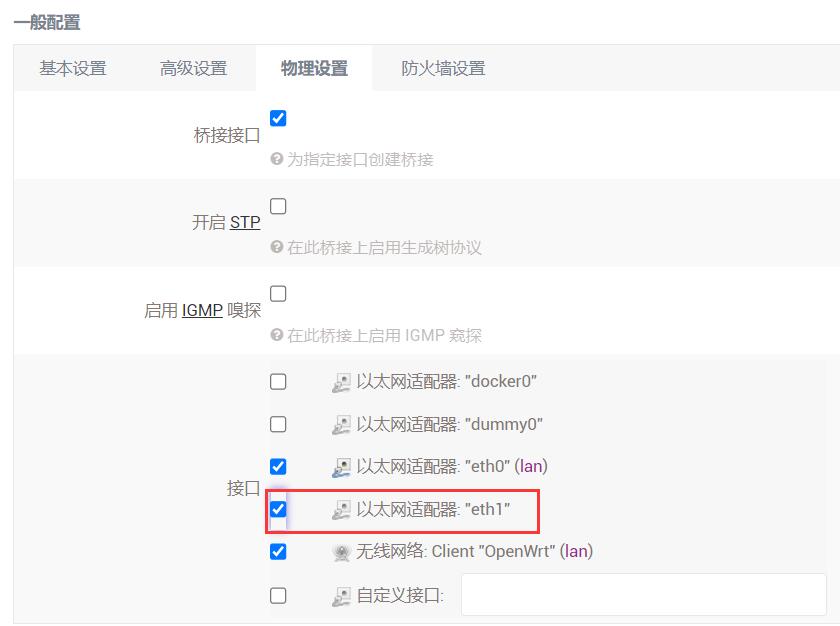
Remove the network cable from the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5 and insert it into the 2.5G Ethernet port (eth1). After the PC's network card successfully connects to the 2.5G port, refresh the management page, click on "Network - Interfaces", and then click "EDIT":
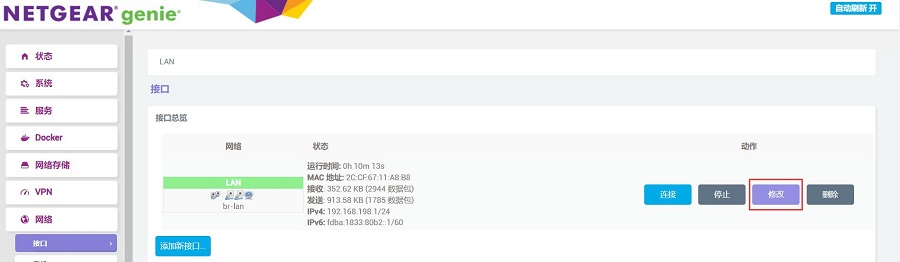
In the "Physical Settings", remove the checkmark from in front of eth0, and then click the "SAVE" button.
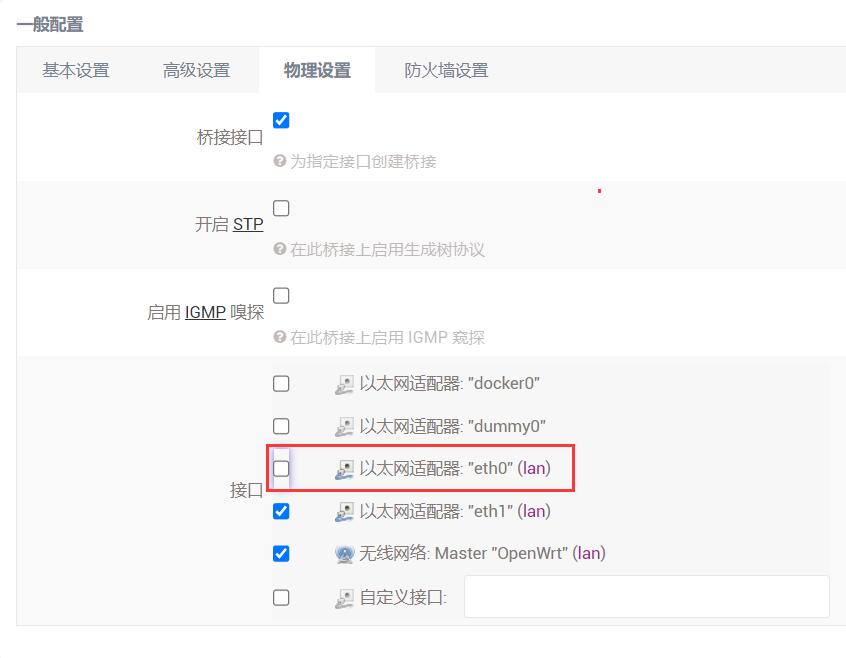
Go back to "Network - Interfaces", and click "Add new interface":
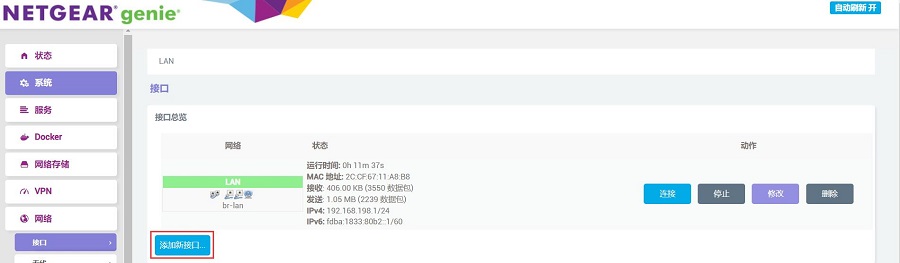
Set "Name of the new interface" as WAN, choose "DHCP client" for "Protocol of the new interface," select "eth0" for "Cover the following interface," and then click the "SUBMIT" button:
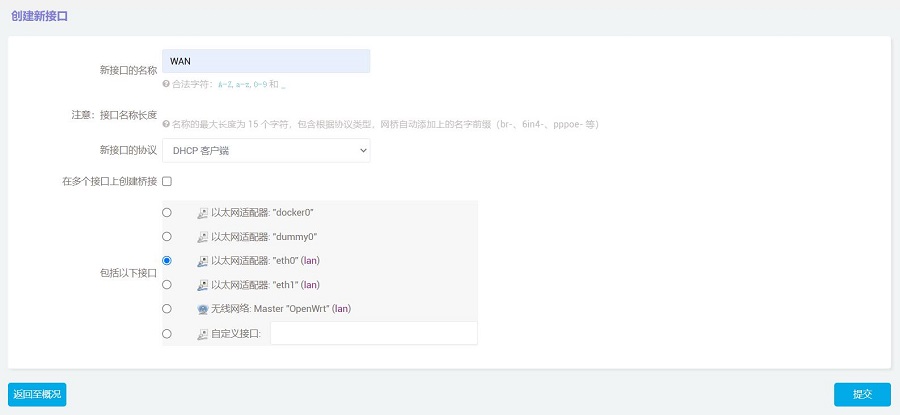
In the "Firewall Settings", select the WAN and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button:
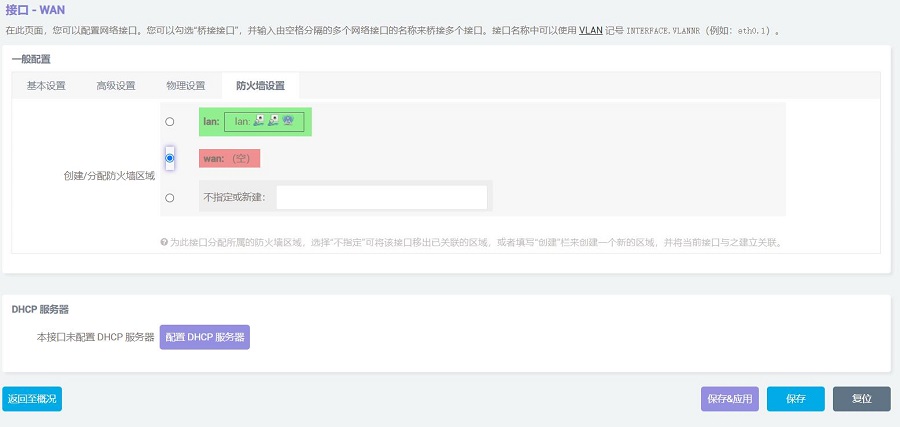
Plug the network cable connected to the Internet into the native Ethernet port of the Raspberry Pi 5, then go back to "Network - Interfaces". After a moment, you will see that the newly created WAN interface has obtained an IP address. This way, the PC can access the internal network through the 2.5G Ethernet port (eth1). At this point, the network structure is such that the Gigabit Ethernet port (connected to the Internet on the Raspberry Pi) is the incoming connection, and the 2.5G Ethernet port (connected to the internal network on the expansion board) is the outgoing connection.
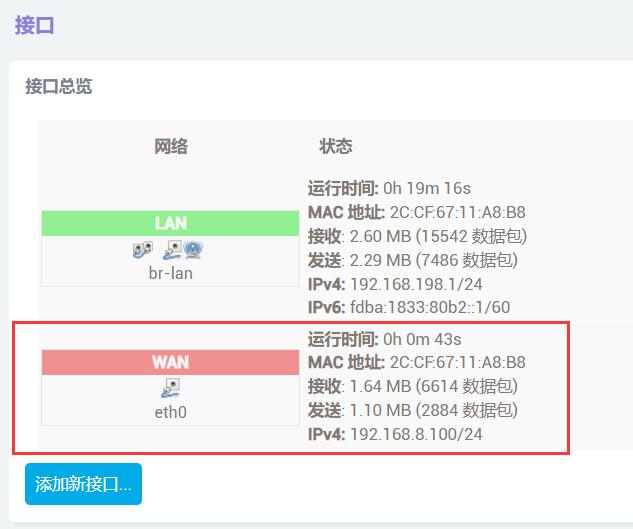
We insert a USB3.0-supported USB drive or mobile hard disk into the USB3.0 port of the Raspberry Pi 5, and refer to the following link to configure this USB drive or mobile hard disk as a shared directory:
After setting it up, enter \\192.168.198.1 in the File Explorer (the address is that of the expansion board and may differ based on actual conditions), and you will be able to see the mapped shared directory:
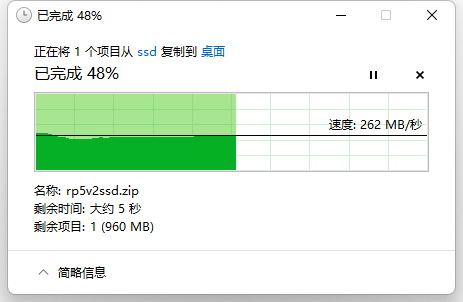
Read test for SSD:
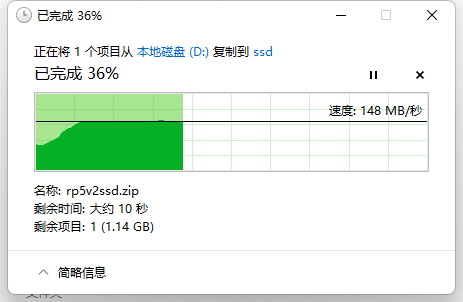
Write test for SSD:
Note: The speed test can be affected by the network environment and the testing method. Speeds should be considered based on actual results; this test is for reference only.
6.4 Other Applications
The wireless module of the Raspberry Pi 5 can function as a wireless AP or as a wireless WAN port. For the implementation of these applications, please refer to the following link:
1. Use the Raspberry Pi's built-in WiFi as a wireless AP (in master mode)
2. Use the Raspberry Pi's built-in WiFi as a Client
VII. PoE Ethernet Introduction
Contact Us
Email: mcuzone@vip.qq.com
Tel: +86(0)13957118045
If there are any omissions, errors, or infringements on this page, please contact us through the above methods. Thank you!
Copyright 2004-2024 Wildchip




 QQ:8204136
QQ:8204136