1002 RPi0 4G Cat1 (EN):修订间差异
(创建页面,内容为“== '''关键词''' == 树莓派Raspberry Pi Zero、Zero 2W、Cat1 4G LTE、USB2.0、USB Type-C、扩展板、Nano SIM、eSIM、RPi-Connect、远程连接、免驱即插即用 == '''一、简介''' == 树莓派Zero CAT1是一款尺寸只有65*30mm的4G LTE扩展板,基于树莓派Zero系列(包括Zero、Zero W(H)以及Zero 2W)尺寸设计,利用树莓派Zero板子反面引出的USB和电源的镀金测试点,进行外设扩展。扩展板分USB版和…”) |
|||
| (未显示2个用户的25个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
[[1002 RPi0 4G Cat1|切换语言为中文]] | |||
== ''' | == '''Keywords''' == | ||
Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero 2W, Cat1 4G LTE Expansion board, Nano SIM, RPi-Connect, Remote connection, Driver-free, Plug and play | |||
4G | == '''I. Introduction''' == | ||
The Raspberry Pi Zero CAT1 is a 4G LTE expansion board measuring only 65*30mm in size. It is designed based on the Raspberry Pi Zero series (including the Zero, Zero W(H), and Zero 2W). It utilizes the gold-plated test points on the backside of the Raspberry Pi Zero board for USB and power to enable peripheral expansion. | |||
The expansion board comes in two versions: the USB version and the Probe version. The Probe version connects the expansion board to the Zero's USB port via pogo pins. In this case, it is no longer possible to connect USB devices such as keyboard or mouse to the Raspberry Pi Zero's micro USB port. but we can control the device through a remote connection. The USB version (without pogo pins) can be used with the Raspberry Pi 3B, 4B, and 5. The expansion board uses a recessed design, which facilitates installation on top of boards like the Raspberry Pi 3B/4B/5, ensuring it does not affect or minimally affects the external connections of the 40-pin header. | |||
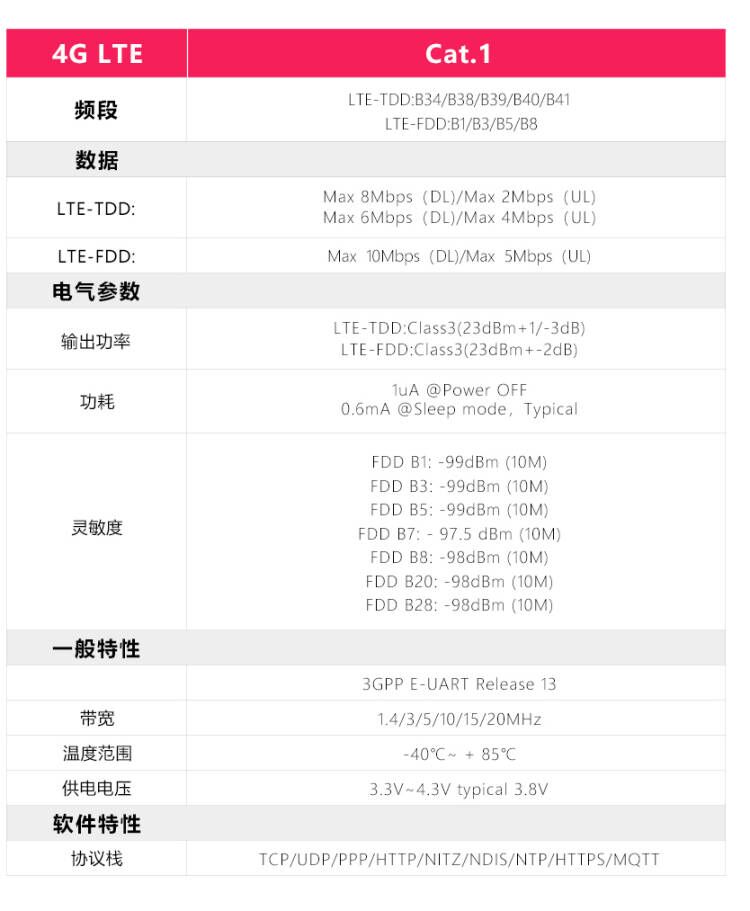
4G Cat1 is a cost-effective module designed for medium-speed IoT applications around 10Mbps. The 10Mbps downlink and 5Mbps uplink speeds can meet the vast majority of networking and transmission needs. The CAT1 expansion board is driver-free and plug-and-play under the official Raspberry Pi operating system. | |||
'''''(To use the 4G module, the band supported by your local service provider must match the parameters of the 4G module. Therefore, please verify whether this 4G module is suitable for your area before making a purchase.)''''' | |||
== '''II. Hardware Spec''' == | |||
1. The '''Probe''' version connects to the Raspberry Pi Zero series' pogo pins to achieve power supply and communication. | |||
Powered through the Zero's MicroUSB power port. '''''At this point, the Raspberry Pi Zero's own micro USB, the onboard USB-C port, and the 1.25mm 4-pin interface cannot be used to connect any external devices or power sources.''''' | |||
2. The '''USB''' version (without soldering pogo pins) | |||
Power supply:5V input,USB-C or 1.25mm 4-pin USB, choose one of the two options to use.. | |||
3. One 4G CAT1 LTE and a Nano SIM card slot; | |||
4. One IPEX 1 connector. | |||
5. Debug Serial Port and AT main serial port: 2.54mm-3Pin,both at 3.3V voltage level. | |||
6. Two LEDs: | |||
::One STAT LED:CAT1 is functioning normally. | |||
::One NET LED: 1.8 seconds on and 0.2 seconds off indicating successful network registration. | |||
::1.8 seconds off and 0.2 seconds on indicating that the device has not registered onto the network, suggesting that the SIM card and antenna should be checked. | |||
7. The reserved BooT and reset button is on the back side reverse side. | |||
(If there is a need to perform a button reset, you can solder the buttons yourself.) | |||
8. Size: 65*30*6.6mm;M2.5mm mounting holes. | |||
9. PCB: UL and ROHS certification, fire protection rating of 94V-0. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_21.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_21.jpg | ||
| 第30行: | 第47行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_22.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_22.jpg | ||
== ''' | == '''III. Work with Raspberry Pi OS''' == | ||
=== 3.1 | === 3.1 USB version === | ||
If connecting to a Raspberry Pi Zero series board, it generally requires the use of an expansion board with a USB interface. So you just need to enable USB Host mode in the config.txt file. | |||
Here, we are assembling the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W using our company's [[1005 RPi0-2U2E(双百兆网络双USB)|RPi0_2U2E Board]], and then connecting the USB version. | |||
The USB version occupies the right-side [[1005 RPi0-2U2E(双百兆网络双USB)|RPi0_2U2E Board]] (as shown in the image below). This USB port cannot be used to connect any external devices; otherwise, the 4G functionality will not work. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_12.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_12.jpg | ||
After booting the system, execute <code>ifconfig -a</code>, and you will see eth2, which corresponds to the 4G CAT1 interface; while eth0 and eth1 are the two 100Mbps Ethernet ports on the [[1005 RPi0-2U2E(双百兆网络双USB)|RPi0_2U2E Board]]. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_14.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_14.jpg | ||
=== 3.2 Probe version === | |||
==== 3.2.1 Preparation ==== | |||
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W has only one USB port, which is now occupied by the 4G module, so there are no USB ports available for a keyboard or mouse. Subsequent operations can only be performed through a WiFi or 4G connection. Therefore, when flashing the system, you need to pre-configure it to set up WiFi and enable SSH to proceed further (if you are using a Raspberry Pi Zero W or Zero WH, the usage method is the same). | |||
If you are using the Raspberry Pi Zero, which lacks WiFi functionality, you would need to debug all business logic and set it up to run on startup on another expansion board. If you do not have any subsequent need to connect other USB devices and the 4G Cat1 is only used to provide network access, you can use the Probe version. Otherwise, it is recommended to use the USB version. | |||
Hardware: Please plug the power supply into the USB power port marked "PWR" on the Zero 2W. If you plug it into another USB port or the USB port on the expansion board, it will cause the 4G module to be shielded. | |||
Wiring diagram: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_20.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_20.jpg | ||
The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz | |||
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in: | |||
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit | |||
(If using the first-generation Raspberry Pi Zero board, which only supports 32-bit systems, please pay attention to the version you download.) | |||
==== 3.2.2 | ==== 3.2.2 Flashing system (Setup required for WiFi connection and SSH service) ==== | ||
Open the Imager, select the “Raspberry Pi Device”, “Choose Use Custom”, and “Storge”, then click "NEXT." | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_01.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_01.jpg | ||
Then click "Edit Settings" : | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_02.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_02.jpg | ||
In the pop-up window, under the GENERAL tab, you can set the hostname, username, and password, the default WiFi connection, and the region: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_03.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_03.jpg | ||
Under the SERVICES tab, please set up to enable the SSH service: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_04.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_04.jpg | ||
After completing the settings, click "Save," return to the previous page, and then click "Yes": | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_05.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_05.jpg | ||
Click "Yes" in the warning window: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_06.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_06.jpg | ||
This will start the burning process. After the burning is complete, use this TF card to boot the system. The system will automatically log in with the preset username and password and connect to the preconfigured WiFi (provided the device is within range of the WiFi hotspot). | |||
If the system stop at the Raspberry Pi logo and fails to boot: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_58.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_58.jpg | ||
Please carefully check whether the pogo pins are aligned with the gold-plated contacts. Additionally, on the PC, open the <code>config.txt</code> file located in the root directory of the TF card to check the USB initialization script: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_41.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_41.jpg | ||
You need to confirm that the three red-boxed areas in the following image are all configured completely. If not, please manually add the missing parts and save the file: | |||
<code># otg_mode=1</code> | <code># otg_mode=1</code> (It is recommended to comment out as follow) | ||
<code>dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=host</code> | <code>dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=host</code> (These two areas must be ensured to be included.) | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_57.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_57.jpg | ||
==== 3.2.3 | ==== 3.2.3 Control via SSH through WiFi ==== | ||
After the system starts, if the WiFi connection is successful, the internal network IP will be displayed below the WiFi icon in the top right corner of the desktop: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_07.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_07.jpg | ||
You can also obtain the system's internal IP address by checking the router's backend: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_19.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_19.jpg | ||
Here, we use the MobaXterm for SSH. The download link for MobaXterm is: | |||
https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download-home-edition.html | https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download-home-edition.html | ||
Open the MobaXterm, create a new connection, select SSH, enter the IP address of the Raspberry Pi OS in the "Remote Host", and enter the login username in the "Specify username", as shown in the following figure:http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_08.jpg | |||
Click "OK," then log in. After logging in, we can perform command-line operations on the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W using MobaXterm: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_23.jpg | |||
Now we check the connection status of the 4G module: | |||
<code>lsusb</code> | <code>lsusb</code> | ||
| 第136行: | 第153行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_24.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_24.jpg | ||
It can be seen that the 4G module has connected. | |||
Using <code>ifconfig -a</code> to check the network interfaces, it can be seen that the 4G module is identified as eth0 and has obtained an IP address: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_25.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_25.jpg | ||
==== 3.2.4 | ==== 3.2.4 How to use AT commands ==== | ||
Execute the command in the SSH terminal: | |||
<code>ls /dev</code> | <code>ls /dev</code> | ||
You should be able to see three devices named ttyACM0, ttyACM1, and ttyACM2 under the dev directory: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_27.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_27.jpg | ||
Install minicom: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get install minicom</code> | <code>sudo apt-get install minicom</code> | ||
| 第157行: | 第174行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_28.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_28.jpg | ||
Open AT Command serial port by minicom: | |||
<code>sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0</code> | <code>sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0</code> | ||
Note: When using a serial port, ensure that after entering this port, you can input and run AT commands without any garbled output or unexpected jumps in the results. | |||
The following uses minicom as an example: | |||
Then directly type the AT command and press Enter to see the result. If you need to view the echo, please type the command: <code>ate1</code>: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_29.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_29.jpg | ||
Common AT commands: | |||
1 | 1) Check if the SIM card is detected: | ||
<code>at+cpin?</code> | <code>at+cpin?</code> | ||
Return ready to indicate the card has been recognized, if return error, you need to check the hardware. | |||
2 | 2) Check antenna signal quality: | ||
<code>at+csq</code> | <code>at+csq</code> | ||
Return values between 26 and 31 indicate a good signal, with 31 representing a full signal strength; return values between 20 and 25 indicate a barely acceptable signal; return values below 20 indicate a poor signal or that the antenna might not be connected. | |||
3 | 3) Check network registration status: | ||
<code>at+cops?</code> | <code>at+cops?</code> | ||
Normally, it should return the network supporter's code: 7, where 7 represents 4G. | |||
Note: The above command <code>at+csq</code> should not include a question mark, while the other two commands require a question mark. | |||
4 | 4) View the SIM card's IMEI code: | ||
<code>at+cgsn</code> | <code>at+cgsn</code> | ||
5. | 5) Reset 4G module (Sometimes, if you reinsert the SIM card, hot swapping may not work; in such cases, you can use this reset command to reset the module.): | ||
<code>at+reset</code> | <code>at+reset</code> | ||
6 | 6) Disable radio frequency: | ||
<code>at+cfun=0</code> | <code>at+cfun=0</code> | ||
Enable radio frequency: | |||
<code>at+cfun=1</code> | <code>at+cfun=1</code> | ||
The two commands mentioned above can be used in pairs to allow the module to re-register with the network without restarting the 4G module. | |||
==== 3.2.5 Enable SIM card hot-swapping ==== | |||
This expansion board supports SIM card hot-swapping, but this feature is disabled by default. To enable it, first remove the SIM card, and then open the AT command serial port: | |||
<code>sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0</code> | |||
Execute: | |||
= | <code>at+csdt=1</code> | ||
If the output is "OK," it indicates that the setting was successful. | |||
You can use <code>AT+CSDT?</code> to check the current status. A return value of <code>1</code> indicates that the SIM card hot-swapping feature has been enabled. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_33.jpg | |||
After hot-swapping the SIM card, execute the following commands separately. If all commands are successful (with <code>eth0</code> being the 4G module), it confirms that hot-swapping is supported: | |||
<code>sudo udhcpc -i eth0</code> | |||
<code>ping www.mcuzone.com -I eth0</code> | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_34.jpg | |||
== '''IV. 4G Application (Remote Control)''' == | |||
RPi-Connect provides a service for secure access to your Raspberry Pi from anywhere. With this service, combined with the Zero Cat1 4G Probe version, you can still remotely access your Raspberry Pi even when outdoors without a Wi-Fi network. Note: To use this service, Bookworm or a newer system must be running. Additionally, only the Raspberry Pi 5, 4, or 400 can use screen sharing. The Zero 2W can only use Remote Shell. The following demonstrates how to configure the remote connection service. | |||
=== 4.1 Install DNS service (only for system version 2024.07.04 and later) === | |||
The 4G CAT1 module is driver-free and can achieve automatic 4G connectivity at each boot. However, to avoid DNS server conflicts, the following settings need to be applied for automatic startup: | |||
Install the DNS server switching software udhcpc: | |||
<code>sudo apt install udhcpc</code> | <code>sudo apt install udhcpc</code> | ||
| 第221行: | 第261行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_18.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_18.jpg | ||
Open rc-local service: | |||
<code>sudo sudo systemctl enable --now rc-local</code> | <code>sudo sudo systemctl enable --now rc-local</code> | ||
Use the following command to open rc.local: | |||
<code>sudo nano /etc/rc.local</code> | <code>sudo nano /etc/rc.local</code> | ||
Add the command you want to execute at startup above the line <code>exit 0</code>, and then save the file (in this example, eth0 represents the 4G module, but the name should match the actual interface identified on your system): | |||
<code>sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0 && sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0 && sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0</code> | <code>sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0 && sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0 && sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0</code> | ||
| 第235行: | 第275行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_23.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_23.jpg | ||
The <code>sleep</code> command is used to delay the execution of subsequent commands by a certain number of seconds. Since the 4G module needs some time to acquire an IP address, to prevent `udhcpc` from failing, it needs to be executed several times with a delay added between each execution. As a result, the 4G network becomes usable approximately 20 seconds after the system boots up. | |||
=== 4.2 | === 4.2 Apply for a Raspberry Pi ID === | ||
If you already have a Raspberry Pi ID, please log in directly. If not, please follow the steps below to apply. | |||
Open the website at https://id.raspberrypi.com/, and enter the email address and password you wish to use: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_12.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_12.jpg | ||
After creating the account, you need to verify it by entering your email: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_13.jpg | ||
| 第250行: | 第290行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_14.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_14.jpg | ||
After verification is complete, the ID can be used. | |||
=== 4.3 | === 4.3 Install Remote Service === | ||
Open the SSH terminal and install the Raspberry Pi Connect software. If the installation command indicates that it is already installed, then no additional installation is necessary: | |||
<code>sudo apt install rpi-connect</code> | <code>sudo apt install rpi-connect</code> | ||
After installation, we enter <code>loginctl enable-linger</code> in the terminal to ensure that the remote service is automatically enabled each time the system restarts: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_32.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_32.jpg | ||
Restart the system. In the graphical interface, select the items in the order shown in the following image to ensure that Raspberry Pi Connect is turned on: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0002_MPS2280iPoE/MPS2280iPoE_08.png | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0002_MPS2280iPoE/MPS2280iPoE_08.png | ||
| 第267行: | 第307行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_13.jpg | ||
Then enter the following in the Raspberry Pi terminal: | |||
<code>rpi-connect signin</code> | <code>rpi-connect signin</code> | ||
| 第273行: | 第313行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_30.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_30.jpg | ||
Now, a URL is displayed, as shown in the image above. Open this URL in a browser (it is recommended to use another computer, as the Zero series can be very slow when opening a browser due to hardware limitations). | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_17.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_17.jpg | ||
Click on "Sign in" and follow the prompts to bind the device. First, you need to set the device name: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_18.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_18.jpg | ||
Click "Create device and sign in": | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_19.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_19.jpg | ||
This completes the binding process, and there will also be a successful message displayed in the terminal: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_31.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1/1002_Zero_4G_Cat1_31.jpg | ||
=== 4.4 | === 4.4 Use remote control === | ||
On your PC, open: <code><nowiki>https://connect.raspberrypi.com/devices</nowiki></code>http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_21.jpg | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_21.jpg | |||
The Zero 2W device just added only shows "Remote shell", indicating that this device can only be controlled through a remote command-line interface. | |||
Click on "Connect" to open the remote command-line interface, where you can then enter commands: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_22.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub/1003_Zero_4G_Cat1-Hub_22.jpg | ||
After configuration is complete, the system will be able to connect to the internet via 4G each time it boots up and will also enable the Raspberry Pi Connect remote service. This way, we can control the device through a remote command-line interface from a PC. | |||
{{ | {{Contact_Us_icon}} | ||
2024年11月15日 (五) 13:09的最新版本
Keywords
Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero 2W, Cat1 4G LTE Expansion board, Nano SIM, RPi-Connect, Remote connection, Driver-free, Plug and play
I. Introduction
The Raspberry Pi Zero CAT1 is a 4G LTE expansion board measuring only 65*30mm in size. It is designed based on the Raspberry Pi Zero series (including the Zero, Zero W(H), and Zero 2W). It utilizes the gold-plated test points on the backside of the Raspberry Pi Zero board for USB and power to enable peripheral expansion.
The expansion board comes in two versions: the USB version and the Probe version. The Probe version connects the expansion board to the Zero's USB port via pogo pins. In this case, it is no longer possible to connect USB devices such as keyboard or mouse to the Raspberry Pi Zero's micro USB port. but we can control the device through a remote connection. The USB version (without pogo pins) can be used with the Raspberry Pi 3B, 4B, and 5. The expansion board uses a recessed design, which facilitates installation on top of boards like the Raspberry Pi 3B/4B/5, ensuring it does not affect or minimally affects the external connections of the 40-pin header.
4G Cat1 is a cost-effective module designed for medium-speed IoT applications around 10Mbps. The 10Mbps downlink and 5Mbps uplink speeds can meet the vast majority of networking and transmission needs. The CAT1 expansion board is driver-free and plug-and-play under the official Raspberry Pi operating system.
(To use the 4G module, the band supported by your local service provider must match the parameters of the 4G module. Therefore, please verify whether this 4G module is suitable for your area before making a purchase.)
II. Hardware Spec
1. The Probe version connects to the Raspberry Pi Zero series' pogo pins to achieve power supply and communication.
Powered through the Zero's MicroUSB power port. At this point, the Raspberry Pi Zero's own micro USB, the onboard USB-C port, and the 1.25mm 4-pin interface cannot be used to connect any external devices or power sources.
2. The USB version (without soldering pogo pins)
Power supply:5V input,USB-C or 1.25mm 4-pin USB, choose one of the two options to use..
3. One 4G CAT1 LTE and a Nano SIM card slot;
4. One IPEX 1 connector.
5. Debug Serial Port and AT main serial port: 2.54mm-3Pin,both at 3.3V voltage level.
6. Two LEDs:
- One STAT LED:CAT1 is functioning normally.
- One NET LED: 1.8 seconds on and 0.2 seconds off indicating successful network registration.
- 1.8 seconds off and 0.2 seconds on indicating that the device has not registered onto the network, suggesting that the SIM card and antenna should be checked.
7. The reserved BooT and reset button is on the back side reverse side.
(If there is a need to perform a button reset, you can solder the buttons yourself.)
8. Size: 65*30*6.6mm;M2.5mm mounting holes.
9. PCB: UL and ROHS certification, fire protection rating of 94V-0.

III. Work with Raspberry Pi OS
3.1 USB version
If connecting to a Raspberry Pi Zero series board, it generally requires the use of an expansion board with a USB interface. So you just need to enable USB Host mode in the config.txt file.
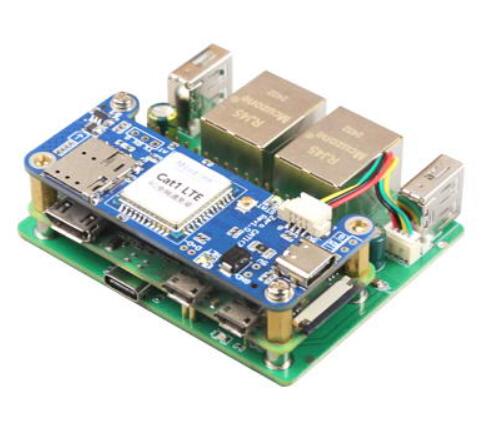
Here, we are assembling the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W using our company's RPi0_2U2E Board, and then connecting the USB version.
The USB version occupies the right-side RPi0_2U2E Board (as shown in the image below). This USB port cannot be used to connect any external devices; otherwise, the 4G functionality will not work.

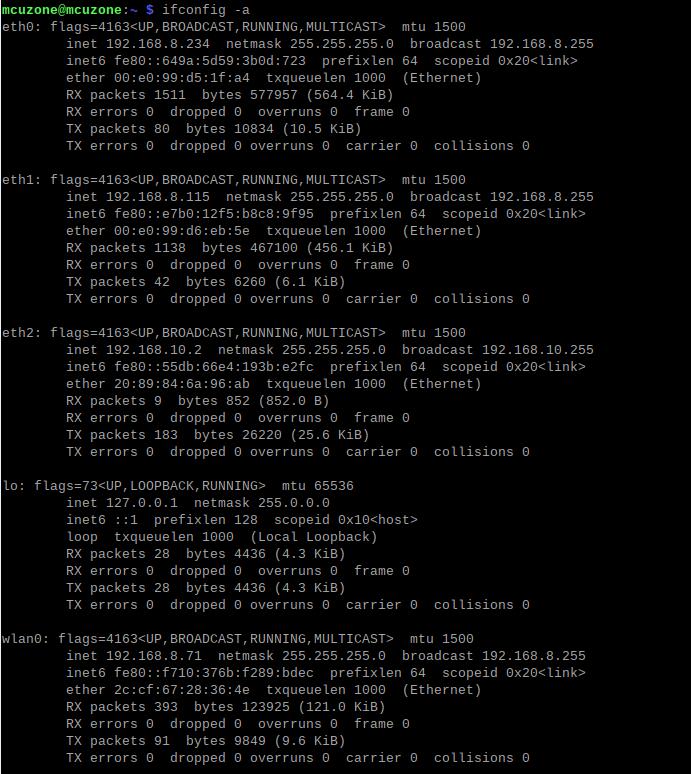
After booting the system, execute ifconfig -a, and you will see eth2, which corresponds to the 4G CAT1 interface; while eth0 and eth1 are the two 100Mbps Ethernet ports on the RPi0_2U2E Board.
3.2 Probe version
3.2.1 Preparation
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W has only one USB port, which is now occupied by the 4G module, so there are no USB ports available for a keyboard or mouse. Subsequent operations can only be performed through a WiFi or 4G connection. Therefore, when flashing the system, you need to pre-configure it to set up WiFi and enable SSH to proceed further (if you are using a Raspberry Pi Zero W or Zero WH, the usage method is the same).
If you are using the Raspberry Pi Zero, which lacks WiFi functionality, you would need to debug all business logic and set it up to run on startup on another expansion board. If you do not have any subsequent need to connect other USB devices and the 4G Cat1 is only used to provide network access, you can use the Probe version. Otherwise, it is recommended to use the USB version.
Hardware: Please plug the power supply into the USB power port marked "PWR" on the Zero 2W. If you plug it into another USB port or the USB port on the expansion board, it will cause the 4G module to be shielded.
Wiring diagram:

The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit
(If using the first-generation Raspberry Pi Zero board, which only supports 32-bit systems, please pay attention to the version you download.)
3.2.2 Flashing system (Setup required for WiFi connection and SSH service)
Open the Imager, select the “Raspberry Pi Device”, “Choose Use Custom”, and “Storge”, then click "NEXT."
Then click "Edit Settings" :
In the pop-up window, under the GENERAL tab, you can set the hostname, username, and password, the default WiFi connection, and the region:
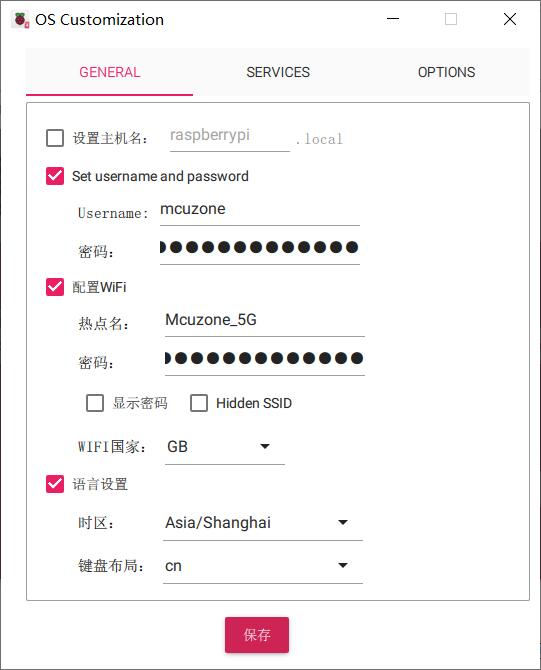
Under the SERVICES tab, please set up to enable the SSH service:
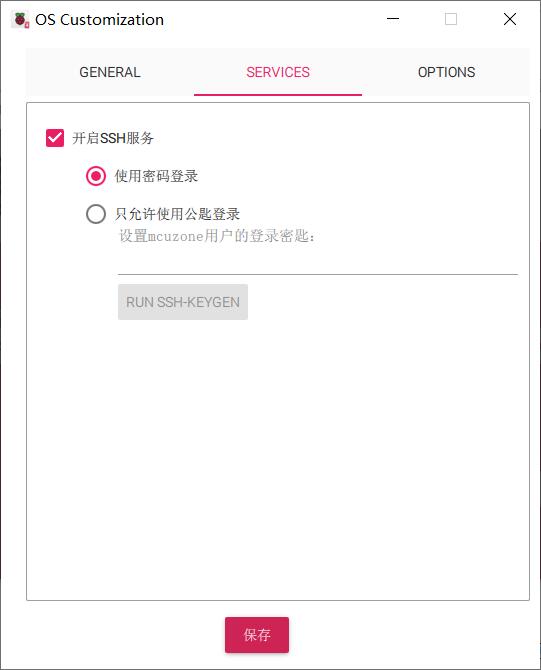
After completing the settings, click "Save," return to the previous page, and then click "Yes":
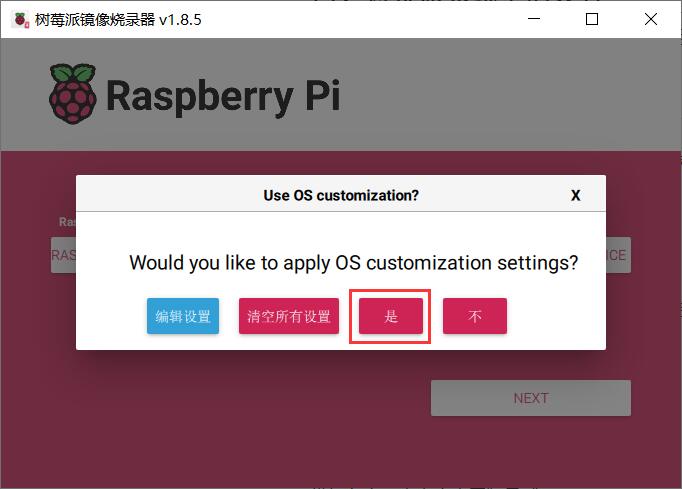
Click "Yes" in the warning window:
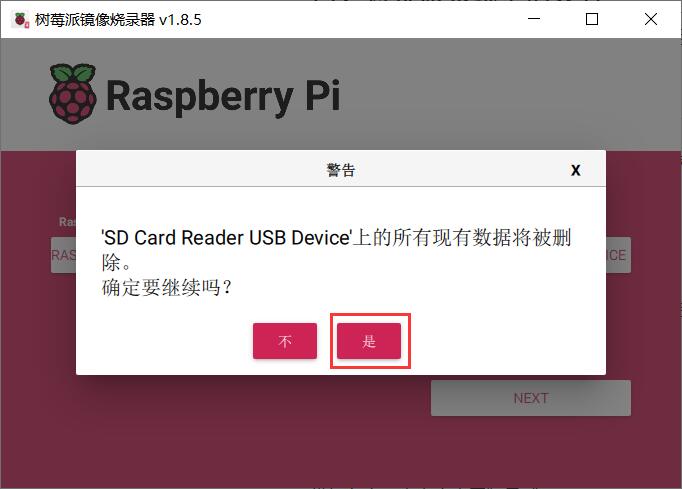
This will start the burning process. After the burning is complete, use this TF card to boot the system. The system will automatically log in with the preset username and password and connect to the preconfigured WiFi (provided the device is within range of the WiFi hotspot).
If the system stop at the Raspberry Pi logo and fails to boot:

Please carefully check whether the pogo pins are aligned with the gold-plated contacts. Additionally, on the PC, open the config.txt file located in the root directory of the TF card to check the USB initialization script:
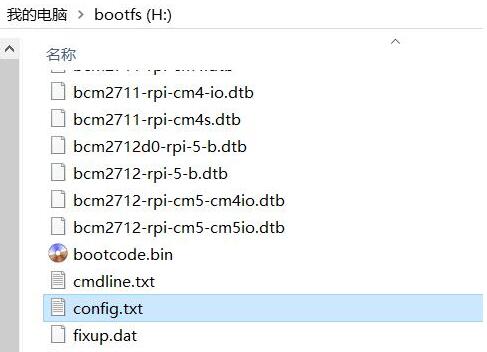
You need to confirm that the three red-boxed areas in the following image are all configured completely. If not, please manually add the missing parts and save the file:
# otg_mode=1 (It is recommended to comment out as follow)
dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=host (These two areas must be ensured to be included.)
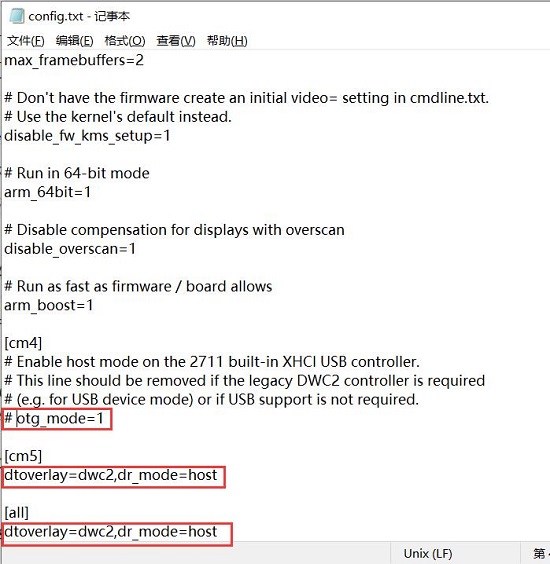
3.2.3 Control via SSH through WiFi
After the system starts, if the WiFi connection is successful, the internal network IP will be displayed below the WiFi icon in the top right corner of the desktop:
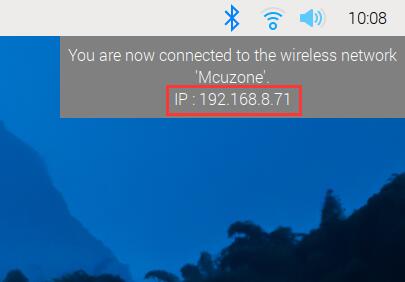
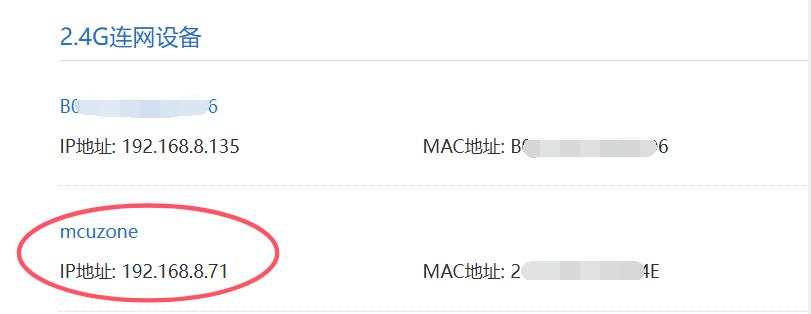
You can also obtain the system's internal IP address by checking the router's backend:
Here, we use the MobaXterm for SSH. The download link for MobaXterm is:
https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download-home-edition.html
Open the MobaXterm, create a new connection, select SSH, enter the IP address of the Raspberry Pi OS in the "Remote Host", and enter the login username in the "Specify username", as shown in the following figure: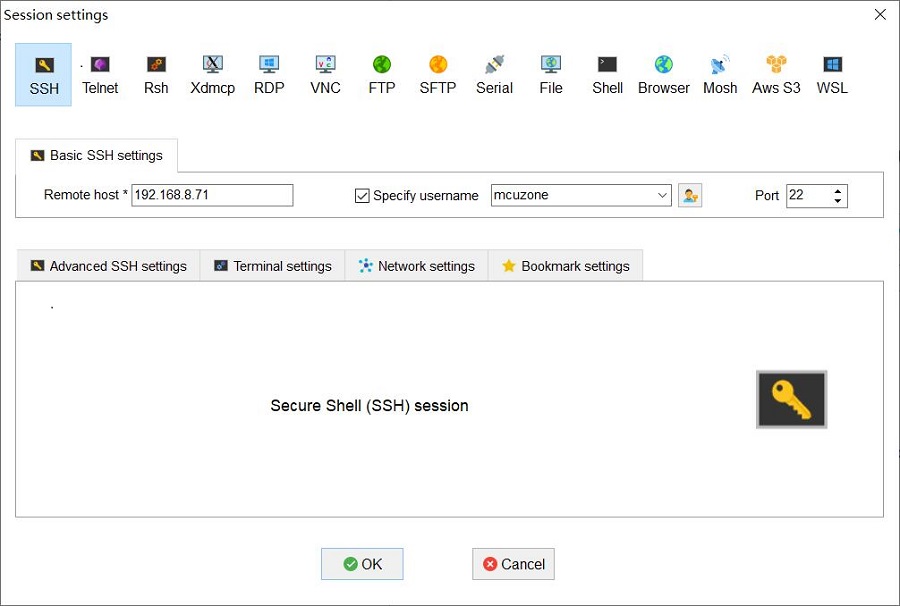
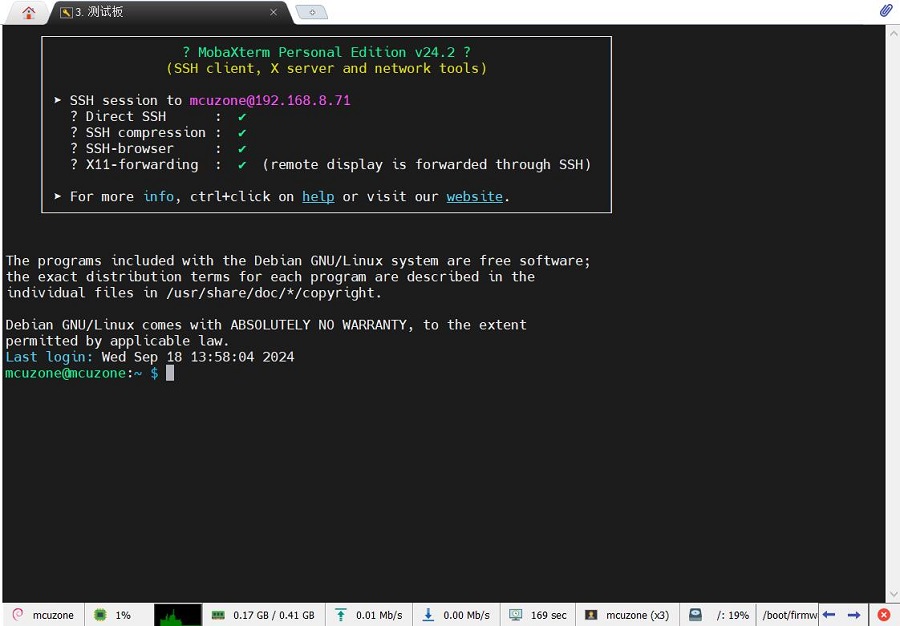
Click "OK," then log in. After logging in, we can perform command-line operations on the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W using MobaXterm:
Now we check the connection status of the 4G module:
lsusb
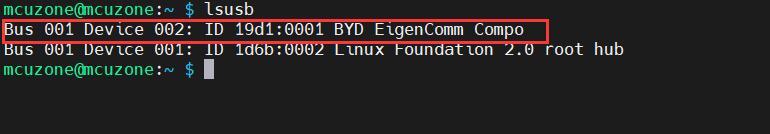
It can be seen that the 4G module has connected.
Using ifconfig -a to check the network interfaces, it can be seen that the 4G module is identified as eth0 and has obtained an IP address:
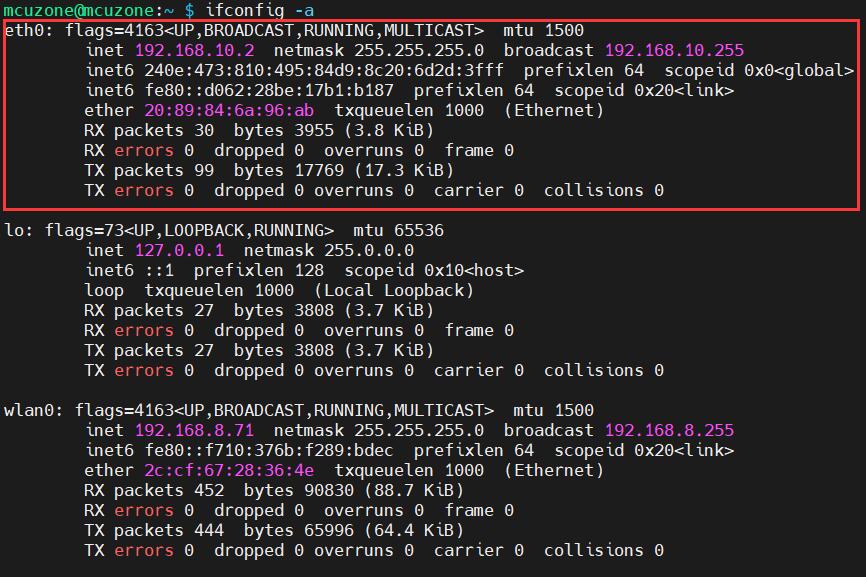
3.2.4 How to use AT commands
Execute the command in the SSH terminal:
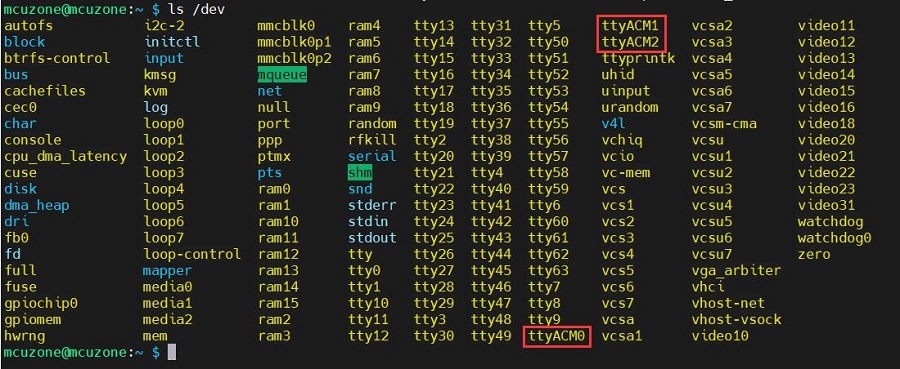
ls /dev
You should be able to see three devices named ttyACM0, ttyACM1, and ttyACM2 under the dev directory:
Install minicom:
sudo apt-get install minicom
Open AT Command serial port by minicom:
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0
Note: When using a serial port, ensure that after entering this port, you can input and run AT commands without any garbled output or unexpected jumps in the results.
The following uses minicom as an example:
Then directly type the AT command and press Enter to see the result. If you need to view the echo, please type the command: ate1:

Common AT commands:
1) Check if the SIM card is detected:
at+cpin?
Return ready to indicate the card has been recognized, if return error, you need to check the hardware.
2) Check antenna signal quality:
at+csq
Return values between 26 and 31 indicate a good signal, with 31 representing a full signal strength; return values between 20 and 25 indicate a barely acceptable signal; return values below 20 indicate a poor signal or that the antenna might not be connected.
3) Check network registration status:
at+cops?
Normally, it should return the network supporter's code: 7, where 7 represents 4G.
Note: The above command at+csq should not include a question mark, while the other two commands require a question mark.
4) View the SIM card's IMEI code:
at+cgsn
5) Reset 4G module (Sometimes, if you reinsert the SIM card, hot swapping may not work; in such cases, you can use this reset command to reset the module.):
at+reset
6) Disable radio frequency:
at+cfun=0
Enable radio frequency:
at+cfun=1
The two commands mentioned above can be used in pairs to allow the module to re-register with the network without restarting the 4G module.
3.2.5 Enable SIM card hot-swapping
This expansion board supports SIM card hot-swapping, but this feature is disabled by default. To enable it, first remove the SIM card, and then open the AT command serial port:
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0
Execute:
at+csdt=1
If the output is "OK," it indicates that the setting was successful.
You can use AT+CSDT? to check the current status. A return value of 1 indicates that the SIM card hot-swapping feature has been enabled.

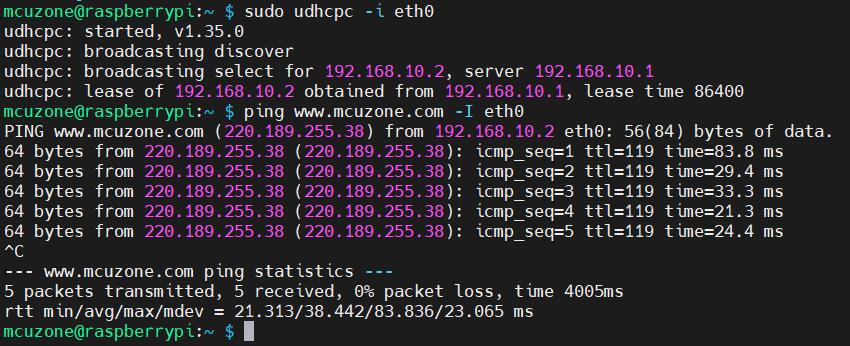
After hot-swapping the SIM card, execute the following commands separately. If all commands are successful (with eth0 being the 4G module), it confirms that hot-swapping is supported:
sudo udhcpc -i eth0
ping www.mcuzone.com -I eth0
IV. 4G Application (Remote Control)
RPi-Connect provides a service for secure access to your Raspberry Pi from anywhere. With this service, combined with the Zero Cat1 4G Probe version, you can still remotely access your Raspberry Pi even when outdoors without a Wi-Fi network. Note: To use this service, Bookworm or a newer system must be running. Additionally, only the Raspberry Pi 5, 4, or 400 can use screen sharing. The Zero 2W can only use Remote Shell. The following demonstrates how to configure the remote connection service.
4.1 Install DNS service (only for system version 2024.07.04 and later)
The 4G CAT1 module is driver-free and can achieve automatic 4G connectivity at each boot. However, to avoid DNS server conflicts, the following settings need to be applied for automatic startup:
Install the DNS server switching software udhcpc:
sudo apt install udhcpc

Open rc-local service:
sudo sudo systemctl enable --now rc-local
Use the following command to open rc.local:
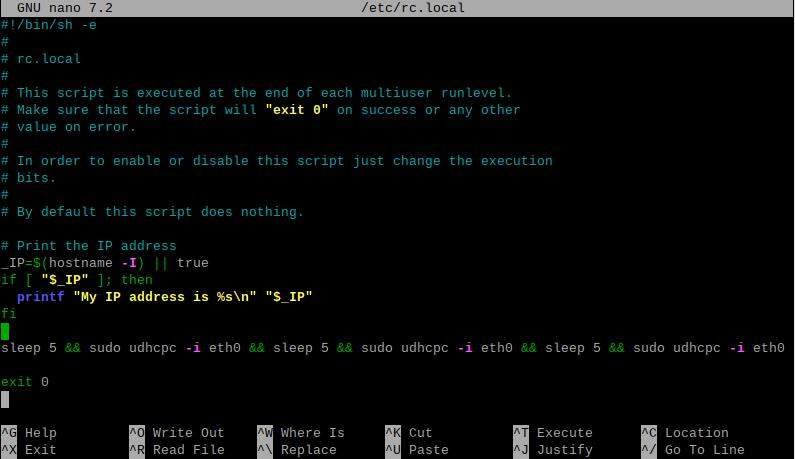
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
Add the command you want to execute at startup above the line exit 0, and then save the file (in this example, eth0 represents the 4G module, but the name should match the actual interface identified on your system):
sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0 && sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0 && sleep 5 && sudo udhcpc -i eth0
The sleep command is used to delay the execution of subsequent commands by a certain number of seconds. Since the 4G module needs some time to acquire an IP address, to prevent `udhcpc` from failing, it needs to be executed several times with a delay added between each execution. As a result, the 4G network becomes usable approximately 20 seconds after the system boots up.
4.2 Apply for a Raspberry Pi ID
If you already have a Raspberry Pi ID, please log in directly. If not, please follow the steps below to apply.
Open the website at https://id.raspberrypi.com/, and enter the email address and password you wish to use:
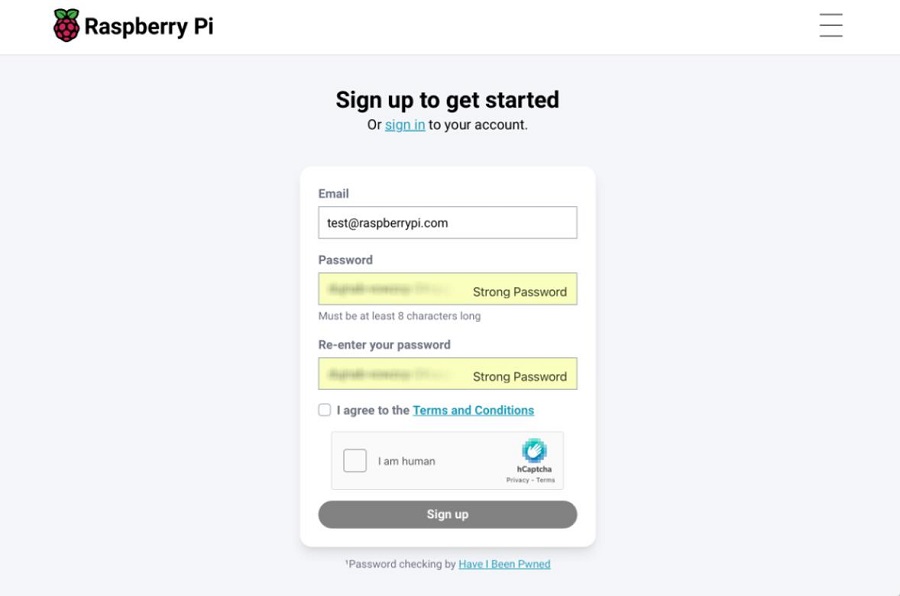
After creating the account, you need to verify it by entering your email:
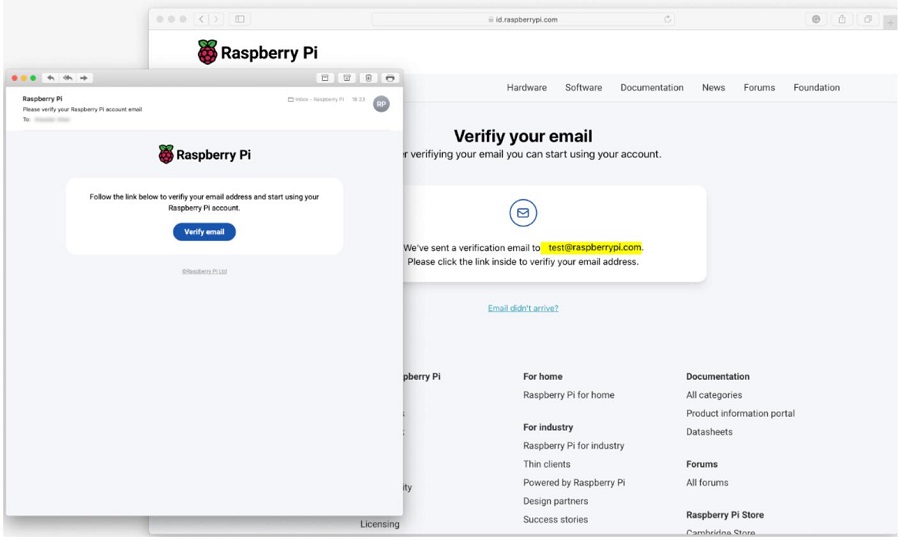
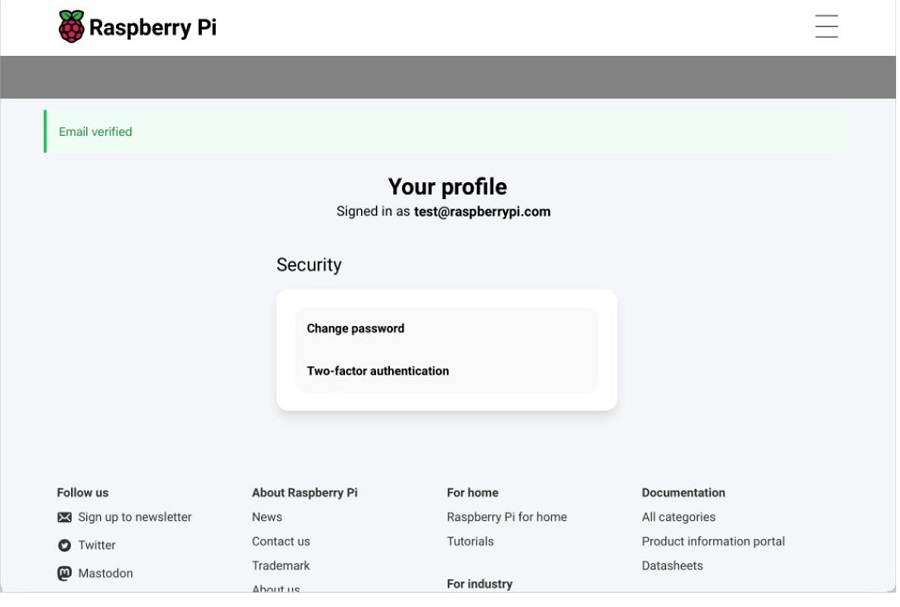
After verification is complete, the ID can be used.
4.3 Install Remote Service
Open the SSH terminal and install the Raspberry Pi Connect software. If the installation command indicates that it is already installed, then no additional installation is necessary:
sudo apt install rpi-connect
After installation, we enter loginctl enable-linger in the terminal to ensure that the remote service is automatically enabled each time the system restarts:

Restart the system. In the graphical interface, select the items in the order shown in the following image to ensure that Raspberry Pi Connect is turned on:
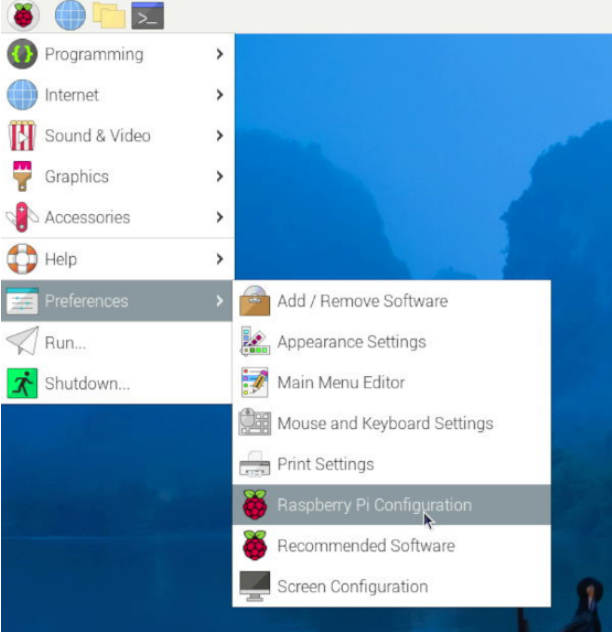
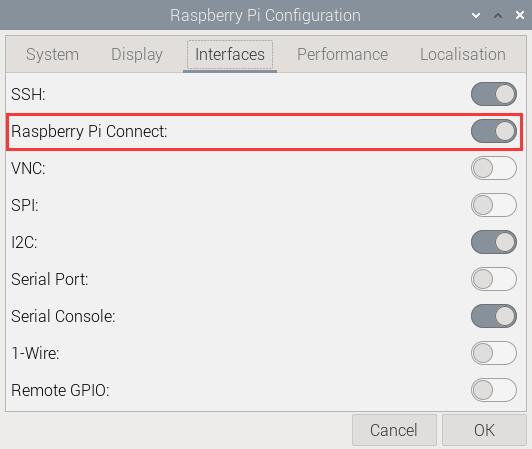
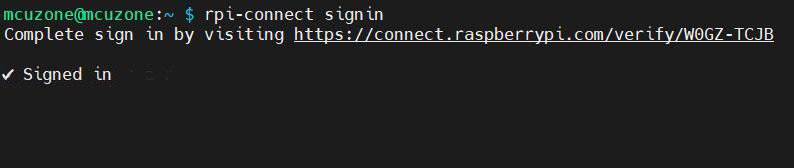
Then enter the following in the Raspberry Pi terminal:
rpi-connect signin
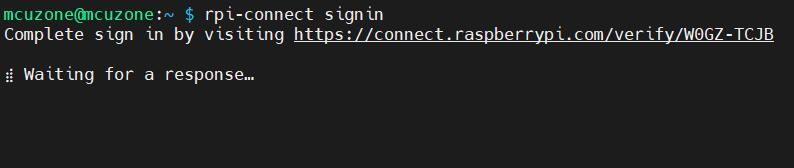
Now, a URL is displayed, as shown in the image above. Open this URL in a browser (it is recommended to use another computer, as the Zero series can be very slow when opening a browser due to hardware limitations).
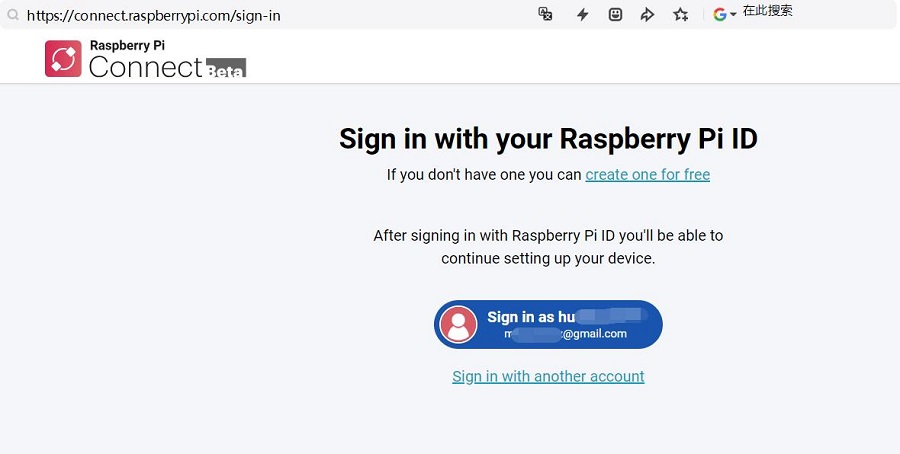
Click on "Sign in" and follow the prompts to bind the device. First, you need to set the device name:
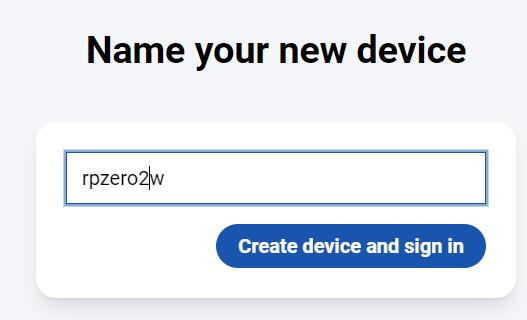
Click "Create device and sign in":
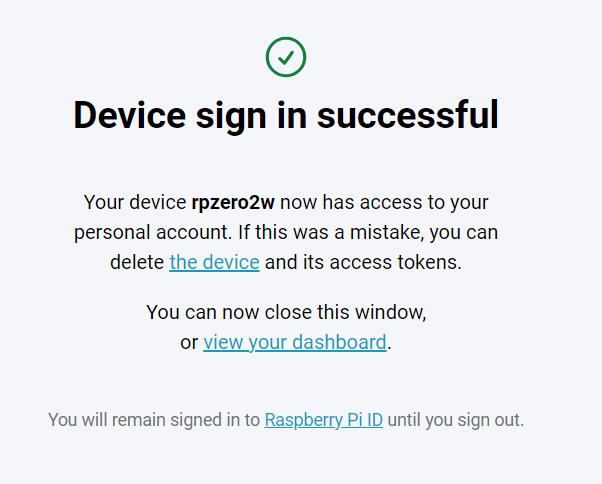
This completes the binding process, and there will also be a successful message displayed in the terminal:
4.4 Use remote control
On your PC, open: https://connect.raspberrypi.com/devices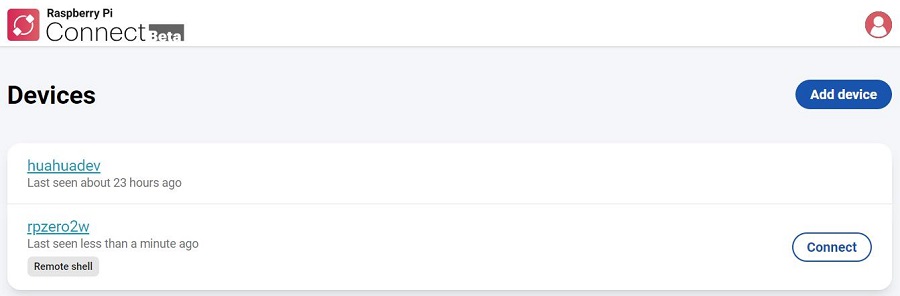
The Zero 2W device just added only shows "Remote shell", indicating that this device can only be controlled through a remote command-line interface.
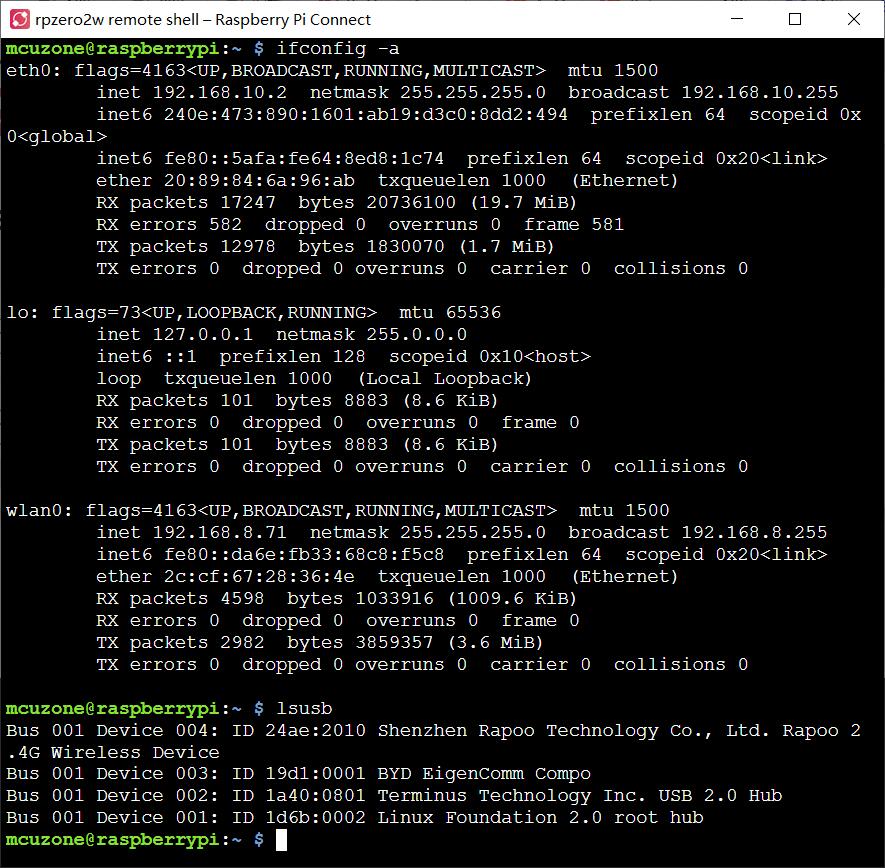
Click on "Connect" to open the remote command-line interface, where you can then enter commands:
After configuration is complete, the system will be able to connect to the internet via 4G each time it boots up and will also enable the Raspberry Pi Connect remote service. This way, we can control the device through a remote command-line interface from a PC.
Contact Us
Email: mcuzone@vip.qq.com
Tel: +86(0)13957118045
If there are any omissions, errors, or infringements on this page, please contact us through the above methods. Thank you!
Copyright 2004-2024 Wildchip




 QQ:8204136
QQ:8204136