1006 RPi0 4G MiniPCIe(Expand 4G Module via MiniPCIe):修订间差异
(创建页面,内容为“== '''关键词''' == 树莓派、 Raspberry Pi Zero、Cat1 4G LTE、USB2.0-A、以太网、扩展板、SSH == '''一、简介''' == Zero系列小巧且预留了非常多的扩展接口,特别是板子反面引出了USB和电源的镀金测试点,我们可以借助这两组USB和电源测试点进行多种类型的外设扩展。本扩展板实际就是一个USB HUB集线器,通过顶针将扩展板和Zero的USB口连接起来,通过USB扩展四路USB…”) |
|||
| (未显示同一用户的11个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
[[1006 RPi0 4G MiniPCIe(MiniPCIe扩展4G模组)|切换语言为中文]] | |||
== ''' | == '''Keywords''' == | ||
Raspberry Pi, Raspberry Pi Zero, Cat1 4G LTE, USB2.0-A, Ethernet, Expansion Board, SSH | |||
4G | == '''I. Introduction''' == | ||
The Zero series is compact and offers many expansion interfaces. The underside of the board features gold-plated test points for USB and power connections. These USB and power test points allow us to connect various types of peripherals for expansion. This expansion board is a USB hub, connecting the expansion board to the USB port of the Zero via pogo pins. It extends four USB ports through the USB connection: one USB port is converted to a 100Mbps wired Ethernet connection, one USB port is connected to a MiniPCIe 4G Cat1 module, and two USB2.0-A host interfaces are provided. | |||
The 4G LTE module is a high-cost-performance module aimed at medium-speed IoT applications, capable of meeting the majority of connectivity and transmission needs. The 4G LTE module supports Qualcomm 4G/GPS, NL668-EU/EAU/AM, GoTone EG25-G. | |||
2. | == '''II. Hardware Spec''' == | ||
2.1 Use gold-plated pogo pins to connect the Raspberry Pi Zero series, eliminating the need for external cables; | |||
2. | 2.2 The two groups of gold-plated pogo pins are used separately for power supply and USB communication. | ||
2. | 2.3 The expansion board is equipped with a USB-C power supply interface, which can power the entire system. The Micro USB port on the Zero can also be used for power. | ||
2. | 2.4 The onboard USB hub expands the Zero's USB into four ports: one port is used for connecting a MiniPCIe 4G LTE Cat1 module, one is a USB to 10/100Mbps Ethernet adapter, and two are USB host interfaces. | ||
2. | 2.5 The 4G LTE module supports Qualcomm 4G/GPS, NL668-EU/EAU/AM, GoTone EG25-G. | ||
2. | 2.6 The 4G LTE Cat1 module is a plug-and-play in most systems, driver-free and does not require manual dialing, usually recognized as the eth1 network card. | ||
2. | 2.7 The 4G LTE Cat module uses a Nano-sized SIM card and offers the option of either an SMA antenna or a first-generation IPEX antenna. | ||
2. | 2.8 The expansion board supports other Pi with USB contacts in the same position, such as the Orange Pi Zero 2W. | ||
2. | 2.9 Onboard PWR/MODE/ACT LED. | ||
2. | 2.10 Onboard reset button for 4G module; | ||
2.11 An optional aluminum alloy enclosure is available. | |||
Note 1: After connecting this expansion board, the Micro USB port on the Zero will no longer be usable. | |||
Note 2: In some systems, it is necessary to disable the OTG function and set the USB mode to Host mode. | |||
Note 3: The expansion board supports all versions of the Raspberry Pi Zero, including the Zero, Zero W, Zero WH, and Zero 2W. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_25.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_25.jpg | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/ | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_27.jpg | ||
== ''' | == '''III. Work with Raspberry Pi OS''' == | ||
This document uses the Raspberry Pi OS and OpenWrt system for testing. | |||
The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz | |||
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in: | |||
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit | https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit | ||
(If using the first-generation Raspberry Pi Zero board, which only supports 32-bit systems, please pay attention to the version you download.) | |||
Raspberry | |||
The version of the OpenWrt is: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2709-rpi-2-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.98-20240723.img.gz | |||
=== 3.1 View hardware devices === | |||
==== 3.1.1 View USB devices ==== | |||
Open the terminal in Raspberry Pi OS and enter the command<code>lsusb</code>, as shown in the image below: | |||
==== 3 | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_01.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_01.jpg | ||
Device | Device 002:External USB Hub; | ||
Device | Device 003:USB to 100Mbps Ethernet adapter; | ||
Device 004:USB2.0- | Device 004:USB2.0-A Interface; | ||
Device | Device 005:4G module; | ||
Device 006:USB2.0- | Device 006:USB2.0-A Interface; | ||
If the system stop at the Raspberry Pi logo and fails to boot: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_58.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_58.jpg | ||
or if after booting, the keyboard, mouse, and 4G module cannot be used, please carefully check whether the pogo pins are aligned with the gold-plated contacts. Additionally, on the PC, open the <code>config.txt</code> file located in the root directory of the TF card to check the USB initialization script: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_41.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_41.jpg | ||
You need to confirm that the three red-boxed areas in the following image are all configured completely. If not, please manually add the missing parts and save the file: | |||
<code># otg_mode=1</code> | <code># otg_mode=1</code> (It is recommended to comment out as follow) | ||
<code>dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=host</code> | <code>dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=host</code> (These two areas must be ensured to be included.) | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_57.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1/0007_Zero_4G_Cat1_57.jpg | ||
==== | ==== 3.1.2 View network devices ==== | ||
Open the terminal in Raspberry Pi OS and enter the command <code>ifconfig -a</code>, as shown in the image below: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_02.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_02.jpg | ||
We can see that eth0 is a USB-to-Ethernet adapter, and usb0 is a 4G Cat4 connection (with the IP address in the image above is 10.17.34.16), and wlan0 is the wireless network interface (with the IP address in the image above is 192.168.8.71). | |||
=== | === 3.2 Connect to the system via SSH === | ||
For convenience, it is recommended to use SSH software on the PC to connect to the system and perform terminal operations. We use a PC within the same IP subnet as the Raspberry Pi's wireless network card and connect through MobaXterm: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_03.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_03.jpg | ||
After connecting, most operations can be performed using MobaXterm on the PC side, allowing the entire hardware system to operate without a monitor. The following test operations will be demonstrated using MobaXterm on the PC side. | |||
=== | === 3.3 Test network devices === | ||
==== | ==== 3.3.1 ping tests ==== | ||
When testing, there is a priority order. If there are specific requirements for internal and external networks, please adjust the metric values of each network and the DNS server settings. | |||
Use the -I parameter to specify which network interface to start the ping packet from, as shown below: | |||
<code>ping www.mcuzone.com -I wlan0</code> | <code>ping www.mcuzone.com -I wlan0</code> | ||
| 第160行: | 第115行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_04.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_04.jpg | ||
Priority can be checked by executing the <code>route</code> command; the network card with the smaller metric value will be preferred for communication. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_05.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_05.jpg | ||
We can also force communication through another network by disabling a specific network card. For example, to disable usb0, you can execute the following command: | |||
<code>sudo ifconfig usb0 down</code> | <code>sudo ifconfig usb0 down</code> | ||
And enable usb0 by the following command: | |||
<code>sudo ifconfig usb0 up</code> | <code>sudo ifconfig usb0 up</code> | ||
==== | ==== 3.3.2 Set network adapter priority ==== | ||
For related settings regarding network card priority, please refer to the following link: | |||
[[1001 RPi0 4G Cat1- | [[1001 RPi0 4G Cat1-ETH(100M ETH 4G Cat1 USB2.0-A RS485 version optional)#4.2.2 Set network adapter priority|1. Set network adapter priority]] | ||
[[1001 RPi0 4G Cat1- | [[1001 RPi0 4G Cat1-ETH(100M ETH 4G Cat1 USB2.0-A RS485 version optional)#4.2.3 Using udhcpc to specify DNS servers|2. Using udhcpc to specify DNS servers]] | ||
[[1001 RPi0 4G Cat1- | [[1001 RPi0 4G Cat1-ETH(100M ETH 4G Cat1 USB2.0-A RS485 version optional)#4.2.4 Examples of how to use udhcpc|3. Examples of how to use udhcpc]] | ||
==== | ==== 3.3.3 Test speed by iperf3 ==== | ||
You can download iperf3 (Windows version) in: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/down/Software.asp?ID=10000634 | http://www.mcuzone.com/down/Software.asp?ID=10000634 | ||
Install iperf3 (Linux version) by using the following command: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get install iperf3</code> | <code>sudo apt-get install iperf3</code> | ||
100M Ethernet speed test results: | |||
It is about 92.3Mbps in client mode: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_06.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_06.jpg | ||
It is about 94.8Mbps in server mode: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_07.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_07.jpg | ||
''''' | '''''Note: The USB to 100M Ethernet adapter may not reach full speed due to the performance limitations of the Zero 2W, the USB hub, and the bandwidth usage of the 4G Cat4.''''' | ||
=== | === 3.4 AT Command for 4G Cat4 Module on Raspberry Pi OS === | ||
==== 3.4.1 Open AT Command serial port ==== | |||
To operate 4G Cat1 Module using AT commands on a Raspberry Pi, you first need to open the AT command serial port. The method to open it is as follows: | |||
To open ttyUSB serial port, input the following command: <code>lsusb</code>: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_08.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_08.jpg | ||
Record the ID value of the 4G module: 05c6 90b6 | |||
Use the following command to open the ttyUSB serial port, where the value after echo is the ID recorded above: | |||
<code>sudo modprobe option</code> | <code>sudo modprobe option</code> | ||
| 第223行: | 第176行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_09.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_09.jpg | ||
After execution is complete, the system should have three additional devices: ttyUSB0, ttyUSB1, and ttyUSB2. Input <code>ls /dev</code> to view: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_10.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_10.jpg | ||
Then Open serial port by serial port tool. | |||
Install minicom: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get install minicom</code> | <code>sudo apt-get install minicom</code> | ||
| 第235行: | 第188行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_11.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_11.jpg | ||
Open AT Command serial port by minicom: | |||
<code>sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB0</code> | <code>sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB0</code> | ||
| 第241行: | 第194行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_12.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_12.jpg | ||
Then directly type the AT command and press Enter to see the result. If you need to view the echo, please type the command: <code>ate1</code>: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_13.jpg | ||
==== | Note: The model of the 4G module may change, but the process remains the same. You only need to use <code>lsusb</code> to check the actual USB ID and replace it with the actual value in subsequent commands. Additionally, some 4G Cat1 modules's chipset IDs have already been included in the kernel's supported list, so these Cat1 modules can be automatically recognized as ttyAMAx without the need to add a USB ID. | ||
1) | |||
==== 3.4.2 Common AT commands ==== | |||
1) Check if the SIM card is detected: | |||
<code>at+cpin?</code> | <code>at+cpin?</code> | ||
Return ready to indicate the card has been recognized, if return error, you need to check the hardware. | |||
2) | 2) Check antenna signal quality: | ||
<code>at+csq</code> | <code>at+csq</code> | ||
Return values between 26 and 31 indicate a good signal, with 31 representing a full signal strength; return values between 20 and 25 indicate a barely acceptable signal; return values below 20 indicate a poor signal or that the antenna might not be connected. | |||
3) | 3) Check network registration status: | ||
<code>at+cops?</code> | <code>at+cops?</code> | ||
Normally, it should return the network supporter's code: 7, where 7 represents 4G. | |||
Note: The above command <code>at+csq</code> should not include a question mark, while the other two commands require a question mark. | |||
4) | 4) View the SIM card's IMEI code: | ||
<code>at+cgsn</code> | <code>at+cgsn</code> | ||
5) | 5) Reset 4G module (Sometimes, if you reinsert the SIM card, hot swapping may not work; in such cases, you can use this reset command to reset the module.): | ||
<code>at+reset</code> | <code>at+reset</code> | ||
6) | 6) Disable radio frequency: | ||
<code>at+cfun=0</code> | <code>at+cfun=0</code> | ||
Enable radio frequency: | |||
<code>at+cfun=1</code> | <code>at+cfun=1</code> | ||
The two commands mentioned above can be used in pairs to allow the module to re-register with the network without restarting the 4G module. | |||
== '''IV. Work with OpenWrt System''' == | |||
== | === 4.1 Overview === | ||
This expansion board, when paired with the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W running OpenWrt, can be configured as a one-in-one-out switch mode. The 4G module on the expansion board can serve as the WAN port (for direct 4G internet access), while the Ethernet port is configured as the LAN port for connecting to a PC. | |||
=== | === 4.2 Preparation === | ||
The OpenWrt which be used in this document is: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2709-rpi-2-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.98-20240723.img.gz | |||
After flashing the OpenWrt system and powering it up, we connect an Ethernet cable from the Raspberry Pi's built-in Ethernet port to the PC's Ethernet port. Once the connection between the PC's network card and the Raspberry Pi's Ethernet port is successful, we find Network and Internet settings in Windows, then open the connected network under Ethernet to view the default gateway IP address. This address is the backend configuration page address for the OpenWrt system. As shown in the figure, the address for this test is 192.168.198.1: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_14.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_14.jpg | ||
Then open a web browser and enter 192.168.198.1 to access the OpenWrt system. The default username is <code>root</code>, and the default password is <code>password</code>: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_15.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_15.jpg | ||
=== | === 4.3 Set up the Qualcomm 4G LTE module === | ||
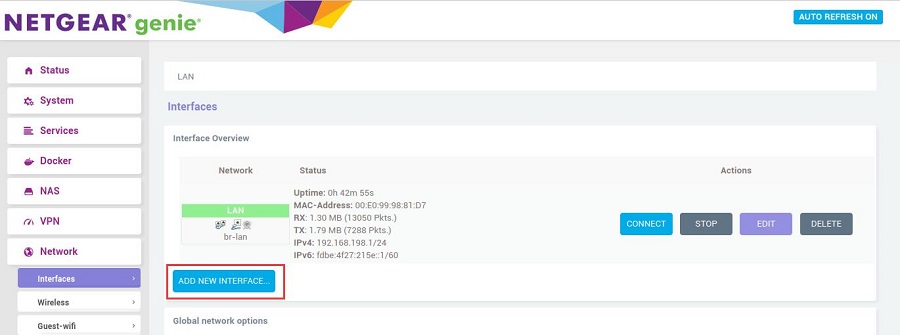
After logging into the OpenWrt system, click on "Network - Interfaces," and then click on "ADD NEW INTERFACE...". | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_16.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_16.jpg | ||
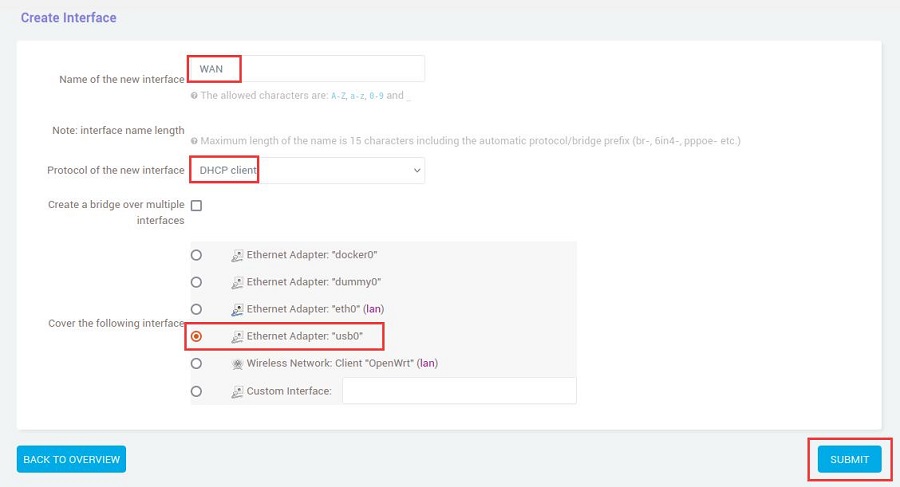
Set it up according to the following picture: set "Name of the new interface" as WAN, choose "DHCP client" for "Protocol of the new interface," select "usb0" for "Cover the following interface," and then click the "SUBMIT" button: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_17.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_17.jpg | ||
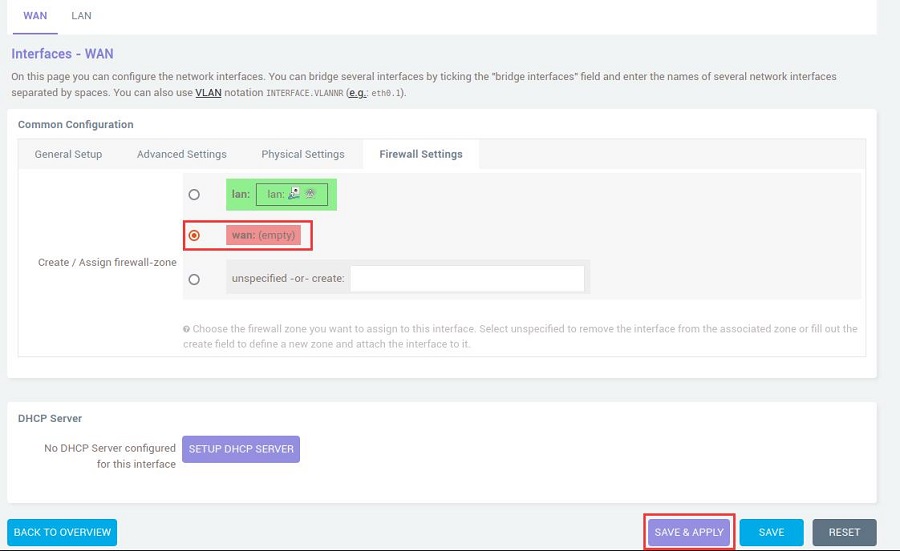
In the "Firewall Settings", select the WAN and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_18.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_18.jpg | ||
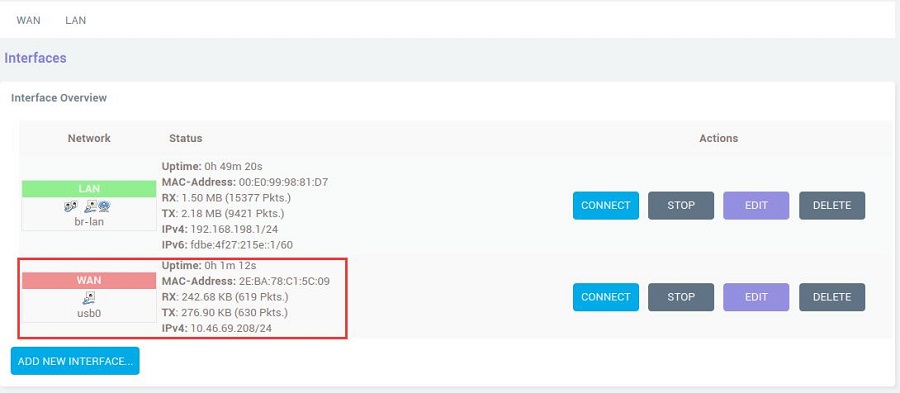
Go back to "Network - Interfaces", wait a moment, and you will see the newly created WAN interface has obtained an IP address. This way, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_19.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_19.jpg | ||
Open https://www.speedtest.cn/ on the PC to test speed. At this point, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module, and the test results are as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_20.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_20.jpg | ||
=== | === 4.4 Set up the CAT4 4G(SOC from CHINA) module === | ||
After logging into the OpenWrt system, click on "Network - Interfaces," and then click on "ADD NEW INTERFACE...". | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_16.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_16.jpg | ||
Set it up according to the following picture: set "Name of the new interface" as WAN, choose "DHCP client" for "Protocol of the new interface," select "eth1" for "Cover the following interface," and then click the "SUBMIT" button: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_21.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_21.jpg | ||
In the "Firewall Settings", select the WAN and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_18.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_18.jpg | ||
Go back to "Network - Interfaces", wait a moment, and you will see the newly created WAN interface has obtained an IP address. This way, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_22.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_22.jpg | ||
Open https://www.speedtest.cn/ on the PC to test speed. At this point, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module, and the test results are as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_23.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe/1006_RPi0_4G_MiniPCIe_23.jpg | ||
{{ | {{Contact_Us_icon}} | ||
2024年11月15日 (五) 10:20的最新版本
Keywords
Raspberry Pi, Raspberry Pi Zero, Cat1 4G LTE, USB2.0-A, Ethernet, Expansion Board, SSH
I. Introduction
The Zero series is compact and offers many expansion interfaces. The underside of the board features gold-plated test points for USB and power connections. These USB and power test points allow us to connect various types of peripherals for expansion. This expansion board is a USB hub, connecting the expansion board to the USB port of the Zero via pogo pins. It extends four USB ports through the USB connection: one USB port is converted to a 100Mbps wired Ethernet connection, one USB port is connected to a MiniPCIe 4G Cat1 module, and two USB2.0-A host interfaces are provided.
The 4G LTE module is a high-cost-performance module aimed at medium-speed IoT applications, capable of meeting the majority of connectivity and transmission needs. The 4G LTE module supports Qualcomm 4G/GPS, NL668-EU/EAU/AM, GoTone EG25-G.
II. Hardware Spec
2.1 Use gold-plated pogo pins to connect the Raspberry Pi Zero series, eliminating the need for external cables;
2.2 The two groups of gold-plated pogo pins are used separately for power supply and USB communication.
2.3 The expansion board is equipped with a USB-C power supply interface, which can power the entire system. The Micro USB port on the Zero can also be used for power.
2.4 The onboard USB hub expands the Zero's USB into four ports: one port is used for connecting a MiniPCIe 4G LTE Cat1 module, one is a USB to 10/100Mbps Ethernet adapter, and two are USB host interfaces.
2.5 The 4G LTE module supports Qualcomm 4G/GPS, NL668-EU/EAU/AM, GoTone EG25-G.
2.6 The 4G LTE Cat1 module is a plug-and-play in most systems, driver-free and does not require manual dialing, usually recognized as the eth1 network card.
2.7 The 4G LTE Cat module uses a Nano-sized SIM card and offers the option of either an SMA antenna or a first-generation IPEX antenna.
2.8 The expansion board supports other Pi with USB contacts in the same position, such as the Orange Pi Zero 2W.
2.9 Onboard PWR/MODE/ACT LED.
2.10 Onboard reset button for 4G module;
2.11 An optional aluminum alloy enclosure is available.
Note 1: After connecting this expansion board, the Micro USB port on the Zero will no longer be usable.
Note 2: In some systems, it is necessary to disable the OTG function and set the USB mode to Host mode.
Note 3: The expansion board supports all versions of the Raspberry Pi Zero, including the Zero, Zero W, Zero WH, and Zero 2W.


III. Work with Raspberry Pi OS
This document uses the Raspberry Pi OS and OpenWrt system for testing.
The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit
(If using the first-generation Raspberry Pi Zero board, which only supports 32-bit systems, please pay attention to the version you download.)
The version of the OpenWrt is: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2709-rpi-2-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.98-20240723.img.gz
3.1 View hardware devices
3.1.1 View USB devices
Open the terminal in Raspberry Pi OS and enter the commandlsusb, as shown in the image below:
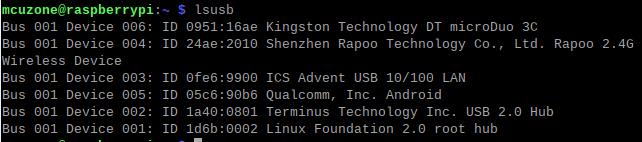
Device 002:External USB Hub;
Device 003:USB to 100Mbps Ethernet adapter;
Device 004:USB2.0-A Interface;
Device 005:4G module;
Device 006:USB2.0-A Interface;
If the system stop at the Raspberry Pi logo and fails to boot:

or if after booting, the keyboard, mouse, and 4G module cannot be used, please carefully check whether the pogo pins are aligned with the gold-plated contacts. Additionally, on the PC, open the config.txt file located in the root directory of the TF card to check the USB initialization script:
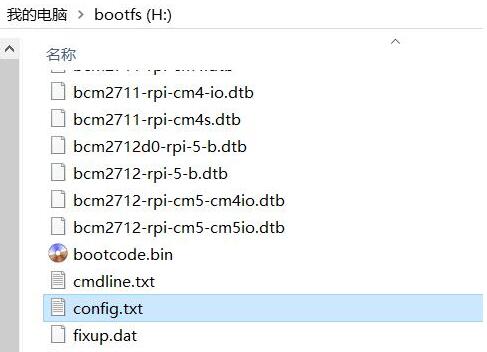
You need to confirm that the three red-boxed areas in the following image are all configured completely. If not, please manually add the missing parts and save the file:
# otg_mode=1 (It is recommended to comment out as follow)
dtoverlay=dwc2,dr_mode=host (These two areas must be ensured to be included.)
3.1.2 View network devices
Open the terminal in Raspberry Pi OS and enter the command ifconfig -a, as shown in the image below:

We can see that eth0 is a USB-to-Ethernet adapter, and usb0 is a 4G Cat4 connection (with the IP address in the image above is 10.17.34.16), and wlan0 is the wireless network interface (with the IP address in the image above is 192.168.8.71).
3.2 Connect to the system via SSH
For convenience, it is recommended to use SSH software on the PC to connect to the system and perform terminal operations. We use a PC within the same IP subnet as the Raspberry Pi's wireless network card and connect through MobaXterm:

After connecting, most operations can be performed using MobaXterm on the PC side, allowing the entire hardware system to operate without a monitor. The following test operations will be demonstrated using MobaXterm on the PC side.
3.3 Test network devices
3.3.1 ping tests
When testing, there is a priority order. If there are specific requirements for internal and external networks, please adjust the metric values of each network and the DNS server settings.
Use the -I parameter to specify which network interface to start the ping packet from, as shown below:
ping www.mcuzone.com -I wlan0
ping www.mcuzone.com -I usb0

Priority can be checked by executing the route command; the network card with the smaller metric value will be preferred for communication.

We can also force communication through another network by disabling a specific network card. For example, to disable usb0, you can execute the following command:
sudo ifconfig usb0 down
And enable usb0 by the following command:
sudo ifconfig usb0 up
3.3.2 Set network adapter priority
For related settings regarding network card priority, please refer to the following link:
1. Set network adapter priority
2. Using udhcpc to specify DNS servers
3. Examples of how to use udhcpc
3.3.3 Test speed by iperf3
You can download iperf3 (Windows version) in:
http://www.mcuzone.com/down/Software.asp?ID=10000634
Install iperf3 (Linux version) by using the following command:
sudo apt-get install iperf3
100M Ethernet speed test results:
It is about 92.3Mbps in client mode:
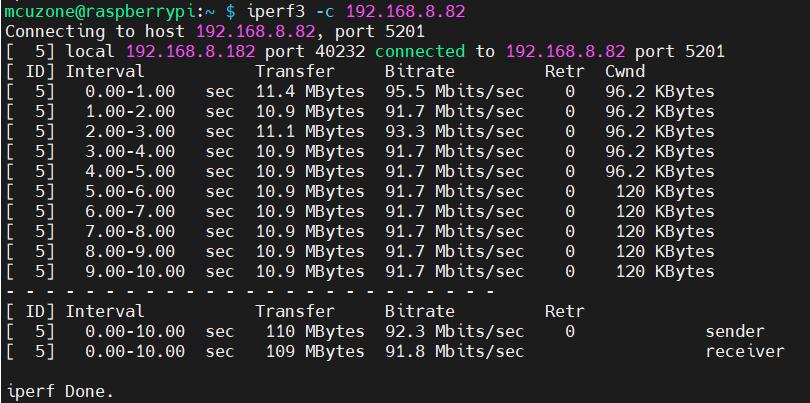
It is about 94.8Mbps in server mode:
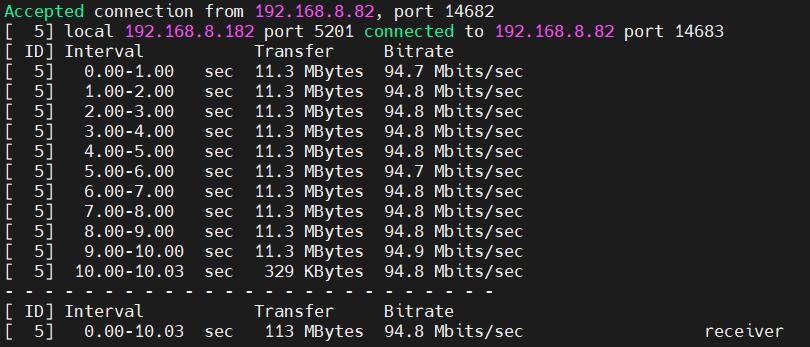
Note: The USB to 100M Ethernet adapter may not reach full speed due to the performance limitations of the Zero 2W, the USB hub, and the bandwidth usage of the 4G Cat4.
3.4 AT Command for 4G Cat4 Module on Raspberry Pi OS
3.4.1 Open AT Command serial port
To operate 4G Cat1 Module using AT commands on a Raspberry Pi, you first need to open the AT command serial port. The method to open it is as follows:
To open ttyUSB serial port, input the following command: lsusb:
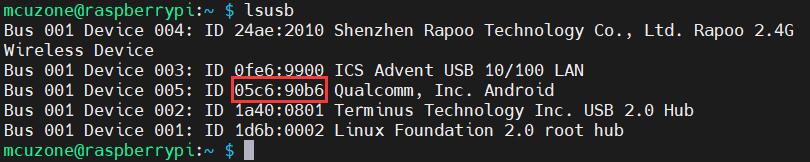
Record the ID value of the 4G module: 05c6 90b6
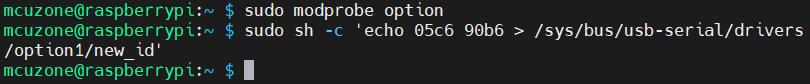
Use the following command to open the ttyUSB serial port, where the value after echo is the ID recorded above:
sudo modprobe option
sudo sh -c 'echo 05c6 90b6 > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/option1/new_id'
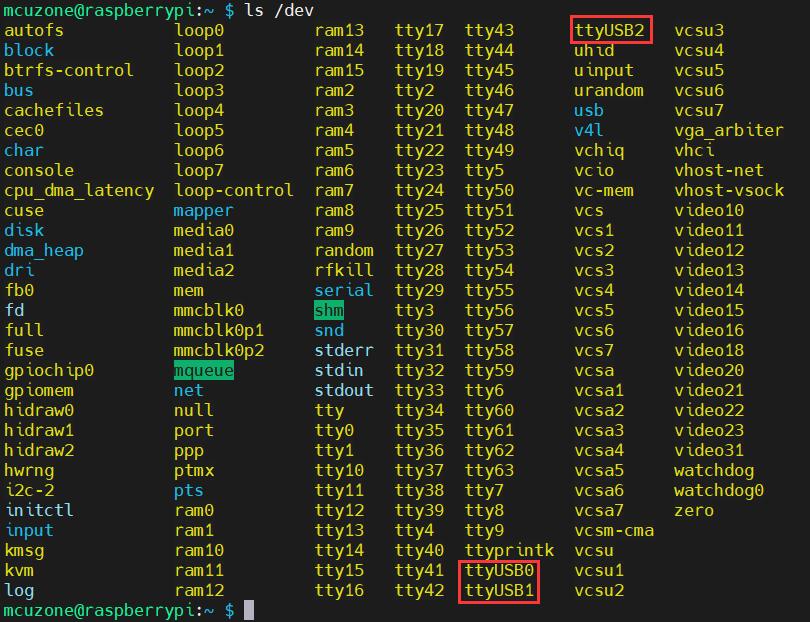
After execution is complete, the system should have three additional devices: ttyUSB0, ttyUSB1, and ttyUSB2. Input ls /dev to view:
Then Open serial port by serial port tool.
Install minicom:
sudo apt-get install minicom
Open AT Command serial port by minicom:
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB0

Then directly type the AT command and press Enter to see the result. If you need to view the echo, please type the command: ate1:
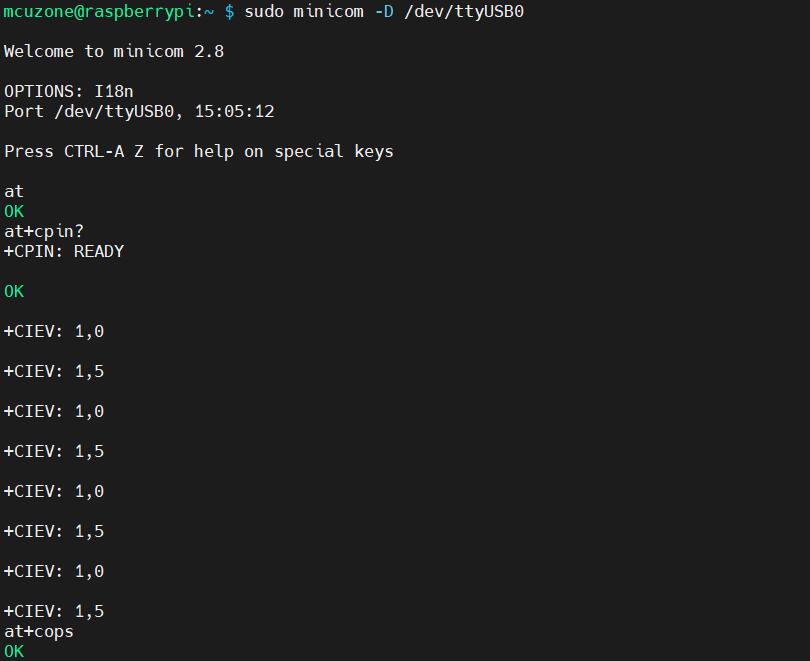
Note: The model of the 4G module may change, but the process remains the same. You only need to use lsusb to check the actual USB ID and replace it with the actual value in subsequent commands. Additionally, some 4G Cat1 modules's chipset IDs have already been included in the kernel's supported list, so these Cat1 modules can be automatically recognized as ttyAMAx without the need to add a USB ID.
3.4.2 Common AT commands
1) Check if the SIM card is detected:
at+cpin?
Return ready to indicate the card has been recognized, if return error, you need to check the hardware.
2) Check antenna signal quality:
at+csq
Return values between 26 and 31 indicate a good signal, with 31 representing a full signal strength; return values between 20 and 25 indicate a barely acceptable signal; return values below 20 indicate a poor signal or that the antenna might not be connected.
3) Check network registration status:
at+cops?
Normally, it should return the network supporter's code: 7, where 7 represents 4G.
Note: The above command at+csq should not include a question mark, while the other two commands require a question mark.
4) View the SIM card's IMEI code:
at+cgsn
5) Reset 4G module (Sometimes, if you reinsert the SIM card, hot swapping may not work; in such cases, you can use this reset command to reset the module.):
at+reset
6) Disable radio frequency:
at+cfun=0
Enable radio frequency:
at+cfun=1
The two commands mentioned above can be used in pairs to allow the module to re-register with the network without restarting the 4G module.
IV. Work with OpenWrt System
4.1 Overview
This expansion board, when paired with the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W running OpenWrt, can be configured as a one-in-one-out switch mode. The 4G module on the expansion board can serve as the WAN port (for direct 4G internet access), while the Ethernet port is configured as the LAN port for connecting to a PC.
4.2 Preparation
The OpenWrt which be used in this document is: openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2709-rpi-2-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.98-20240723.img.gz
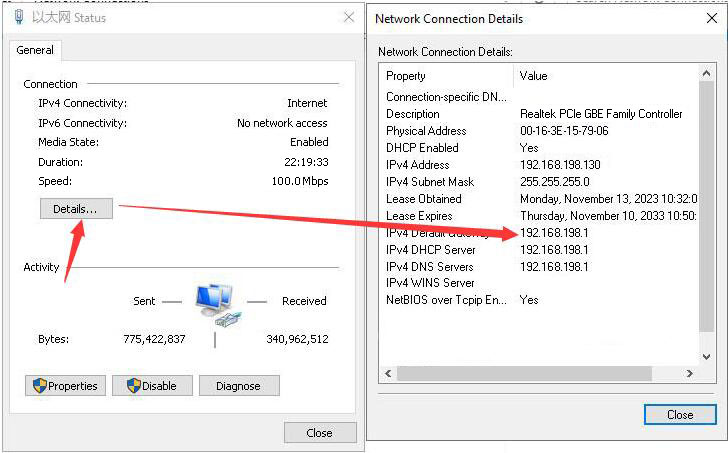
After flashing the OpenWrt system and powering it up, we connect an Ethernet cable from the Raspberry Pi's built-in Ethernet port to the PC's Ethernet port. Once the connection between the PC's network card and the Raspberry Pi's Ethernet port is successful, we find Network and Internet settings in Windows, then open the connected network under Ethernet to view the default gateway IP address. This address is the backend configuration page address for the OpenWrt system. As shown in the figure, the address for this test is 192.168.198.1:
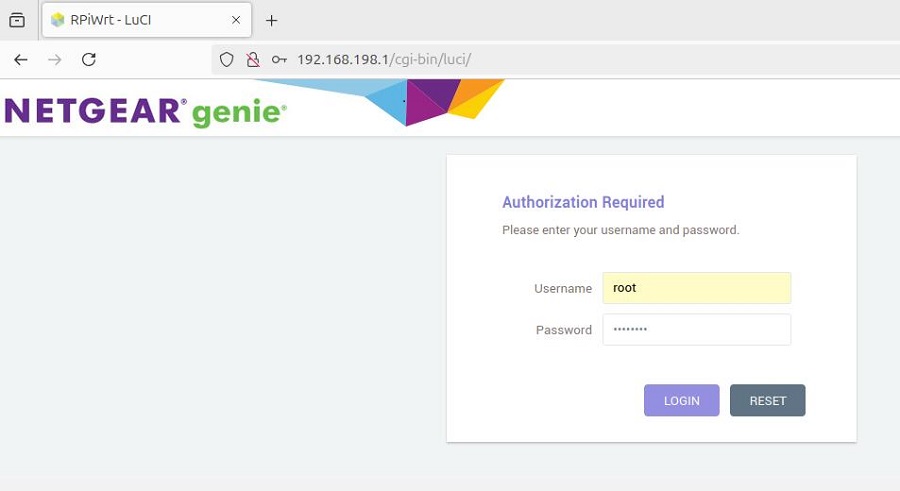
Then open a web browser and enter 192.168.198.1 to access the OpenWrt system. The default username is root, and the default password is password:
4.3 Set up the Qualcomm 4G LTE module
After logging into the OpenWrt system, click on "Network - Interfaces," and then click on "ADD NEW INTERFACE...".
Set it up according to the following picture: set "Name of the new interface" as WAN, choose "DHCP client" for "Protocol of the new interface," select "usb0" for "Cover the following interface," and then click the "SUBMIT" button:
In the "Firewall Settings", select the WAN and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button:
Go back to "Network - Interfaces", wait a moment, and you will see the newly created WAN interface has obtained an IP address. This way, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module:
Open https://www.speedtest.cn/ on the PC to test speed. At this point, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module, and the test results are as follows:

4.4 Set up the CAT4 4G(SOC from CHINA) module
After logging into the OpenWrt system, click on "Network - Interfaces," and then click on "ADD NEW INTERFACE...".

Set it up according to the following picture: set "Name of the new interface" as WAN, choose "DHCP client" for "Protocol of the new interface," select "eth1" for "Cover the following interface," and then click the "SUBMIT" button:
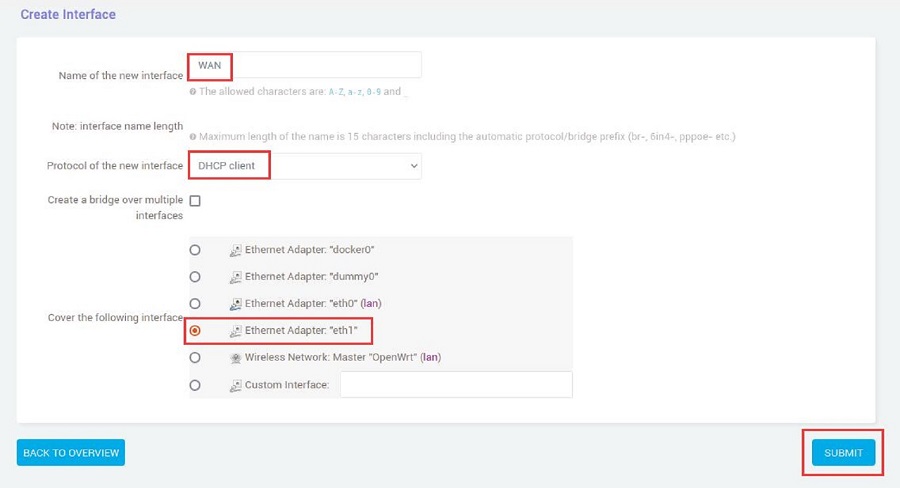
In the "Firewall Settings", select the WAN and then click the "SAVE & APPLY" button:

Go back to "Network - Interfaces", wait a moment, and you will see the newly created WAN interface has obtained an IP address. This way, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module:
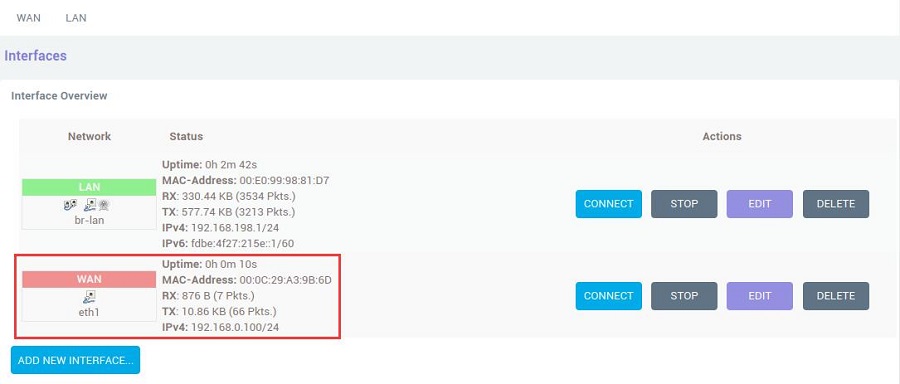
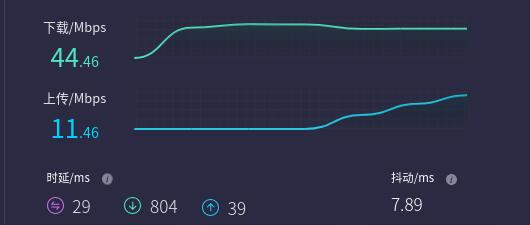
Open https://www.speedtest.cn/ on the PC to test speed. At this point, the PC can access the internet through the 4G LTE module, and the test results are as follows:
Contact Us
Email: mcuzone@vip.qq.com
Tel: +86(0)13957118045
If there are any omissions, errors, or infringements on this page, please contact us through the above methods. Thank you!
Copyright 2004-2024 Wildchip




 QQ:8204136
QQ:8204136