0011 MPW7(WiFi7 on Raspberry Pi 5):修订间差异
(创建页面,内容为“== '''关键词''' == 树莓派5、PCIe扩展、WiFi7、Raspberry Pi5、Ubuntu 和RPi OS。 == '''一、简介''' == 树莓派5板载一个16Pin的PCIe接口,我们可以通过该接口外挂各种PCIe设备。本扩展板就是专为树莓派5设计的WiFi7转接板。在树莓派系统下使用WiFi7需安装驱动,而在Ubuntu系统下免驱即插即用。本模块也支持M.2 E接口的WiFi6和WiFi5。 == '''二、硬件资源''' == 1. 专为树莓派5…”) |
无编辑摘要 |
||
| (未显示同一用户的4个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
[[0011 MPW7(树莓派5的WiFi7)|切换语言为中文]] | |||
== ''' | == '''Keywords''' == | ||
Raspberry Pi 5, PCIe Expansion, WiFi7, Raspberry Pi5, Ubuntu, RPi OS | |||
== ''' | == '''I. Introduction''' == | ||
The Raspberry Pi 5 features a 16-pin PCIe interface, through which various PCIe devices can be connected. This expansion board is specifically designed for the Raspberry Pi 5 to serve as a WiFi 7 adapter. This module requires driver installation to use WiFi 7 on the Raspberry Pi system, while it is plug-and-play under Ubuntu without needing additional drivers. The module also supports WiFi 6 and WiFi 5 via the M.2 E key interface. | |||
== '''II. Hardware Spec''' == | |||
1. PCIe expansion board designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi 5; | |||
2. One M.2 E-Key PCIe interface, supporting the BE200 WiFi 7 module, with hardware also supporting WiFi 6(E) and WiFi 5, such as AX210, AX200, MT7922, and Intel 8265C; | |||
4. | 3. One USB Bluetooth interface (built-in with the WiFi module), exposed via a 1.25mm 4-pin USB connector. To use the Bluetooth function, this USB must be connected to a USB 2.0 port on the Raspberry Pi 5, and it requires the appropriate drivers and profiles to be installed; | ||
4. Reserved CSI/DSI cable routing slots, supporting 22-pin cables with 0.5mm pitch and 15-pin cables with 1mm pitch; | |||
5. Board-mounted power indicator light ('PWR') and one WiFi activity indicator light ('ACT'); | |||
6. Uses an efficient DC-DC circuit; | |||
7. Gold immersion PCB process, lead-free production, certified by UL, compliant with ROHS standards, and has a fire rating of 94V-0; | |||
8. The board has four M2.5 mounting holes, with a recessed design on the top of the board to facilitate the use of the 40-Pin GPIO; | |||
10. | 9. Optional PCB antenna or SMA antenna, with an IPEX4 interface; | ||
10. Optional aluminum alloy enclosure. | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_43.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_43.jpg | ||
== ''' | == '''III. Software Spec''' == | ||
=== 3.1 Overview === | |||
This document uses Raspberry Pi OS and Ubuntu systems, tested with the BE200 (WiFi 7) module. | |||
1)The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz | |||
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in: | |||
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit | |||
2)The version of the Ubuntu system is: ubuntu-24.04-preinstalled-desktop-arm64+raspi.img.xz | |||
You can download the Ubuntu system in: | |||
https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi<!-- | |||
OpenWrt系统版本为:openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2712-rpi-5-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.100-20240805.img.gz | OpenWrt系统版本为:openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2712-rpi-5-squashfs-sysupgrade-linux-6.1.100-20240805.img.gz | ||
--> | --> | ||
== | === 3.2 System flashed onto the SD (TF) card === | ||
[[0005 MPS2242 2280 2280P(Single SSD Expansion Board)#3.2 Boot from TF card|Click here to read the instructions for System flashing]] | |||
== | == '''IV. Work with Raspberry Pi OS''' == | ||
''' | |||
=== 4.1 Installing WiFi 7 driver (BE200) === | |||
'''''Note: Once the WiFi 7 driver (BE200) is successfully installed, the original WiFi module on the Raspberry Pi 5 will no longer be usable!''''' | |||
==== 4.1.1 | This installation procedure also applies to the AX210 (WiFi 6E) and AX200 (WiFi 6) modules. | ||
==== 4.1.1 Update the system and header files ==== | |||
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal: | |||
<code>sudo apt-get update</code> | <code>sudo apt-get update</code> | ||
| 第61行: | 第68行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_01.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_01.jpg | ||
==== 4.1.2 | ==== 4.1.2 Download and extract the source code ==== | ||
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal: | |||
<code>mkdir wifi && cd wifi</code> | <code>mkdir wifi && cd wifi</code> | ||
| 第72行: | 第79行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_10.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_10.jpg | ||
==== 4.1.3 | ==== 4.1.3 Compilation Environment ==== | ||
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal: | |||
<code>sudo make defconfig-iwlwifi-public</code> | <code>sudo make defconfig-iwlwifi-public</code> | ||
| 第81行: | 第88行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_03.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_03.jpg | ||
==== 4.1.4 | ==== 4.1.4 Compile source code ==== | ||
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal: | |||
<code>sudo make -j 4</code> | <code>sudo make -j 4</code> | ||
| 第92行: | 第99行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_05.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_05.jpg | ||
At this point, the system will prompt you to restart. Please do not restart yet. | |||
==== 4.1.5 | ==== 4.1.5 Install firmware (not necessary for AX200 or AX210) ==== | ||
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal: | |||
<code>cd ..</code> | <code>cd ..</code> | ||
| 第111行: | 第118行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_11.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_11.jpg | ||
Then reboot system: | |||
<code>sudo reboot</code> | <code>sudo reboot</code> | ||
=== 4.2 | === 4.2 Test of WiFi 7 module: BE200 === | ||
After restarting the system, we execute <code>lspci</code> in the terminal: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_19.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_19.jpg | ||
You can see the WiFi 7 module. | |||
Execute <code>ifconfig -a</code> to view the information of the wireless network card (wlan0): | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_20.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_20.jpg | ||
At this point, you can use the BE200 (WiFi 7) module to connect to a wireless AP through the network connections settings: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_07.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_07.jpg | ||
In the network connection information, you can also see the network connection using the <code>iwlwifi</code> driver: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_08.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_08.jpg | ||
Connect to the internet (200M broadband) using the BE200 (WiFi 7) module and perform a speed test, results as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_46.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_46.jpg | ||
''''' | '''''Note: Network speed tests are influenced by the network environment and testing methods. The speeds shown are for reference only and may vary based on actual conditions!''''' | ||
''' | '''Connect to the WiFi 7 router and perform a speed test:''' | ||
''''' | '''''Note: All tests here are conducted using SSH to connect to the development board.''''' | ||
The router used is the Xiaomi BE6500 Pro, a WiFi 7 + quad-port 2.5G router. The Raspberry Pi 5 with WiFi 7 is approximately 1 meter away from the router. | |||
Using the BE200 + Raspberry Pi 5, connect to the WiFi 7 wireless network and perform an iperf3 speed test with a Windows system (2.5G USB network card, IP address: 192.168.8.197) connected to the same router: | |||
Speed test with 30 threads, results as follows | |||
<code>iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197 -P 30</code> | <code>iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197 -P 30</code> | ||
| 第154行: | 第161行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_47.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_47.jpg | ||
Speed test with 30 threads, results as follows | |||
<code>iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197</code> | <code>iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197</code> | ||
| 第162行: | 第167行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_48.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_48.jpg | ||
Approximately 500 Mbps. | |||
For comparison, we replaced the WiFi 7 module with a WiFi 6 module (AX210) and performed the same tests. | |||
Speed test with 30 threads, results as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_51.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_51.jpg | ||
Approximately 847 Mbps. | |||
Single-thread speed test, results as follows: | |||
<code>iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197</code> | <code>iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197</code> | ||
| 第178行: | 第183行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_52.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_52.jpg | ||
Approximately 456Mbps。 | |||
''''' | '''''Note: Network speed tests are influenced by the network environment and testing methods. The speeds shown are for reference only and may vary based on actual conditions!''''' | ||
=== 4.3 | === 4.3 Bluetooth Testing === | ||
Connect the 1.25mm 4-pin USB Bluetooth interface to the USB 2.0 port on the Raspberry Pi 5: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_53.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_53.jpg | ||
On Raspberry Pi OS, the Bluetooth module of the Raspberry Pi 5 is recognized directly. Click on the device icon in the top-right corner of the desktop, then click Add Device...: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_32.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_32.jpg | ||
In the opened window, the Bluetooth module will automatically scan for nearby connectable Bluetooth devices, as shown in the figure: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_33.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_33.jpg | ||
Click on the phone to pair with it. The pairing process on Raspberry Pi OS and the phone is shown in the figures below: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_34.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_34.jpg | ||
| 第203行: | 第208行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_37.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_37.jpg | ||
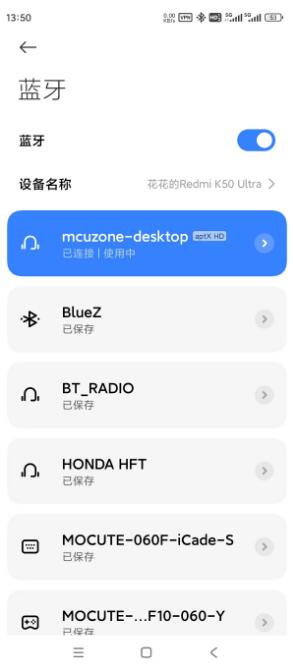
After pairing successfully, click on the 'raspberrypi' device on your phone. Once connected, the Raspberry Pi is recognized as an audio device, as shown in the figure below: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_36.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_36.jpg | ||
In Raspberry Pi OS, you can also see that the connection was successful: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_38.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_38.jpg | ||
== ''' | == '''V. Work with Ubuntu System''' == | ||
The version of Ubuntu used for testing is as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_42.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_42.jpg | ||
=== 5.1 | === 5.1 WiFi7(BE200) === | ||
The BE200 (WiFi 7) module is plug-and-play under Ubuntu and does not require additional drivers. After the system starts, execute <code>lspci</code> in the terminal: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_21.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_21.jpg | ||
You can see the WiFi 7 module. | |||
Execute <code>ifconfig -a</code> to view the information of the WiFi 7 wireless network card (wlp1s0f0). <code>wlan1</code> is the built-in wireless network card of the Raspberry Pi 5: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_22.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_22.jpg | ||
In the 'Wi-Fi' menu in the top-right corner of the screen, there is a 'PCI Wi-Fi' option, which is the WiFi 7 module:http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_12.jpg | |||
After connecting to the wireless AP using the 'PCI Wi-Fi', you can see a wireless WiFi named 'Intel' in the 'All Networks' list. This is the WiFi 7 module. Once connected successfully, you can browse the internet using the WiFi 7 module | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_13.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_13.jpg | ||
Connect to the internet (200M broadband) using the BE200 (WiFi 7) module and perform a speed test, results as follows: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_14.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_14.jpg | ||
''''' | '''''Note: Network speed tests are influenced by the network environment and testing methods. The speeds shown are for reference only and may vary based on actual conditions!''''' | ||
If using the built-in Firefox browser in Ubuntu results in slow performance or frequent unresponsiveness, it is recommended to install the lightweight browser Falkon: | |||
<code>sudo apt install falkon</code> | <code>sudo apt install falkon</code> | ||
=== 5.2 | === 5.2 WiFi6(AX210/AX200) === | ||
The WiFi 6 modules (AX200 and AX210) are also plug-and-play under Ubuntu system and do not require additional drivers. Follow the same steps as above, and the execution results are as follows: | |||
AX200: | AX200: | ||
| 第255行: | 第258行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_24.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_24.jpg | ||
=== 5.3 | |||
=== 5.3 Bluetooth Testing === | |||
Under the Ubuntu system, the Bluetooth module of the Raspberry Pi 5 is recognized directly. Click on the device icon in the top-right corner of the desktop, and you will see that Bluetooth is already turned on: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_25.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_25.jpg | ||
Click on the arrow next to Bluetooth, then click Bluetooth Settings to open the Bluetooth settings: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_26.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_26.jpg | ||
The Bluetooth module will automatically scan for nearby connectable Bluetooth devices, as shown in the figure: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_27.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_27.jpg | ||
We can select the desired Bluetooth device to connect. The following is an example of pairing with a phone: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_28.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_28.jpg | ||
| 第274行: | 第278行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_29.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_29.jpg | ||
After the pairing is successful, the device will show "Connected". You can see this device (phone) in the Bluetooth menu in the top-right corner of the desktop: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_30.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_30.jpg | ||
| 第280行: | 第284行: | ||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_31.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_31.jpg | ||
Ubuntu system can recognized the phone, and the phone recognizes the Raspberry Pi 5 as a headset: | |||
http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_39.jpg | http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/0011_MPW7_39.jpg | ||
| 第311行: | 第315行: | ||
--> | --> | ||
{{ | {{Contact_Us_icon}} | ||
2024年11月11日 (一) 10:22的最新版本
Keywords
Raspberry Pi 5, PCIe Expansion, WiFi7, Raspberry Pi5, Ubuntu, RPi OS
I. Introduction
The Raspberry Pi 5 features a 16-pin PCIe interface, through which various PCIe devices can be connected. This expansion board is specifically designed for the Raspberry Pi 5 to serve as a WiFi 7 adapter. This module requires driver installation to use WiFi 7 on the Raspberry Pi system, while it is plug-and-play under Ubuntu without needing additional drivers. The module also supports WiFi 6 and WiFi 5 via the M.2 E key interface.
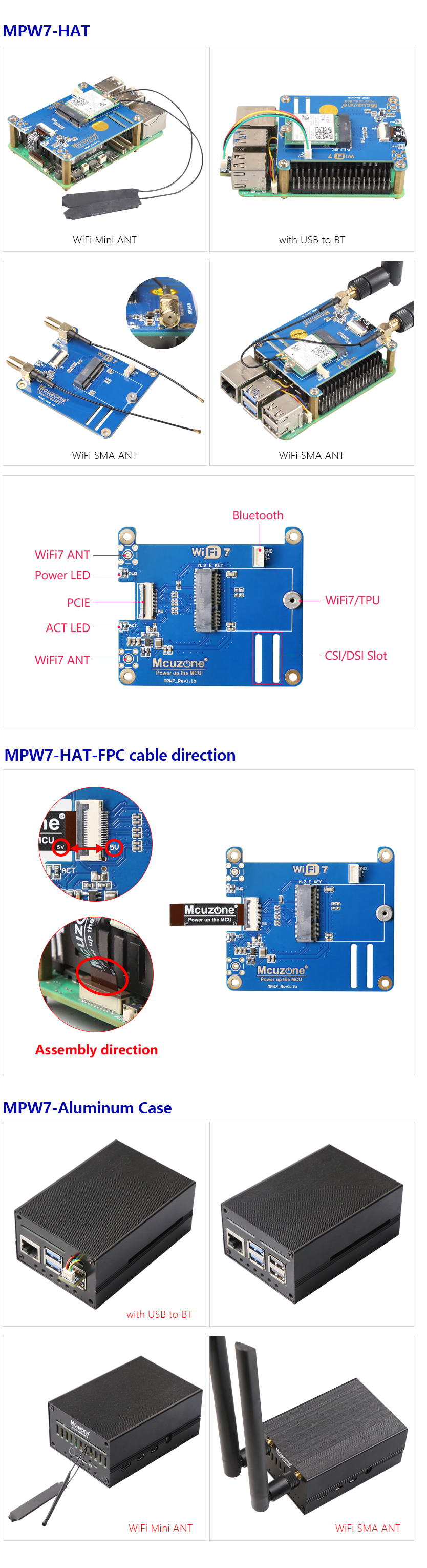
II. Hardware Spec
1. PCIe expansion board designed specifically for the Raspberry Pi 5;
2. One M.2 E-Key PCIe interface, supporting the BE200 WiFi 7 module, with hardware also supporting WiFi 6(E) and WiFi 5, such as AX210, AX200, MT7922, and Intel 8265C;
3. One USB Bluetooth interface (built-in with the WiFi module), exposed via a 1.25mm 4-pin USB connector. To use the Bluetooth function, this USB must be connected to a USB 2.0 port on the Raspberry Pi 5, and it requires the appropriate drivers and profiles to be installed;
4. Reserved CSI/DSI cable routing slots, supporting 22-pin cables with 0.5mm pitch and 15-pin cables with 1mm pitch;
5. Board-mounted power indicator light ('PWR') and one WiFi activity indicator light ('ACT');
6. Uses an efficient DC-DC circuit;
7. Gold immersion PCB process, lead-free production, certified by UL, compliant with ROHS standards, and has a fire rating of 94V-0;
8. The board has four M2.5 mounting holes, with a recessed design on the top of the board to facilitate the use of the 40-Pin GPIO;
9. Optional PCB antenna or SMA antenna, with an IPEX4 interface;
10. Optional aluminum alloy enclosure.
III. Software Spec
3.1 Overview
This document uses Raspberry Pi OS and Ubuntu systems, tested with the BE200 (WiFi 7) module.
1)The version of the Raspberry Pi OS is: 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz
You can download the Raspberry Pi OS in:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-64-bit
2)The version of the Ubuntu system is: ubuntu-24.04-preinstalled-desktop-arm64+raspi.img.xz
You can download the Ubuntu system in:
https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
3.2 System flashed onto the SD (TF) card
Click here to read the instructions for System flashing
IV. Work with Raspberry Pi OS
4.1 Installing WiFi 7 driver (BE200)
Note: Once the WiFi 7 driver (BE200) is successfully installed, the original WiFi module on the Raspberry Pi 5 will no longer be usable!
This installation procedure also applies to the AX210 (WiFi 6E) and AX200 (WiFi 6) modules.
4.1.1 Update the system and header files
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install -y raspberrypi-kernel-headers firmware-iwlwifi flex yacc
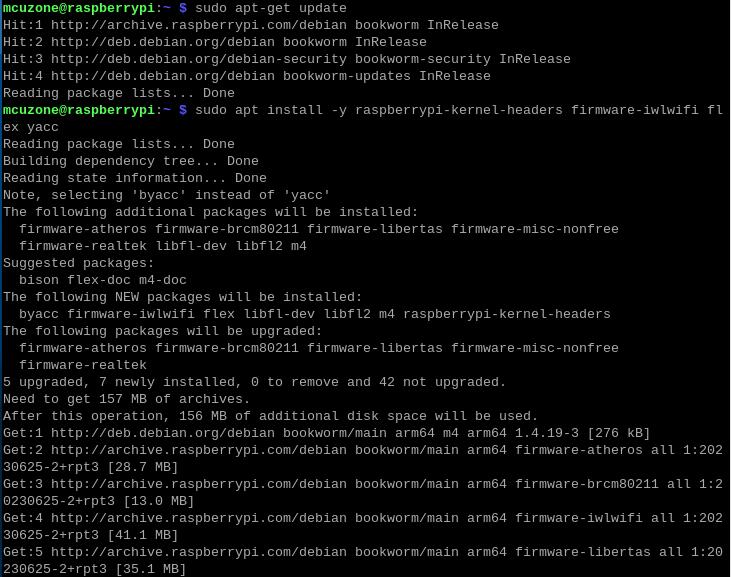
4.1.2 Download and extract the source code
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal:
mkdir wifi && cd wifi
wget http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/backport-iwlwifi-20231029.tar.bz2
sudo tar -xvf backport-iwlwifi-20231029.tar.bz2
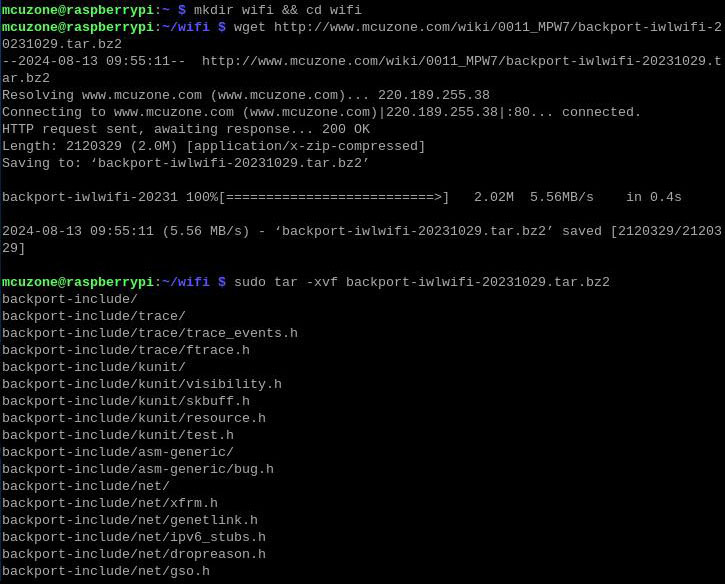
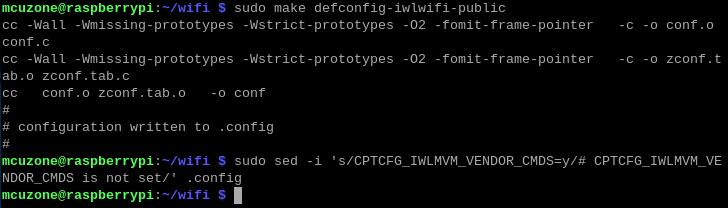
4.1.3 Compilation Environment
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal:
sudo make defconfig-iwlwifi-public
sudo sed -i 's/CPTCFG_IWLMVM_VENDOR_CMDS=y/# CPTCFG_IWLMVM_VENDOR_CMDS is not set/' .config
4.1.4 Compile source code
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal:
sudo make -j 4
sudo make install
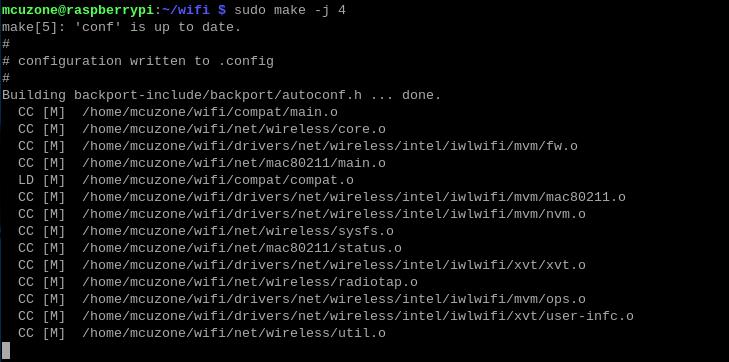
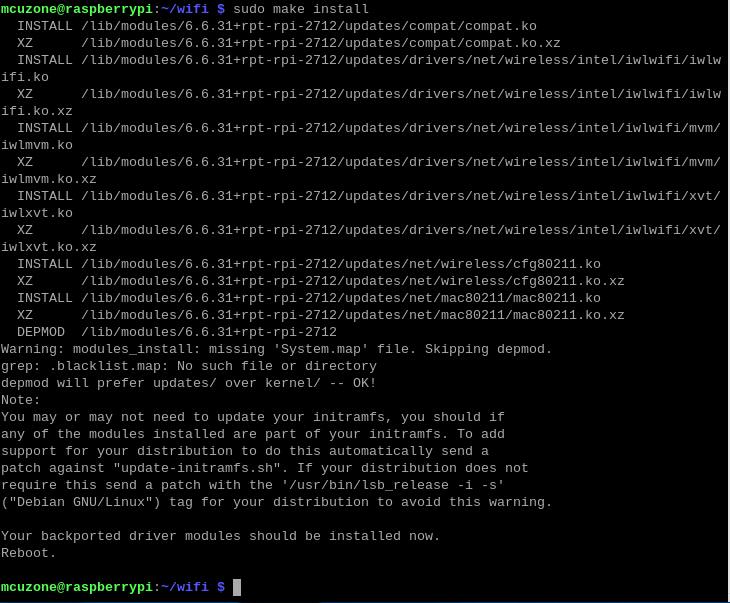
At this point, the system will prompt you to restart. Please do not restart yet.
4.1.5 Install firmware (not necessary for AX200 or AX210)
Execute commands in the Raspberry Pi terminal:
cd ..
cd Downloads
wget http://www.mcuzone.com/wiki/0011_MPW7/firmware_wifi7.zip
unzip firmware_wifi7.zip
sudo cp iwlwifi-gl-c0-fm-c0-86.ucode /lib/firmware
sudo cp iwlwifi-gl-c0-fm-c0.pnvm /lib/firmware
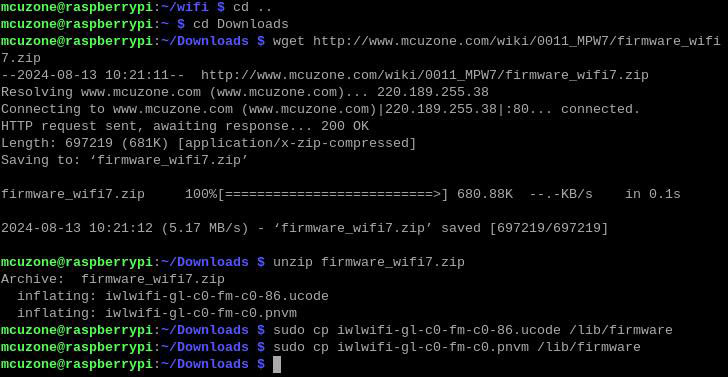
Then reboot system:
sudo reboot
4.2 Test of WiFi 7 module: BE200
After restarting the system, we execute lspci in the terminal:
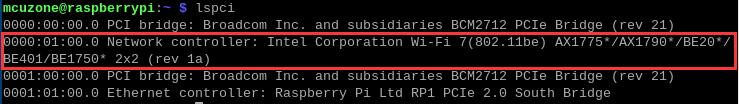
You can see the WiFi 7 module.
Execute ifconfig -a to view the information of the wireless network card (wlan0):
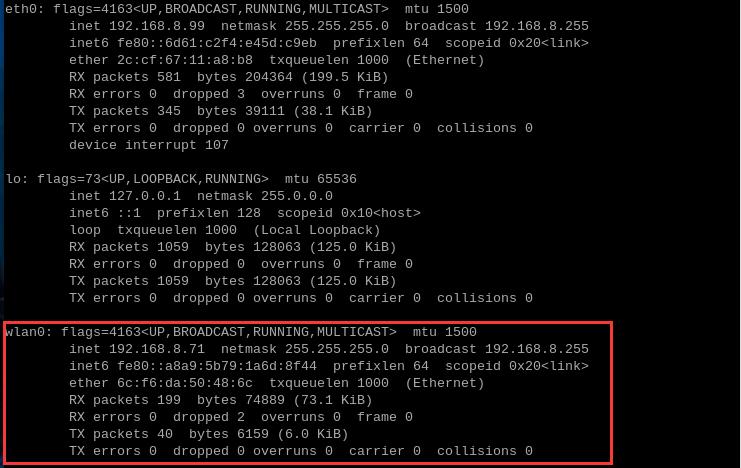
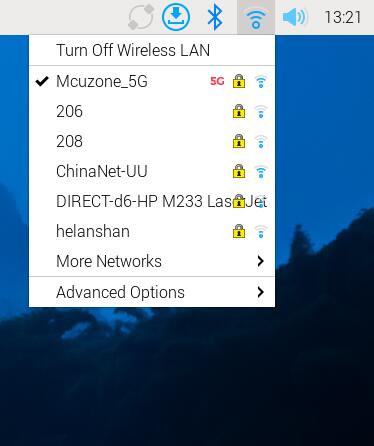
At this point, you can use the BE200 (WiFi 7) module to connect to a wireless AP through the network connections settings:
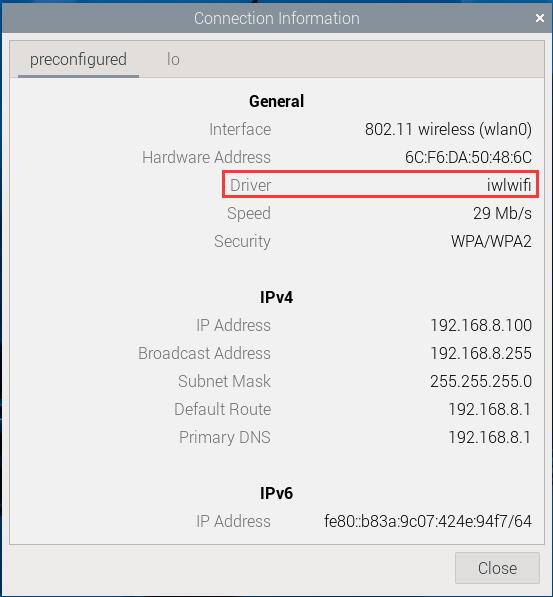
In the network connection information, you can also see the network connection using the iwlwifi driver:
Connect to the internet (200M broadband) using the BE200 (WiFi 7) module and perform a speed test, results as follows:
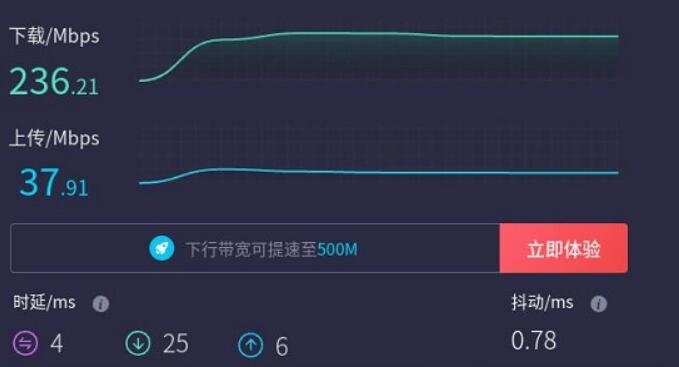
Note: Network speed tests are influenced by the network environment and testing methods. The speeds shown are for reference only and may vary based on actual conditions!
Connect to the WiFi 7 router and perform a speed test:
Note: All tests here are conducted using SSH to connect to the development board.
The router used is the Xiaomi BE6500 Pro, a WiFi 7 + quad-port 2.5G router. The Raspberry Pi 5 with WiFi 7 is approximately 1 meter away from the router.
Using the BE200 + Raspberry Pi 5, connect to the WiFi 7 wireless network and perform an iperf3 speed test with a Windows system (2.5G USB network card, IP address: 192.168.8.197) connected to the same router:
Speed test with 30 threads, results as follows
iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197 -P 30
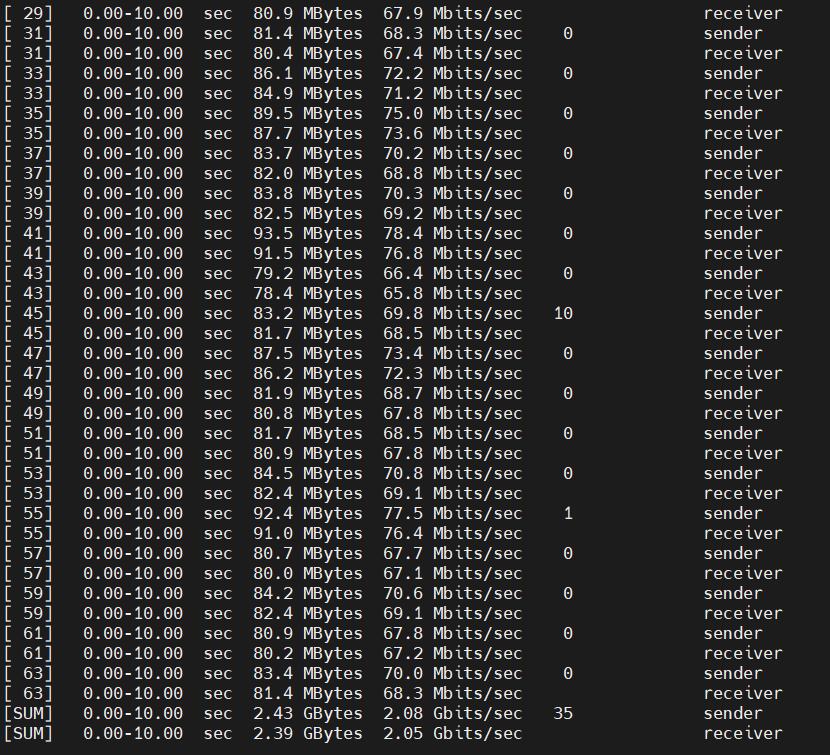
Speed test with 30 threads, results as follows
iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197
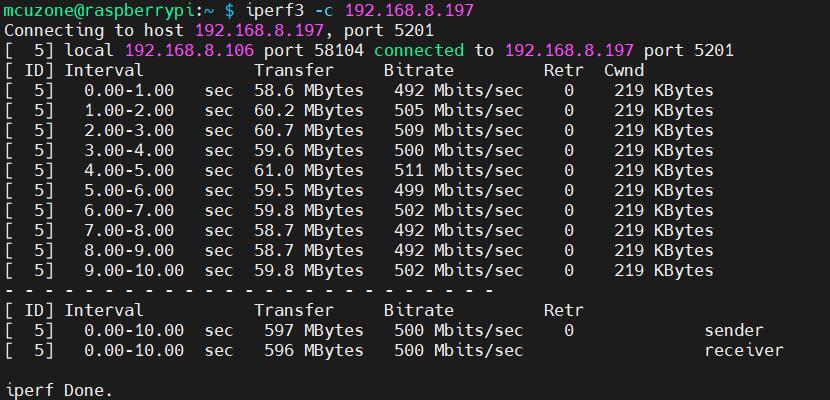
Approximately 500 Mbps.
For comparison, we replaced the WiFi 7 module with a WiFi 6 module (AX210) and performed the same tests.
Speed test with 30 threads, results as follows:
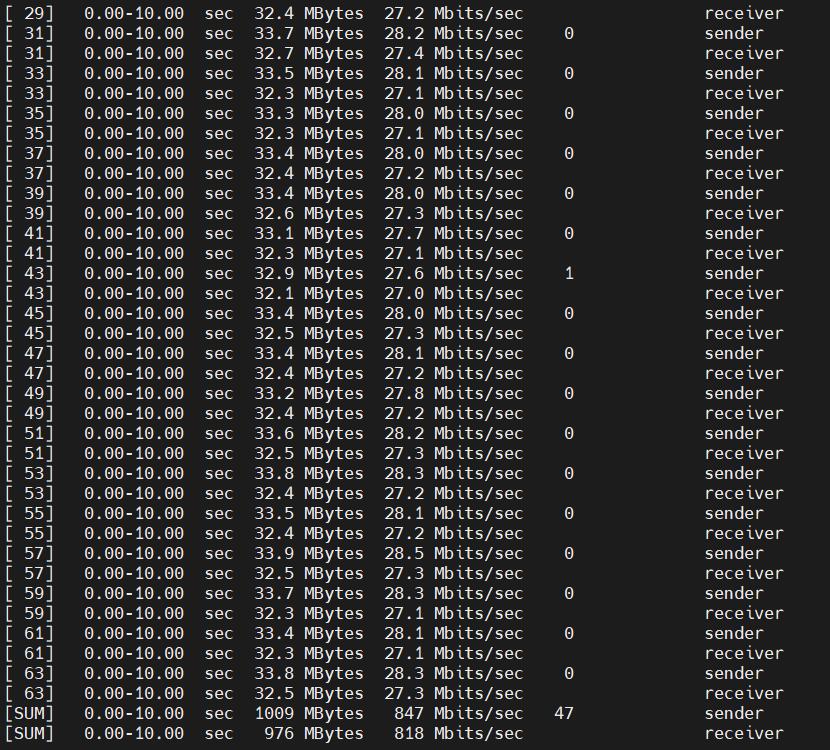
Approximately 847 Mbps.
Single-thread speed test, results as follows:
iperf3 -c 192.168.8.197
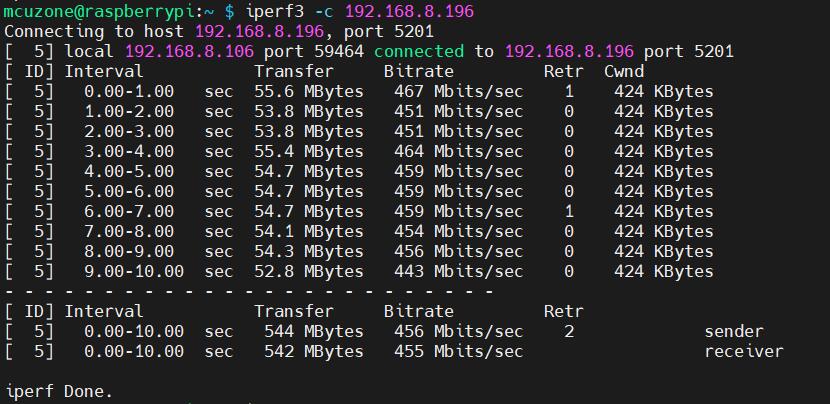
Approximately 456Mbps。
Note: Network speed tests are influenced by the network environment and testing methods. The speeds shown are for reference only and may vary based on actual conditions!
4.3 Bluetooth Testing
Connect the 1.25mm 4-pin USB Bluetooth interface to the USB 2.0 port on the Raspberry Pi 5:
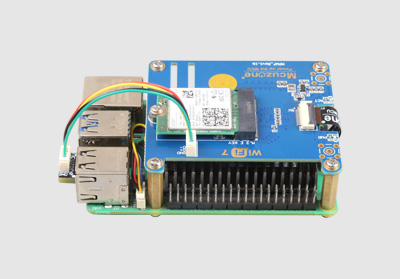
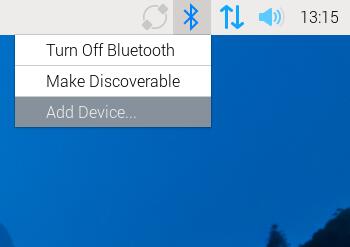
On Raspberry Pi OS, the Bluetooth module of the Raspberry Pi 5 is recognized directly. Click on the device icon in the top-right corner of the desktop, then click Add Device...:
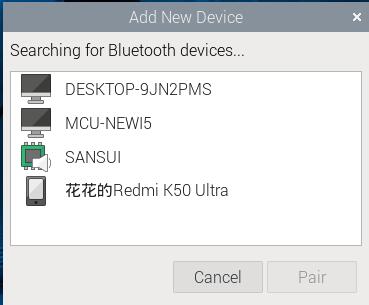
In the opened window, the Bluetooth module will automatically scan for nearby connectable Bluetooth devices, as shown in the figure:
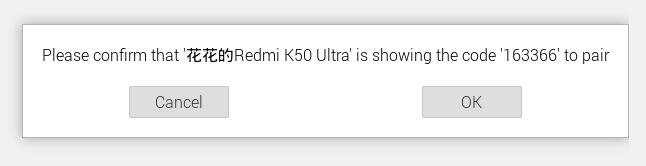
Click on the phone to pair with it. The pairing process on Raspberry Pi OS and the phone is shown in the figures below:
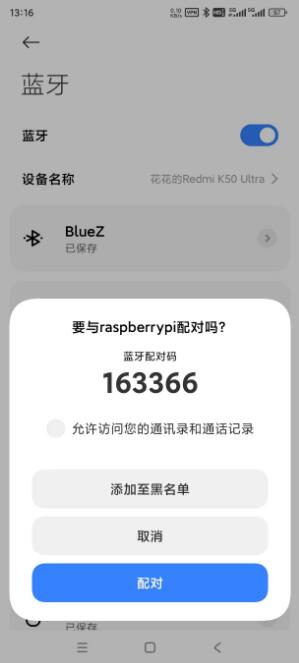
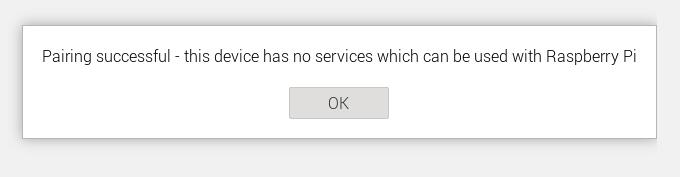
After pairing successfully, click on the 'raspberrypi' device on your phone. Once connected, the Raspberry Pi is recognized as an audio device, as shown in the figure below:
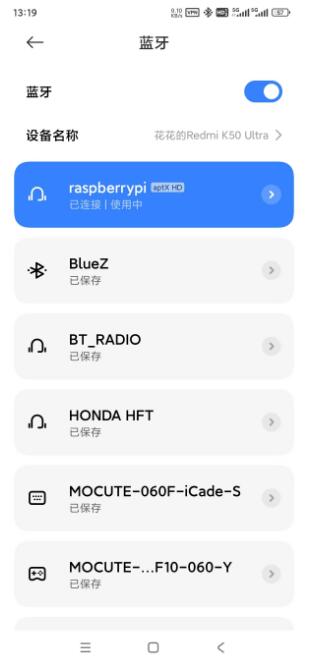
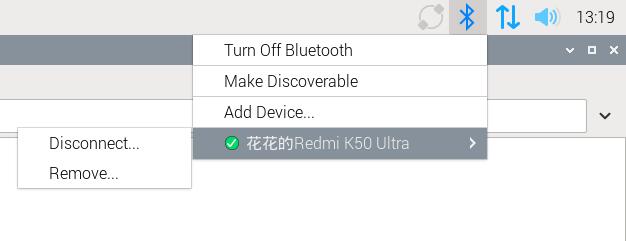
In Raspberry Pi OS, you can also see that the connection was successful:
V. Work with Ubuntu System
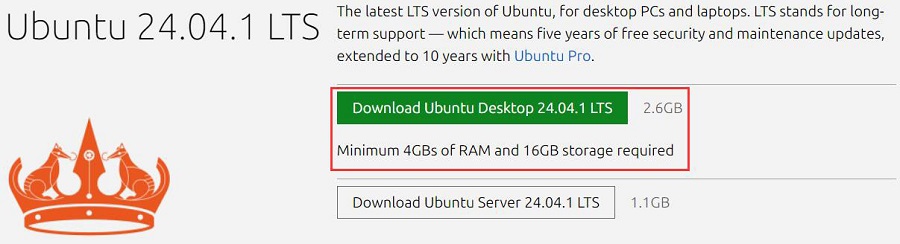
The version of Ubuntu used for testing is as follows:
5.1 WiFi7(BE200)
The BE200 (WiFi 7) module is plug-and-play under Ubuntu and does not require additional drivers. After the system starts, execute lspci in the terminal:
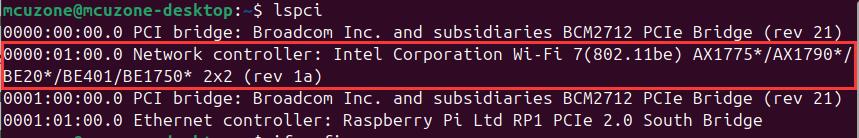
You can see the WiFi 7 module.
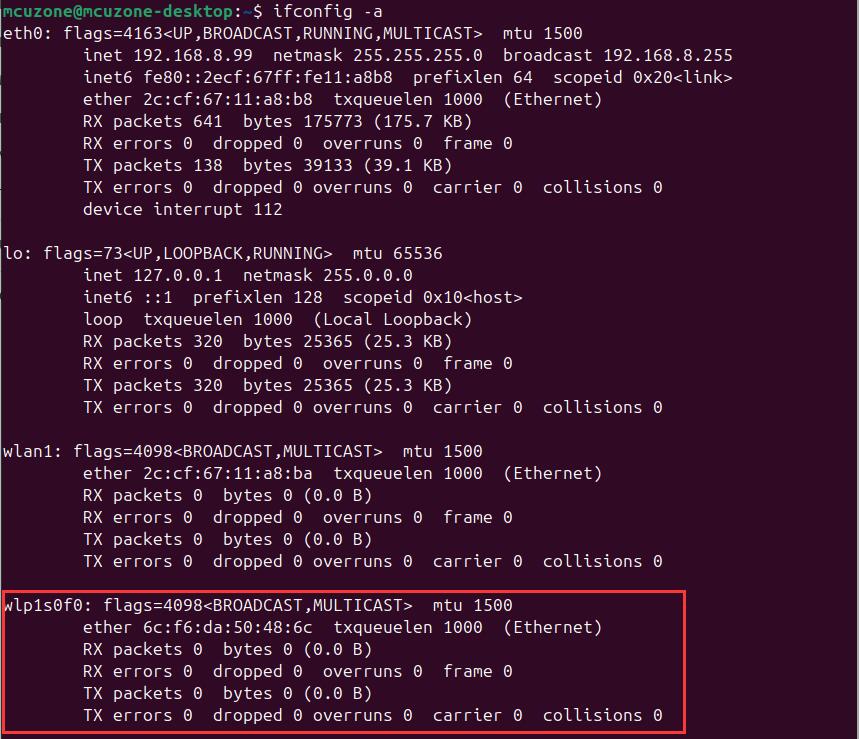
Execute ifconfig -a to view the information of the WiFi 7 wireless network card (wlp1s0f0). wlan1 is the built-in wireless network card of the Raspberry Pi 5:
In the 'Wi-Fi' menu in the top-right corner of the screen, there is a 'PCI Wi-Fi' option, which is the WiFi 7 module: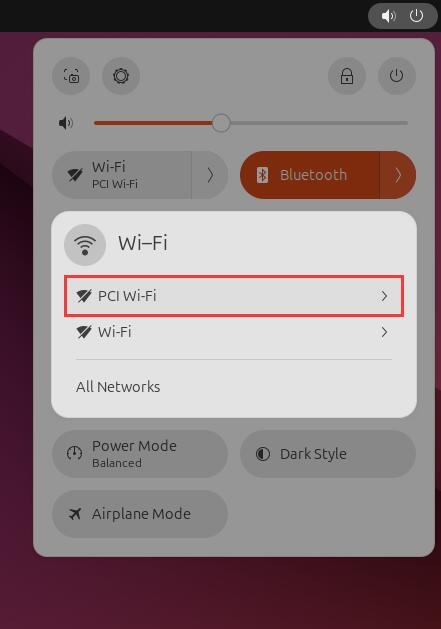
After connecting to the wireless AP using the 'PCI Wi-Fi', you can see a wireless WiFi named 'Intel' in the 'All Networks' list. This is the WiFi 7 module. Once connected successfully, you can browse the internet using the WiFi 7 module
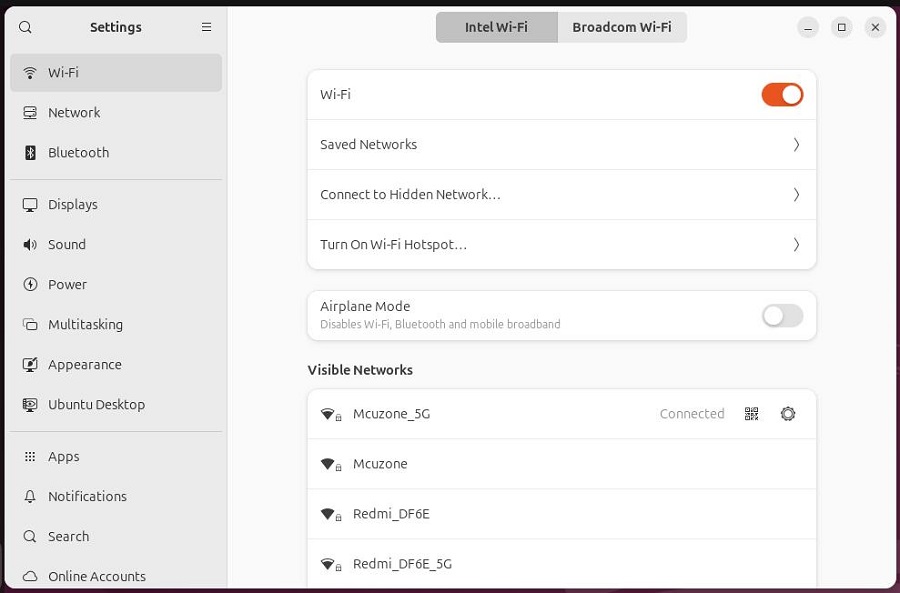
Connect to the internet (200M broadband) using the BE200 (WiFi 7) module and perform a speed test, results as follows:
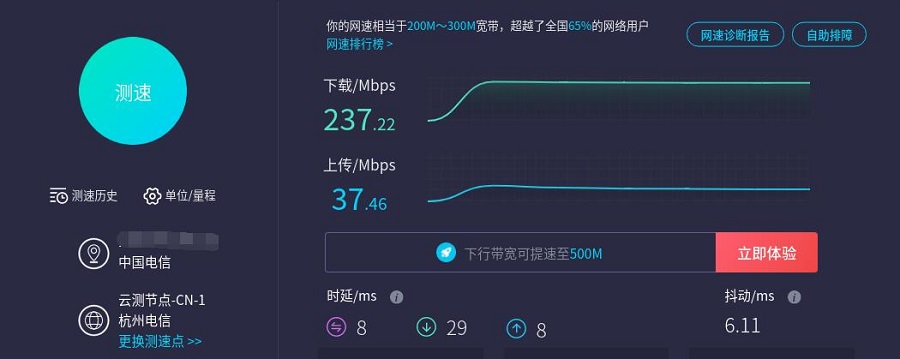
Note: Network speed tests are influenced by the network environment and testing methods. The speeds shown are for reference only and may vary based on actual conditions!
If using the built-in Firefox browser in Ubuntu results in slow performance or frequent unresponsiveness, it is recommended to install the lightweight browser Falkon:
sudo apt install falkon
5.2 WiFi6(AX210/AX200)
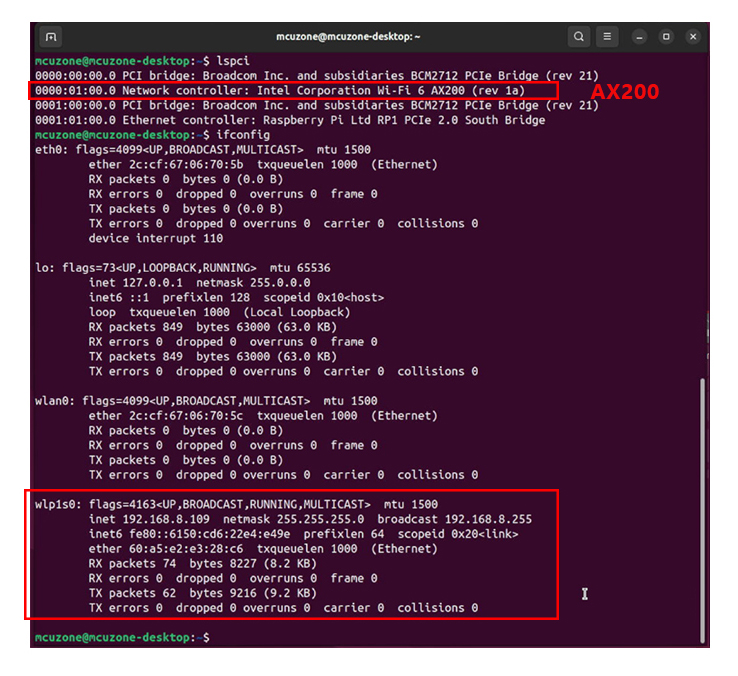
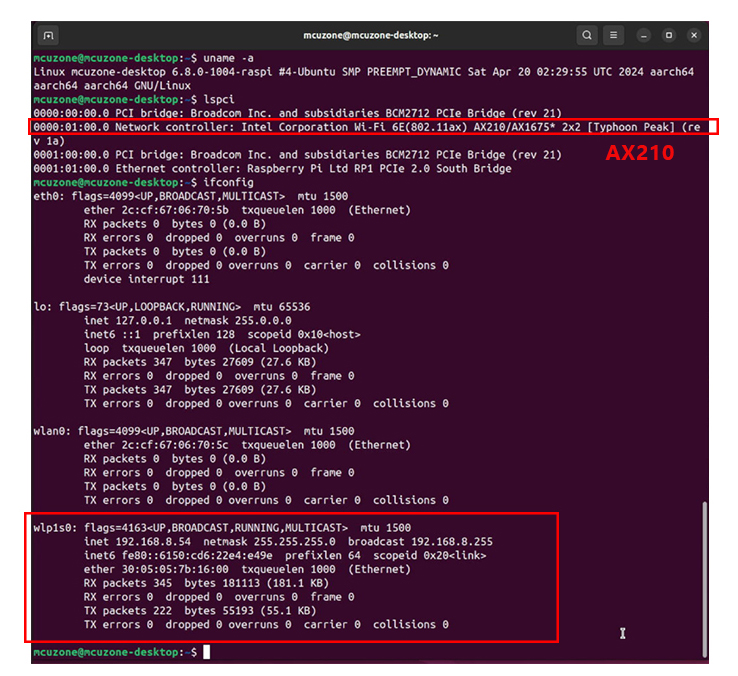
The WiFi 6 modules (AX200 and AX210) are also plug-and-play under Ubuntu system and do not require additional drivers. Follow the same steps as above, and the execution results are as follows:
AX200:
AX210:
5.3 Bluetooth Testing
Under the Ubuntu system, the Bluetooth module of the Raspberry Pi 5 is recognized directly. Click on the device icon in the top-right corner of the desktop, and you will see that Bluetooth is already turned on:
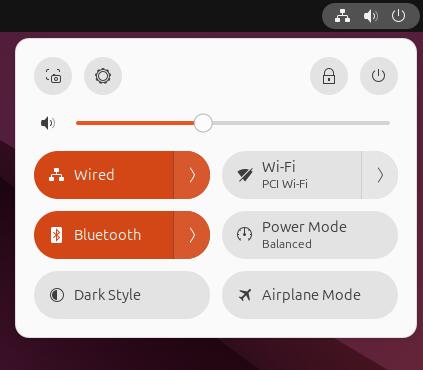
Click on the arrow next to Bluetooth, then click Bluetooth Settings to open the Bluetooth settings:
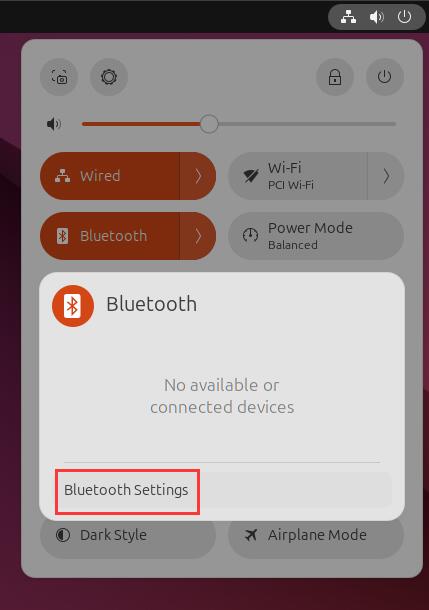
The Bluetooth module will automatically scan for nearby connectable Bluetooth devices, as shown in the figure:
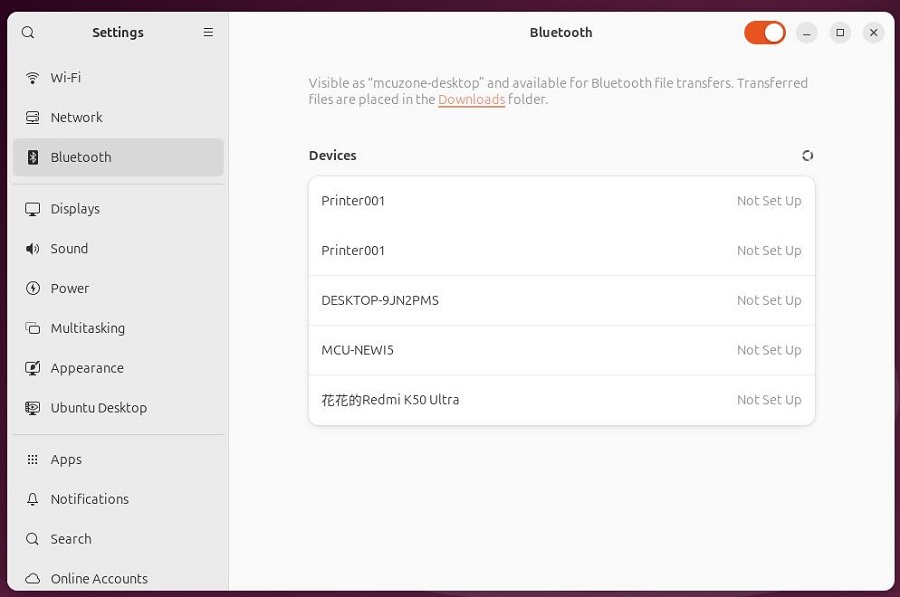
We can select the desired Bluetooth device to connect. The following is an example of pairing with a phone:
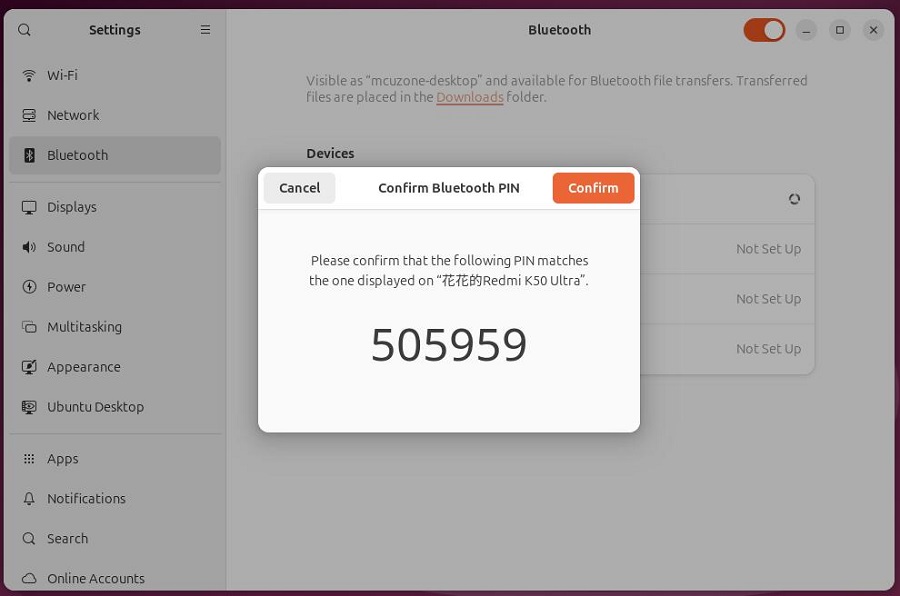
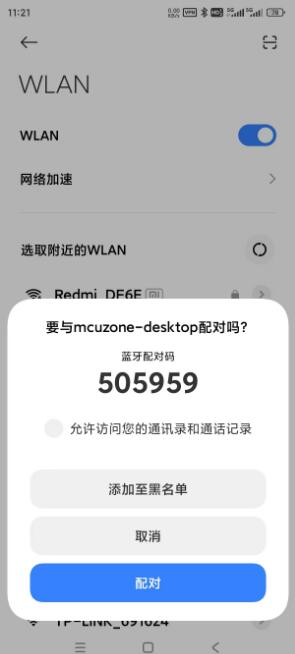
After the pairing is successful, the device will show "Connected". You can see this device (phone) in the Bluetooth menu in the top-right corner of the desktop:
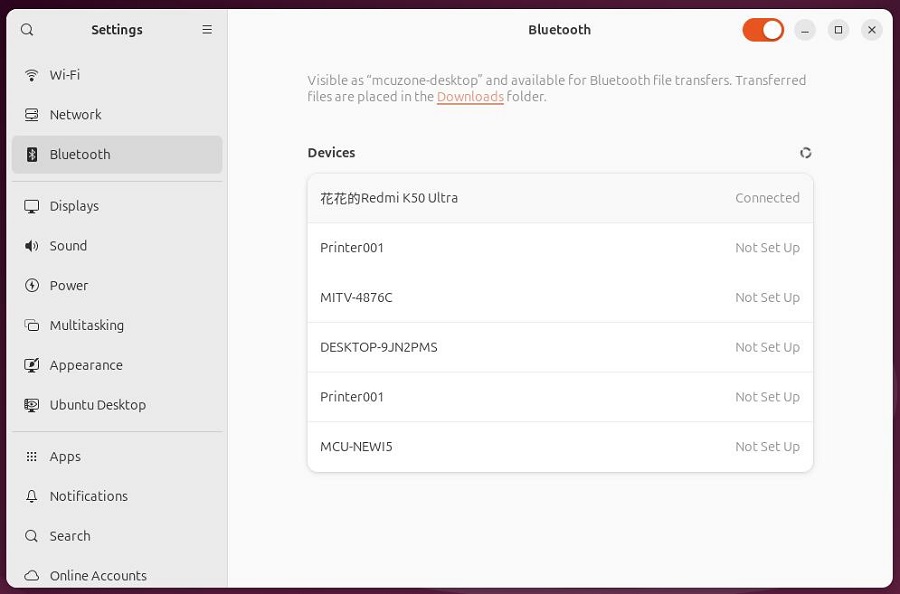
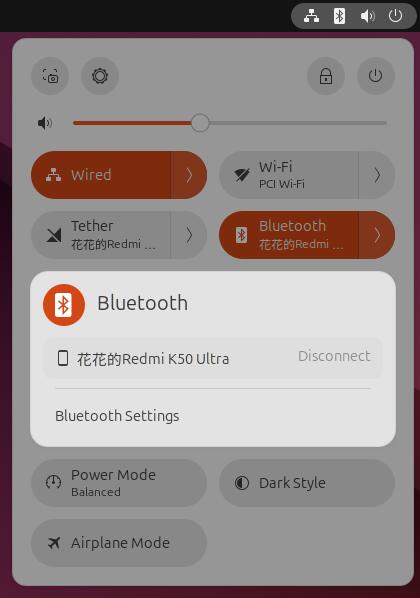
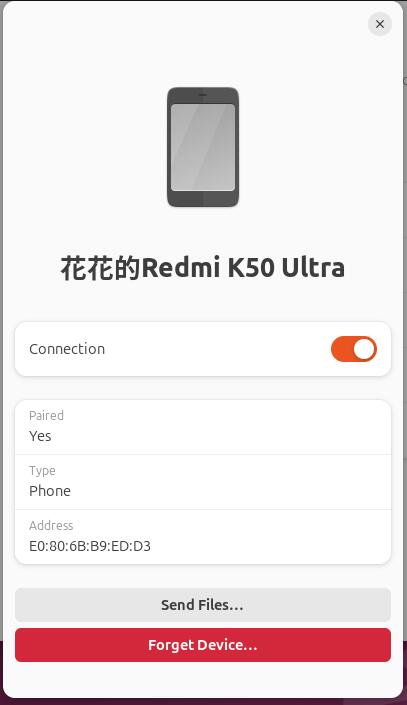
Ubuntu system can recognized the phone, and the phone recognizes the Raspberry Pi 5 as a headset:
Contact Us
Email: mcuzone@vip.qq.com
Tel: +86(0)13957118045
If there are any omissions, errors, or infringements on this page, please contact us through the above methods. Thank you!
Copyright 2004-2024 Wildchip




 QQ:8204136
QQ:8204136